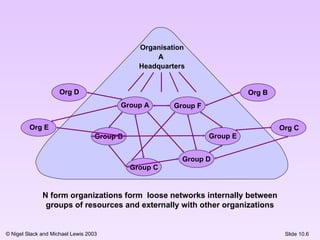
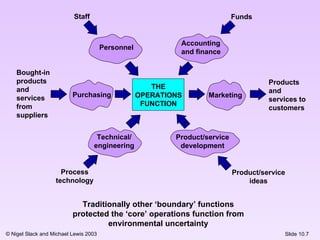
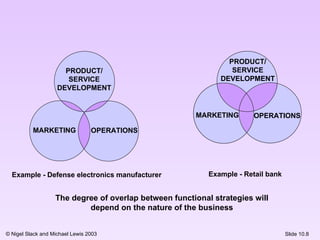
This document discusses different organizational structures and the role of operations functions within organizations. It presents U-form, M-form, and matrix organizational structures and notes that the N-form creates loose internal and external networks. The operations function can take different roles like trainer, governor, facilitator, or curator in relation to central operations. Finally, it shows how the overlap between operations and other functions like marketing and product development can vary depending on the nature of the business.