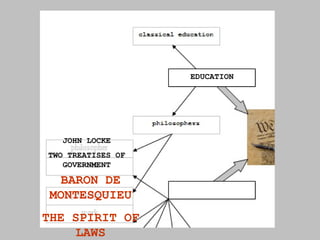
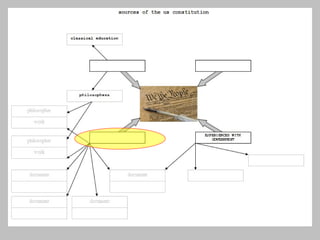
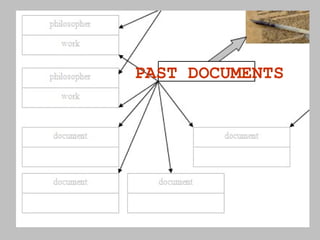
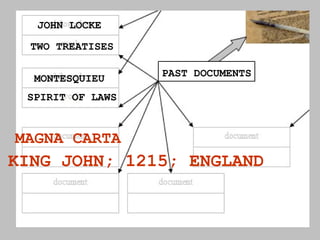
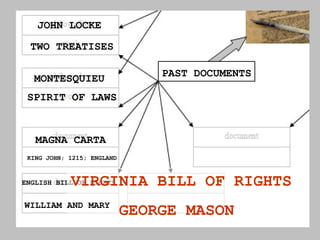
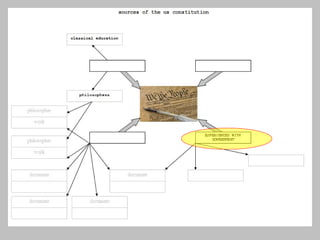
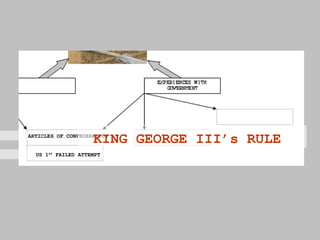
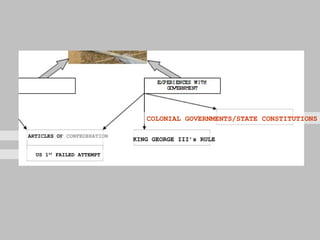
The document discusses the key concepts of what constitutes a state and government. It explains that a state requires a population, territory, and sovereignty (supreme power within its boundaries). A government is the institution through which a society makes and enforces public policies. The document then reviews several theories for how governments came into existence, such as through force, evolution from simpler groups, divine right of rulers, or social contract theory. It also outlines different ways of classifying governments, such as by participation (democracy vs dictatorship), distribution of power (unitary vs federal), and relationship between legislative and executive branches (presidential vs parliamentary).