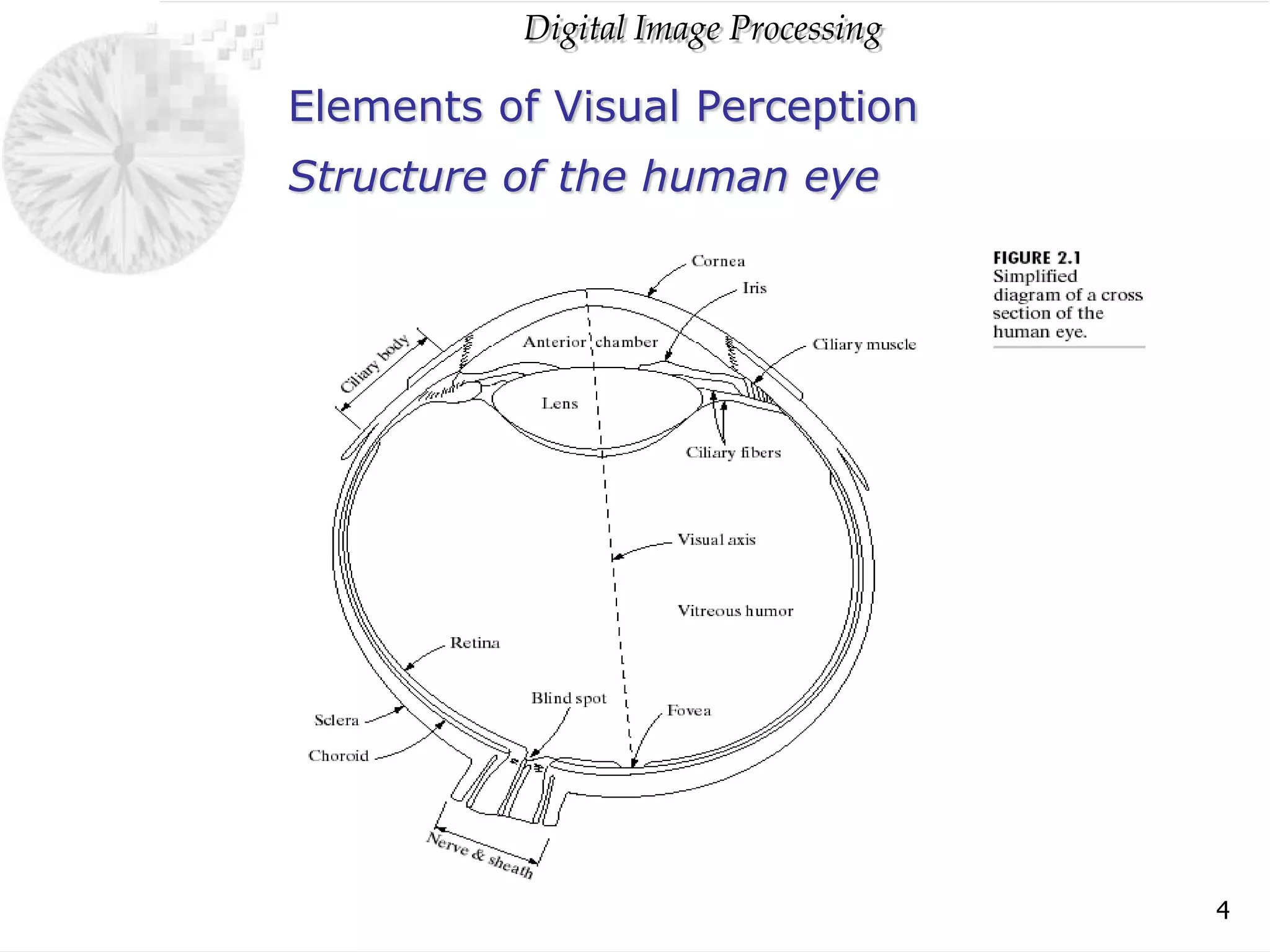
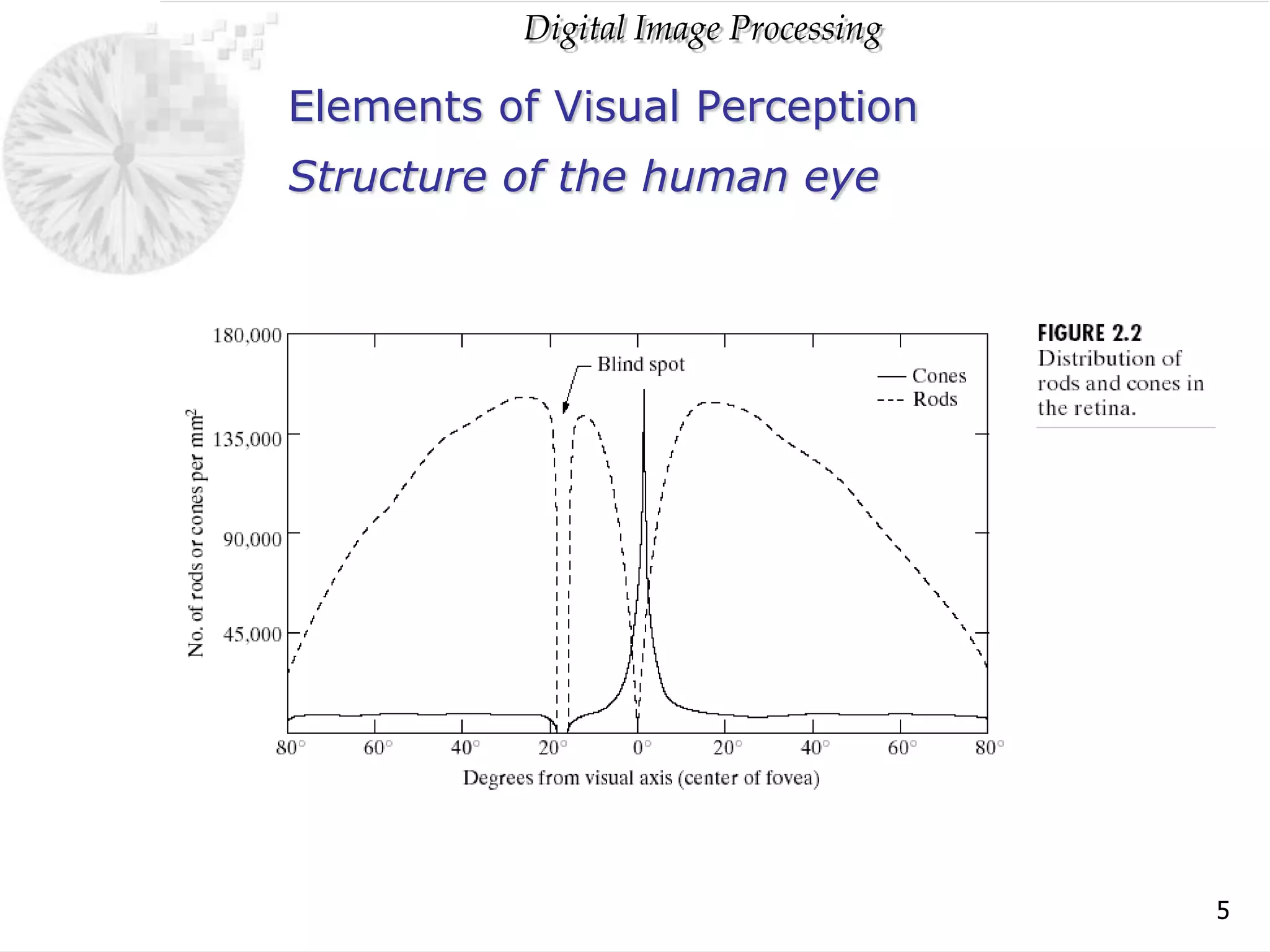
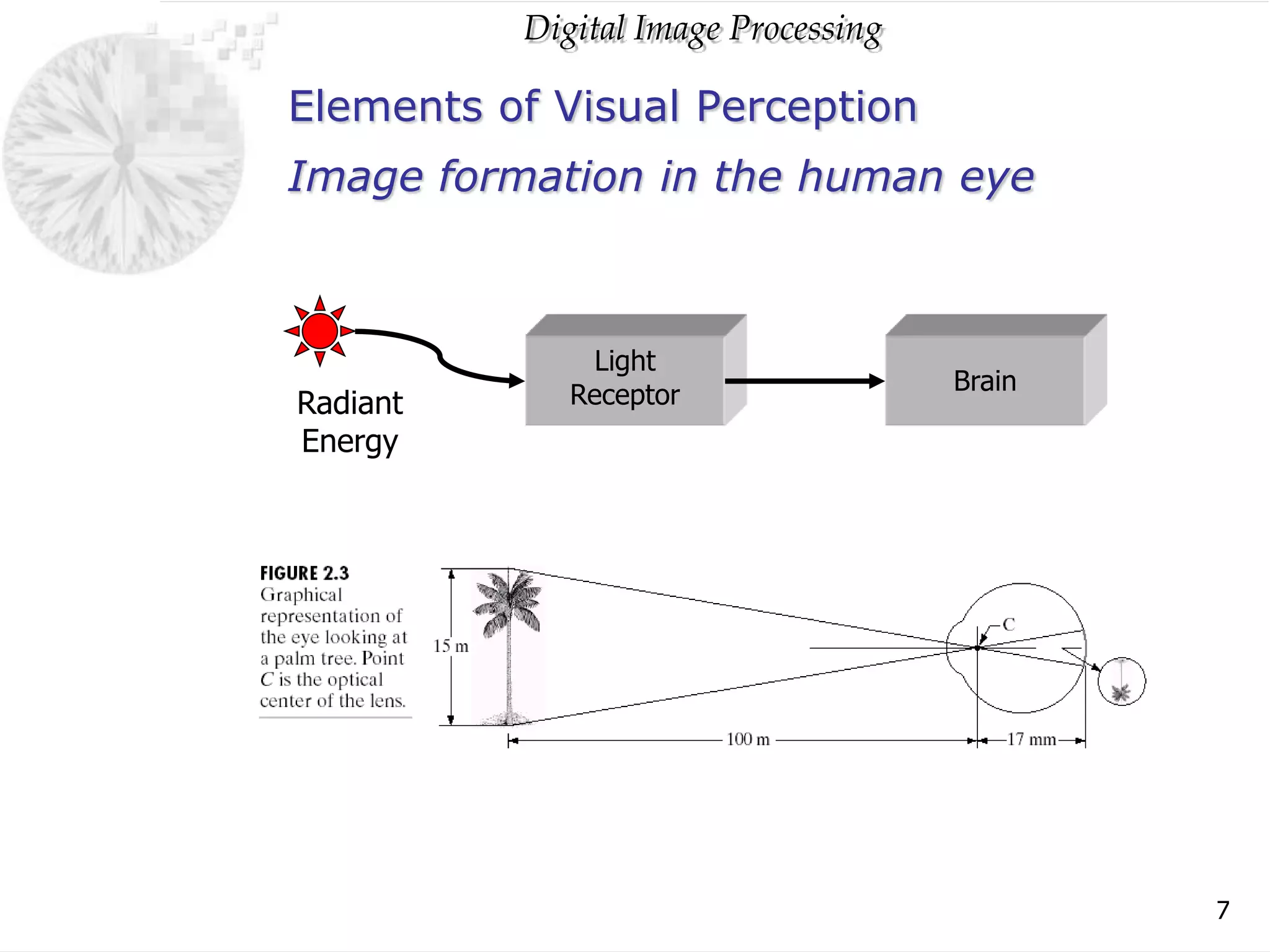
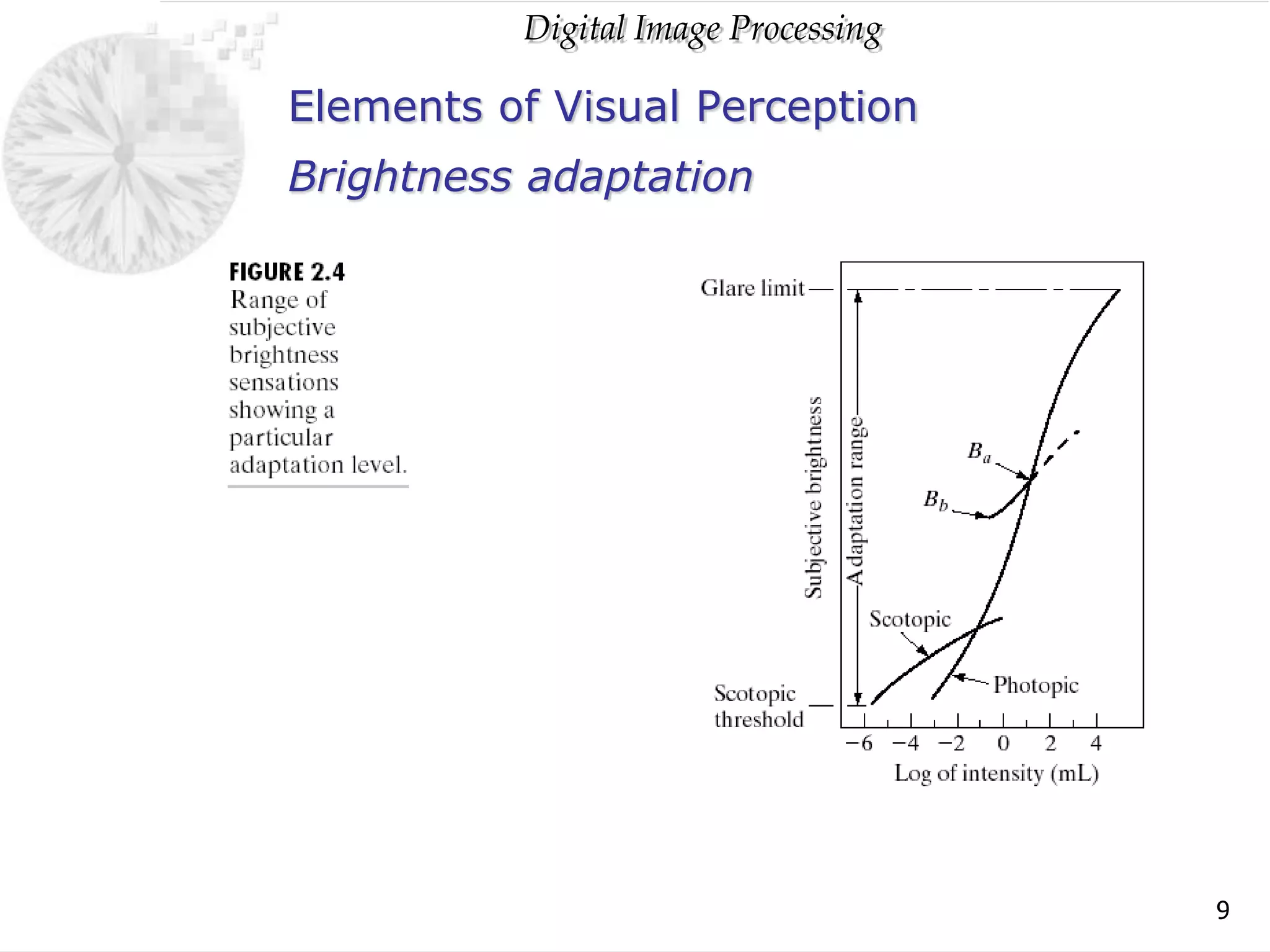
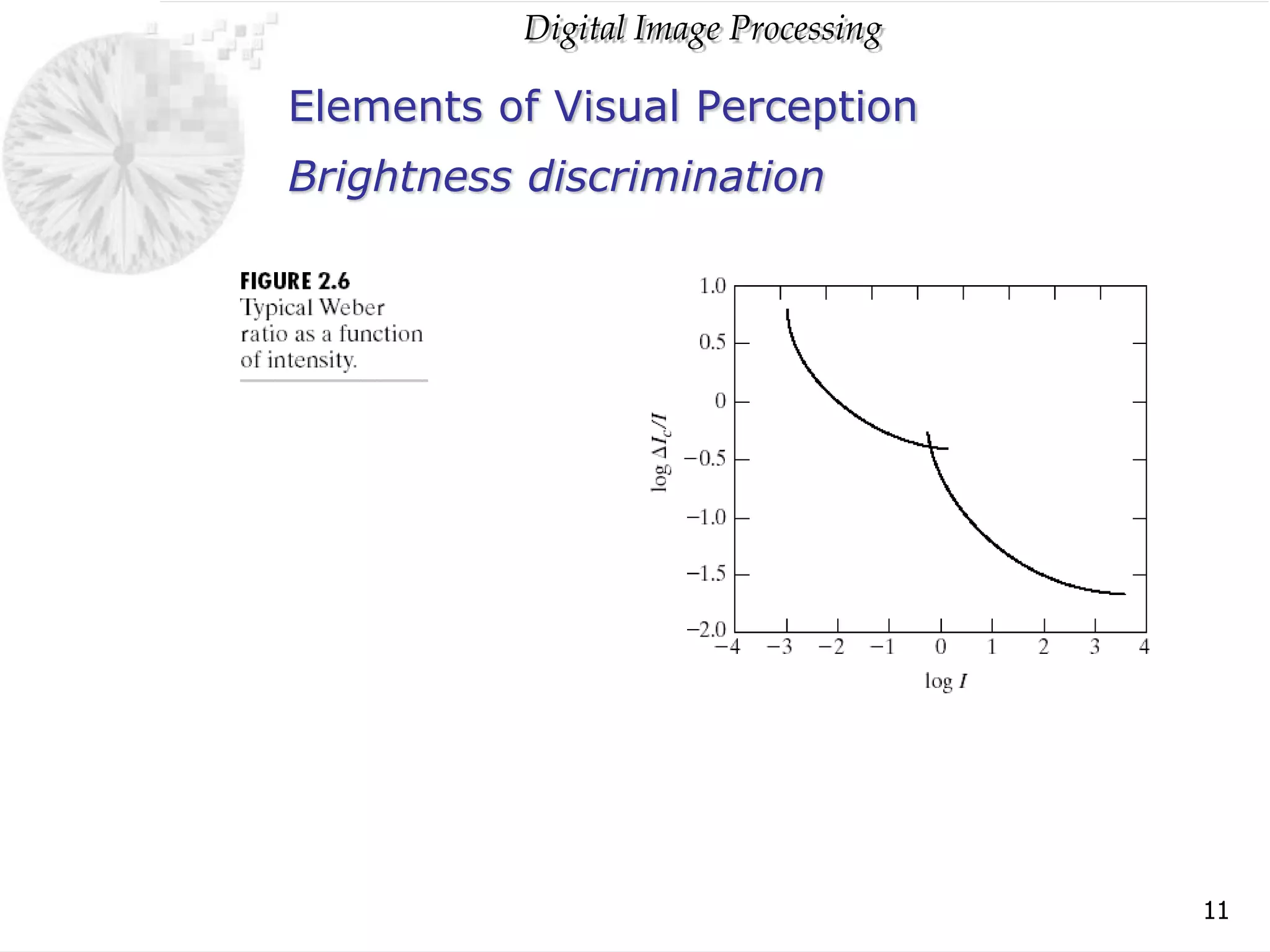
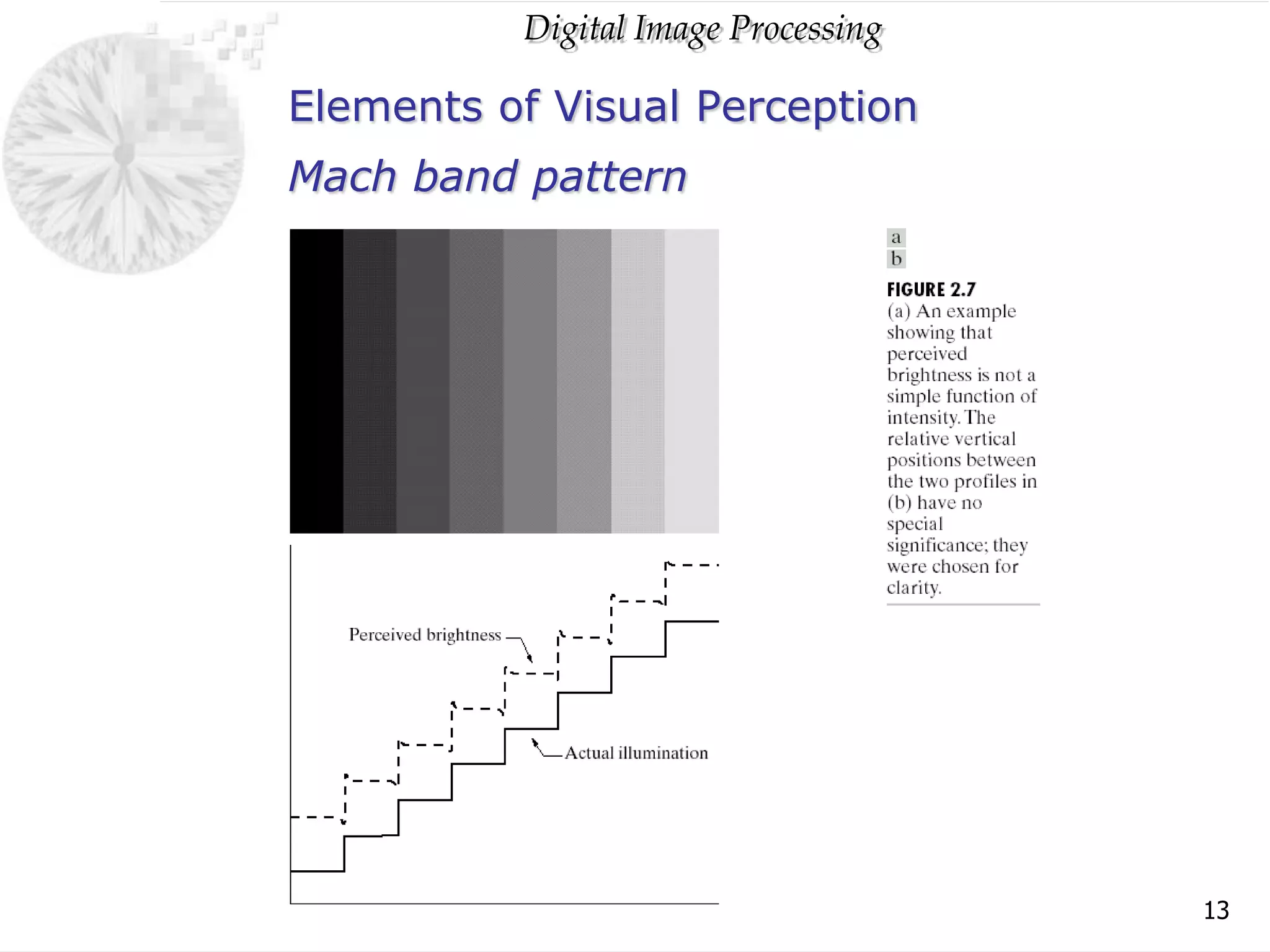
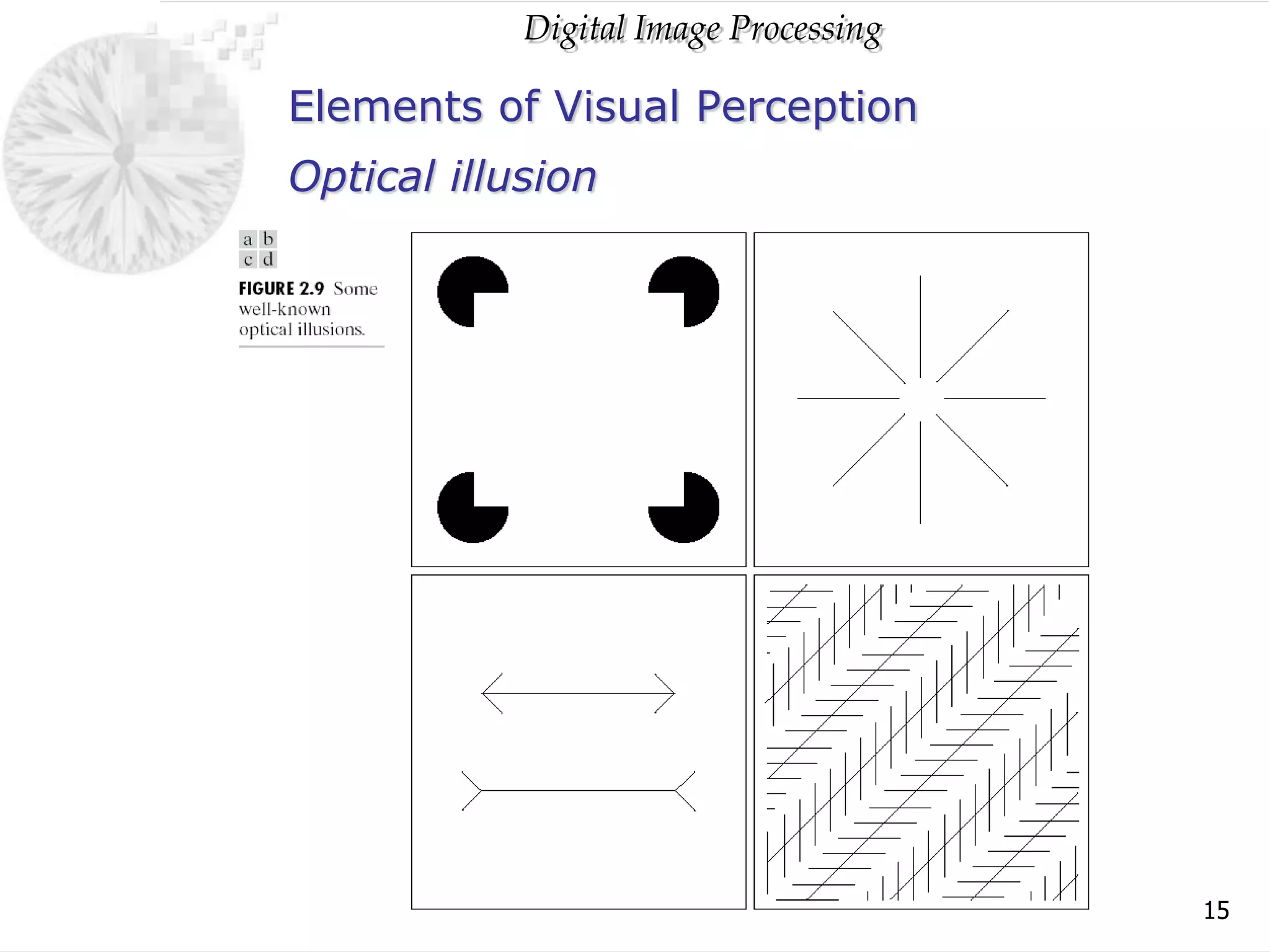
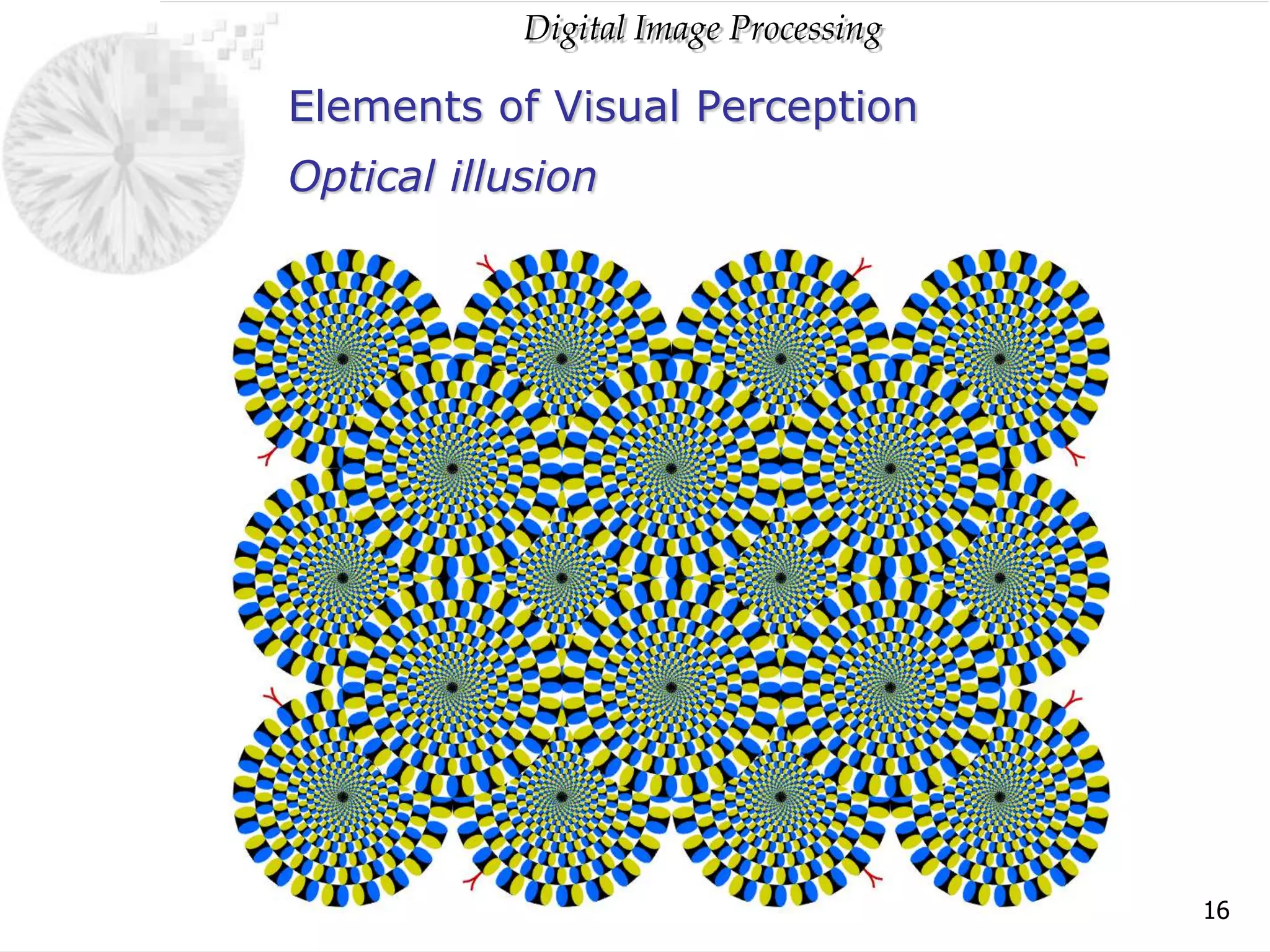
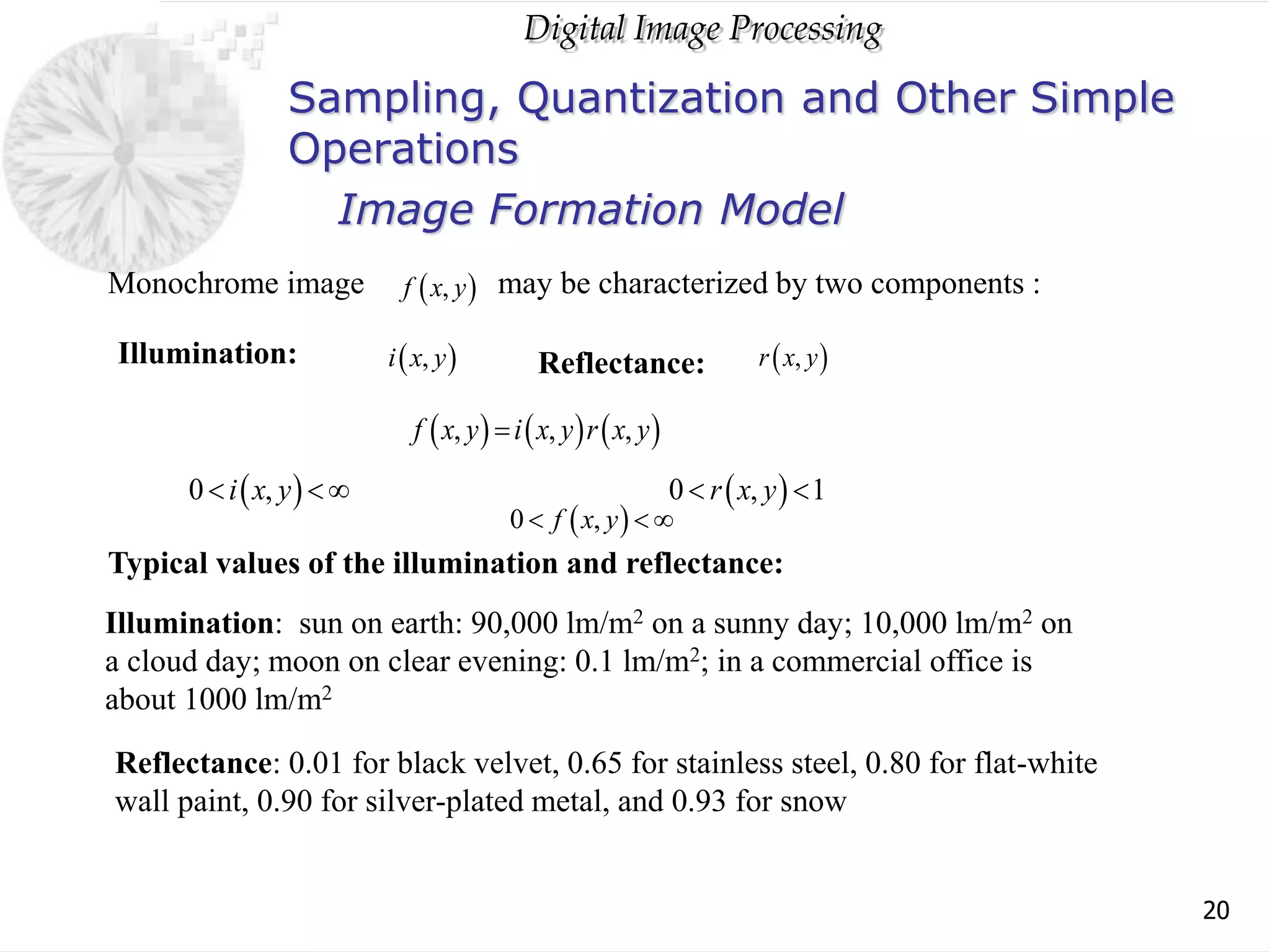
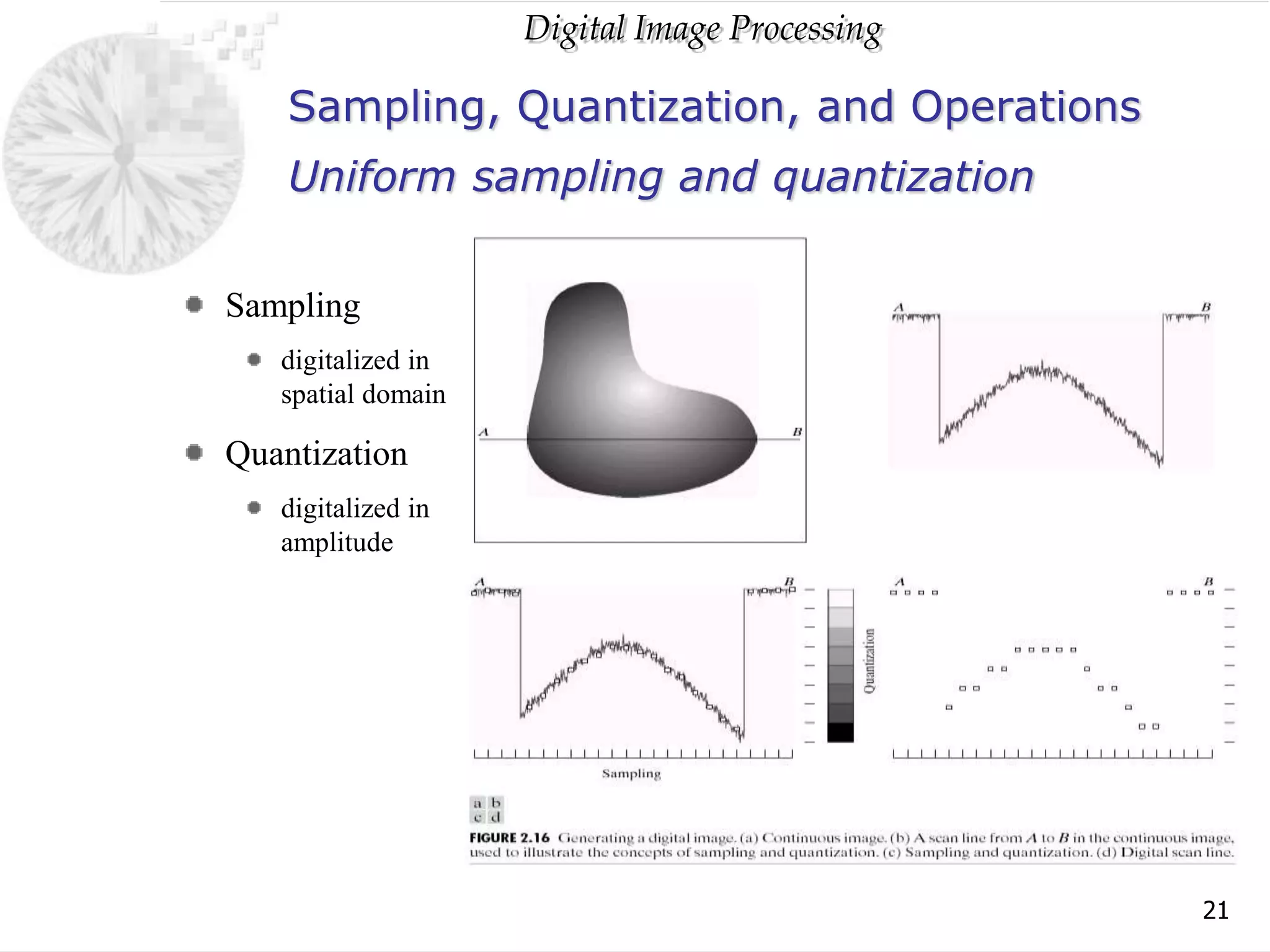
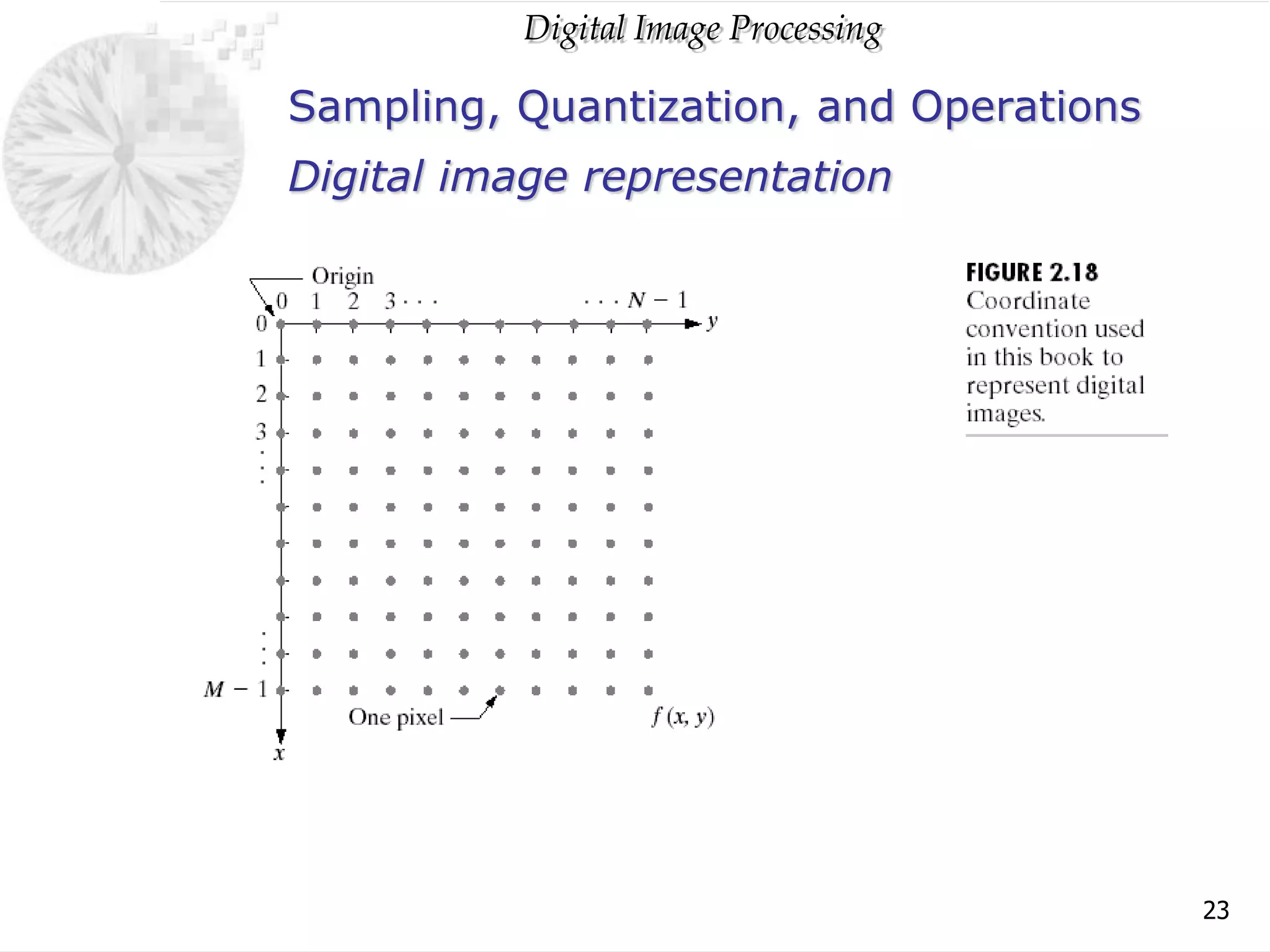
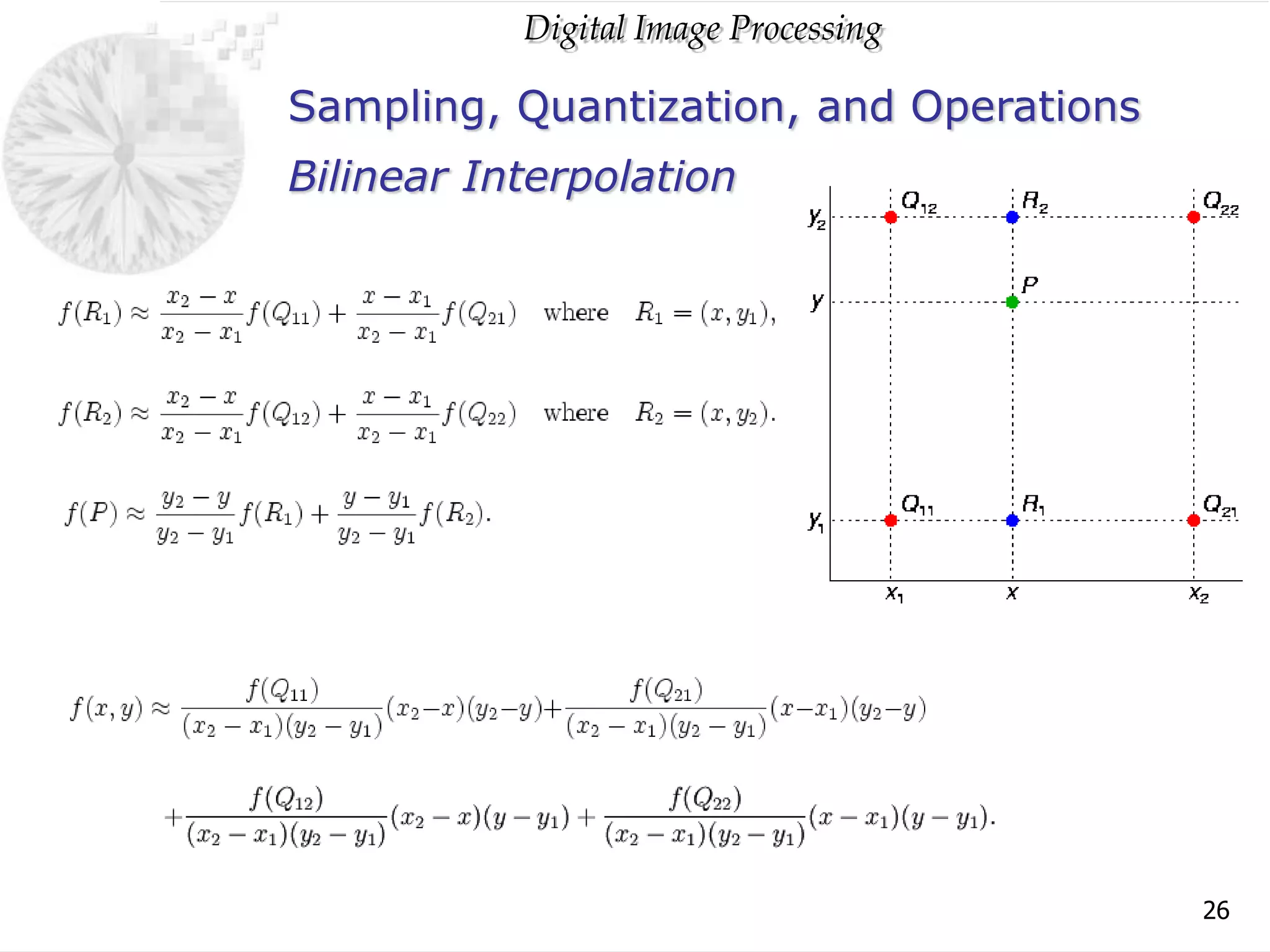
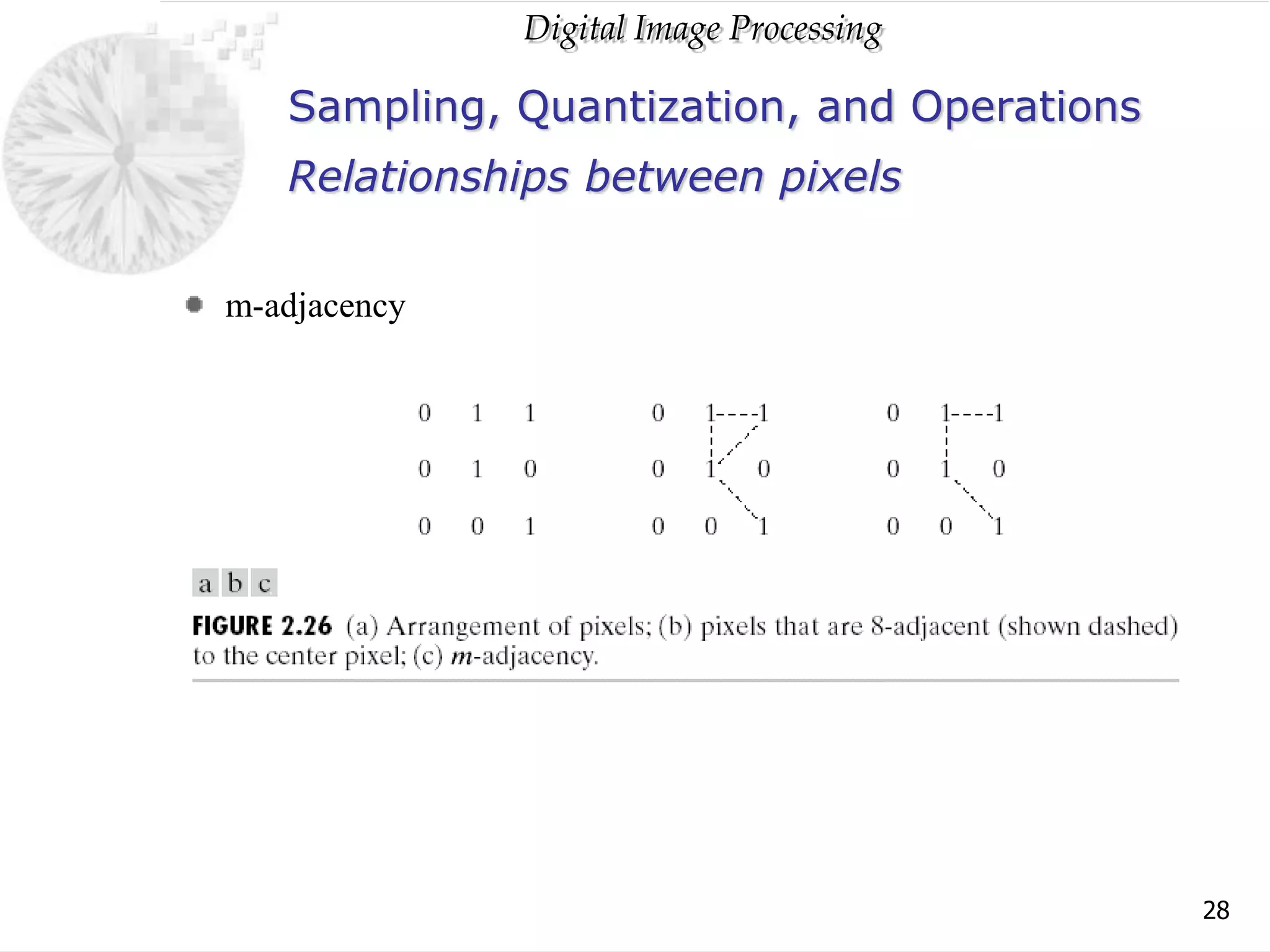
The document discusses elements of visual perception including the structure of the human eye and image formation. It describes the cornea, iris, lens, retina and different types of receptors. It also covers brightness adaptation and discrimination. The next section explains digital image representation through uniform sampling, quantization and pixel relationships. Common operations like arithmetic, logical, and interpolation methods are also summarized.