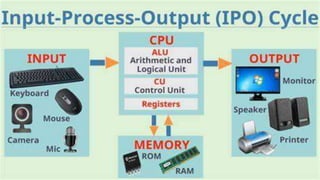
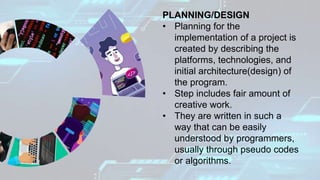
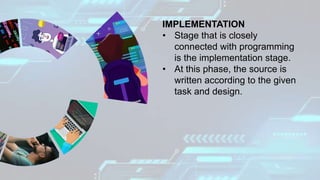
This document provides an introduction to computer programming concepts for grade 10 students, covering input, process, output, and the role of computer programs and programmers. It explains different levels of programming languages from machine code to high-level languages, detailing their characteristics and usage. Additionally, the document outlines the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), including steps like requirement gathering, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.