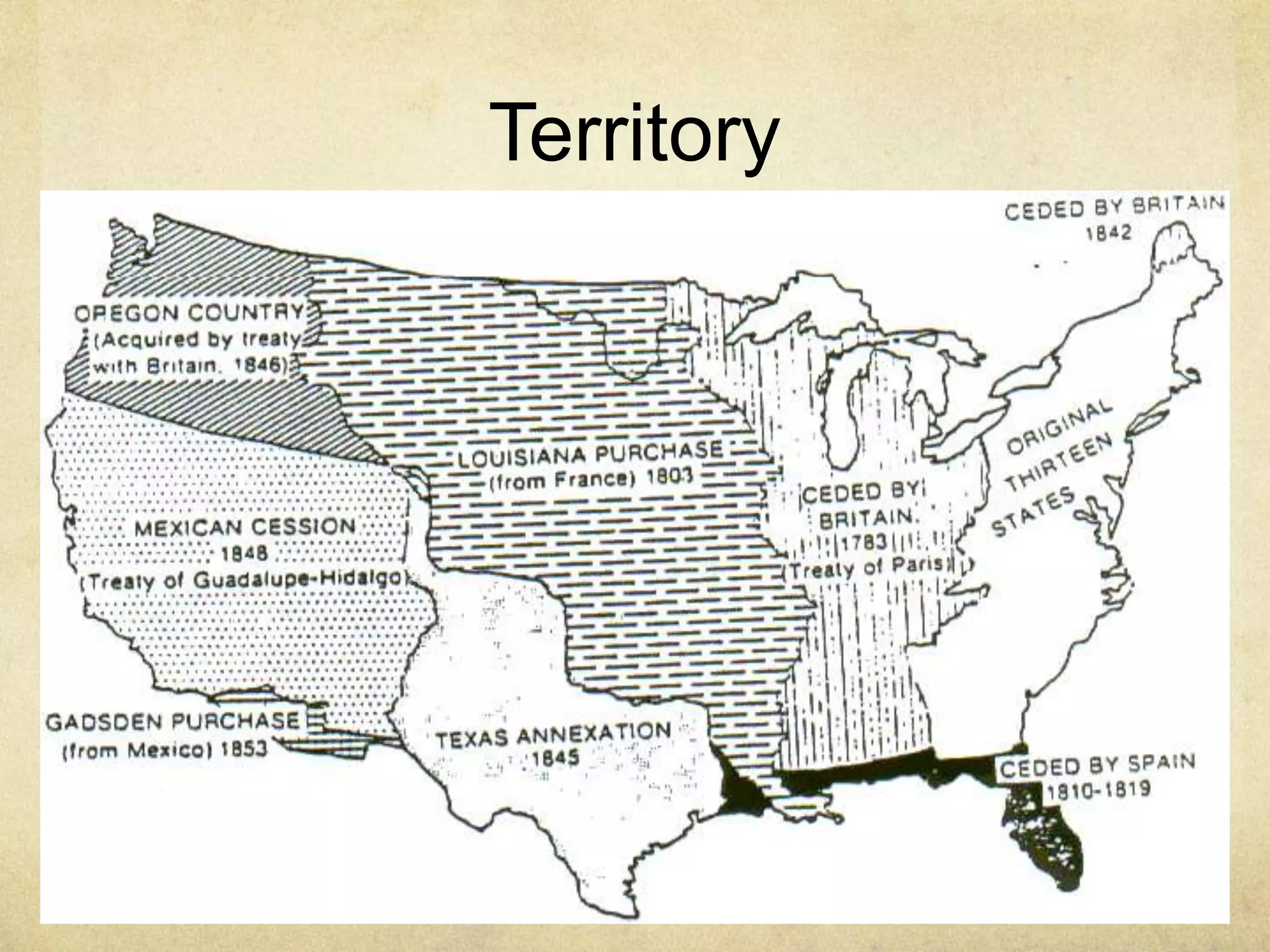
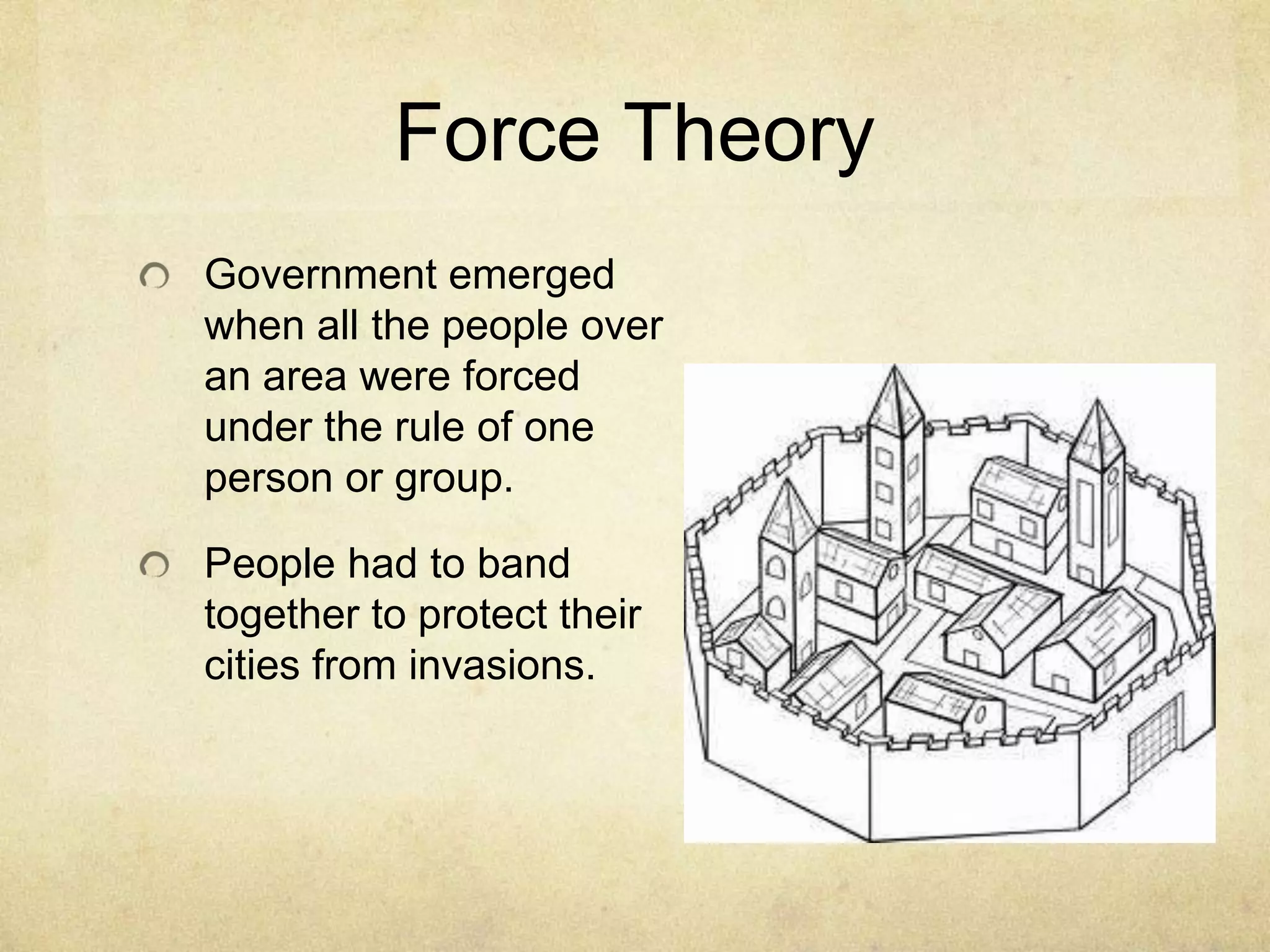
The document discusses the key features and origins of states and governments. It outlines four essential features of a state: population, territory, sovereignty, and government. It then describes four theories for the origin of states: evolutionary theory, force theory, divine right theory, and social contract theory. The social contract theory, proposed by philosophers like Thomas Hobbes and John Locke, suggests that people form governments and surrender some freedoms in exchange for protection of their basic rights from others.