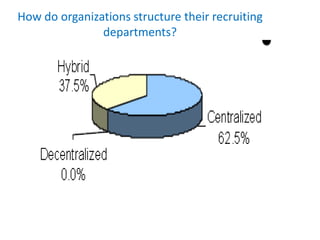
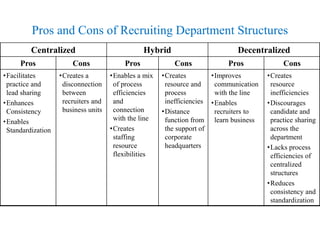
The document discusses recruitment and selection processes. It describes recruitment as generating a pool of job applicants, while selection is choosing candidates most likely to succeed using specific instruments. Effective manpower planning involves having the right number and type of people with the right skills in the right roles. Selection methods can include interviews, testing, and assessments to evaluate candidates. The key is choosing valid and reliable methods suitable for the position and organization.