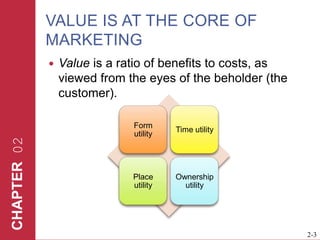
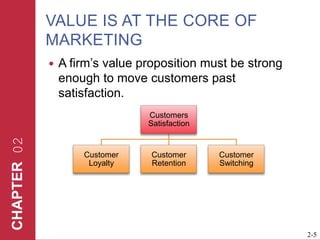
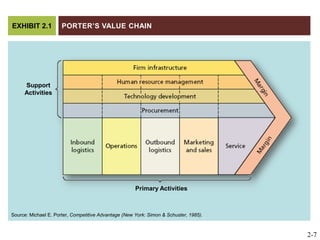
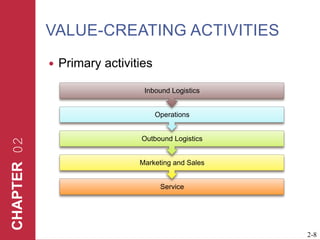
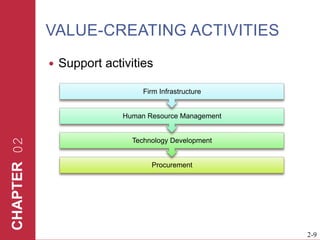
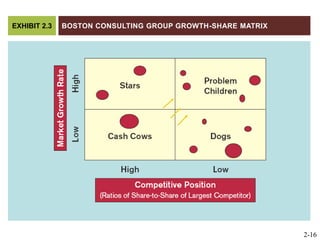
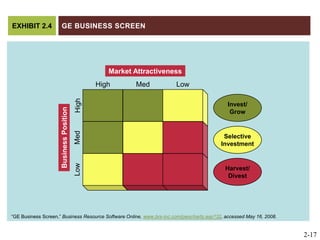
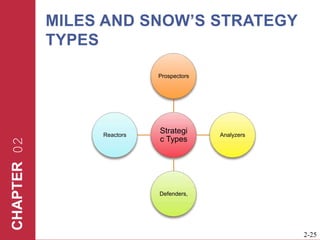
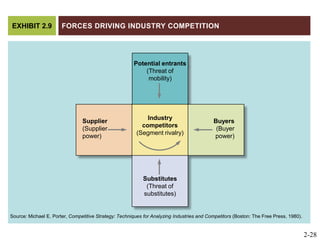
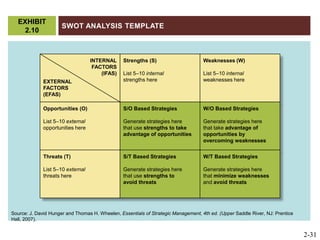
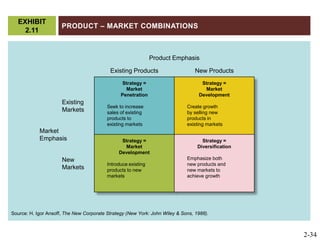
The document discusses key elements of marketing strategy and planning. It begins by defining value as the ratio of benefits to costs from a customer perspective. It then discusses the value proposition, value chain, and Porter's value chain model. It describes marketing planning as both strategic and tactical, involving developing market-driven strategies and implementing specific programs. The document provides a framework for marketing planning, including connecting it to the business plan, performing market research, establishing goals and objectives, developing strategies, and implementation plans. It also discusses various types of organizational strategies, situation analysis including SWOT analysis, and tips for successful marketing planning.