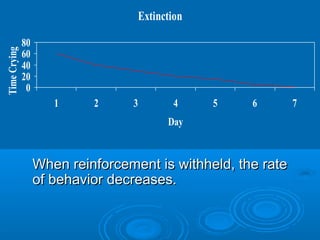
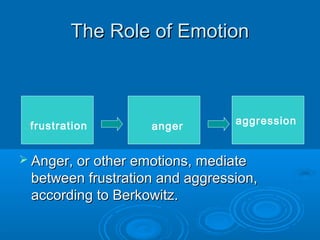
This document discusses key concepts from psychoanalytic learning theory, including drive, cue, response, and reward. It also examines how these concepts apply to teaching a two-year-old to go quietly to bed through techniques like punishment, extinction, and spontaneous recovery. Conflicts are analyzed in terms of approach-avoidance, avoidance-avoidance, approach-approach, and double approach-avoidance. The role of frustration and aggression is explored through the frustration-aggression hypothesis and factors like individual differences in responses, displacement, hostile versus instrumental aggression, and the role of emotions. Psychotherapy techniques aim to teach behavioral coping skills, cue discrimination, relaxation, and use language as a mediator of learning.