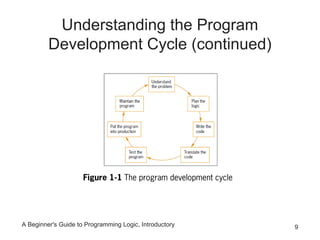
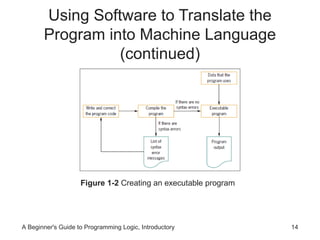
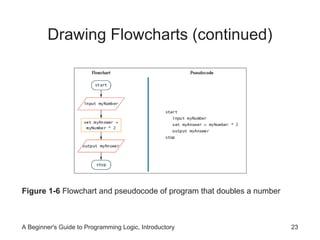
This chapter introduces computer systems and programming, covering hardware, software, programming languages, and the program development cycle. It describes using pseudocode and flowcharts to plan program logic before coding. Testing and debugging programs is discussed, as well as different programming environments and models that have evolved over time. The key steps in programming are understanding the problem, planning the logic, coding, testing, and maintaining programs.