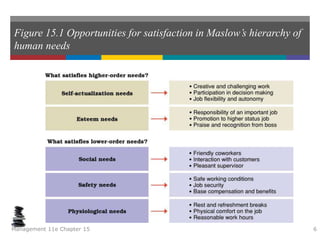
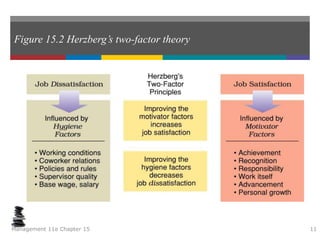
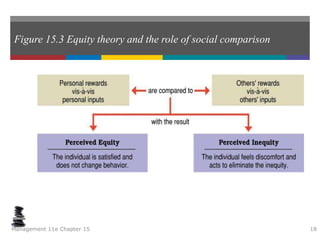
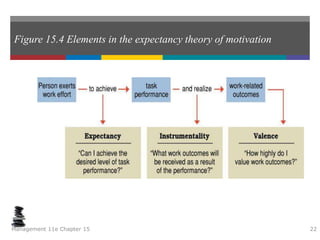
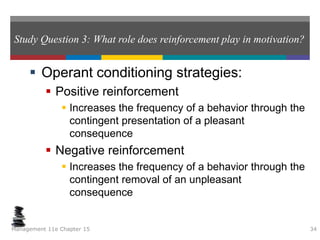
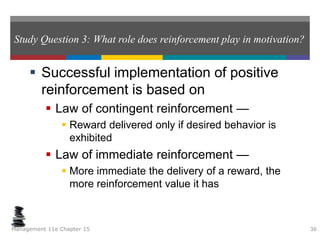
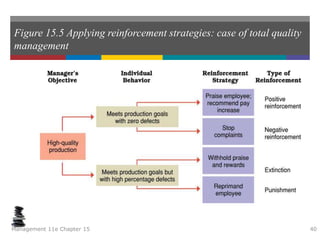
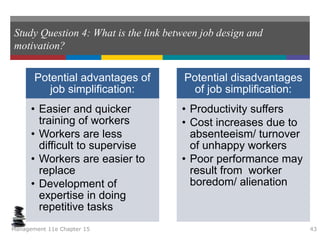
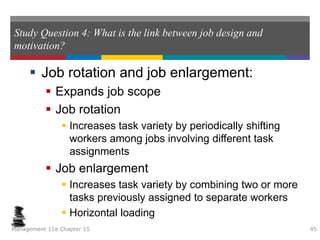
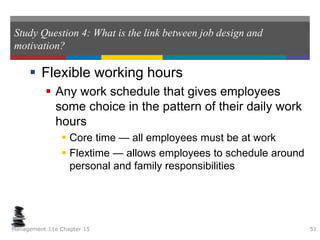
This document summarizes key concepts from a chapter on motivation theory and job design. It discusses how individual needs influence motivation according to various theories, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and ERG theory. It also covers process theories of motivation like equity theory, expectancy theory, goal-setting theory, and reinforcement theory. Finally, it examines the link between job design and motivation, addressing concepts like job simplification, job enrichment, and the job characteristics model.