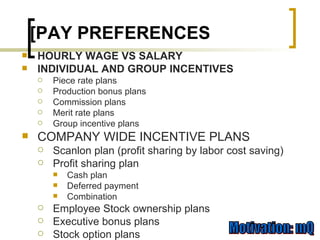
This document discusses motivation and monetary rewards in the workplace. It makes several key points:
1) Pay is most motivating for lower-level employees as it helps satisfy basic needs, while pay is additionally motivating for upper-level employees as it helps gain social status.
2) Pay becomes less important as a sole motivator once basic needs are satisfied, unless it also satisfies higher-order needs like independence and status.
3) Dissatisfaction with pay can result in lower work commitment, absenteeism, and turnover if expectations are not met.