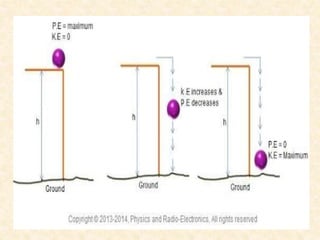
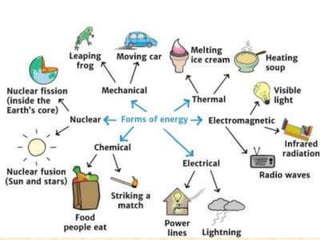
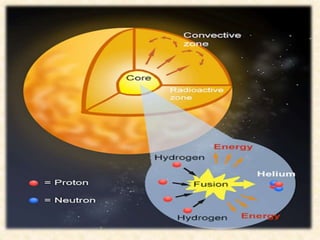
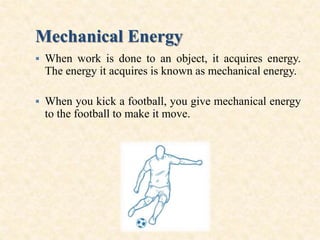
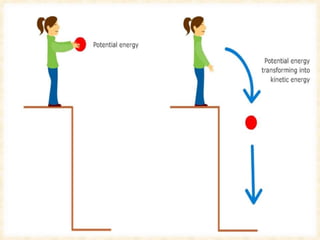
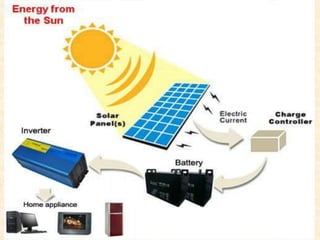
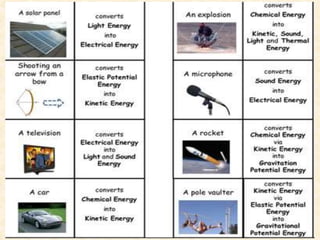
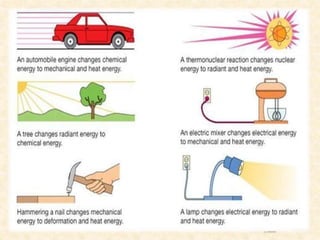
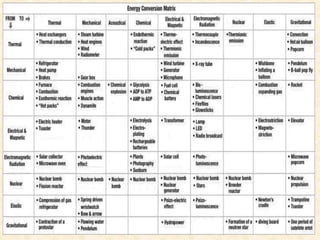
Maga Ram Patel from the Department of Renewable Energy Engineering at MPUAT University in Udaipur, India presented on the basic science of energy conversion. The presentation defined energy as the ability to do work and discussed the law of conservation of energy. It explained that energy can be converted between different states such as potential and kinetic energy, and covered various types of energy including thermal, chemical, electromagnetic, nuclear, mechanical, and others. The presentation emphasized that energy can be converted from one form to another through various processes in nature and technology.