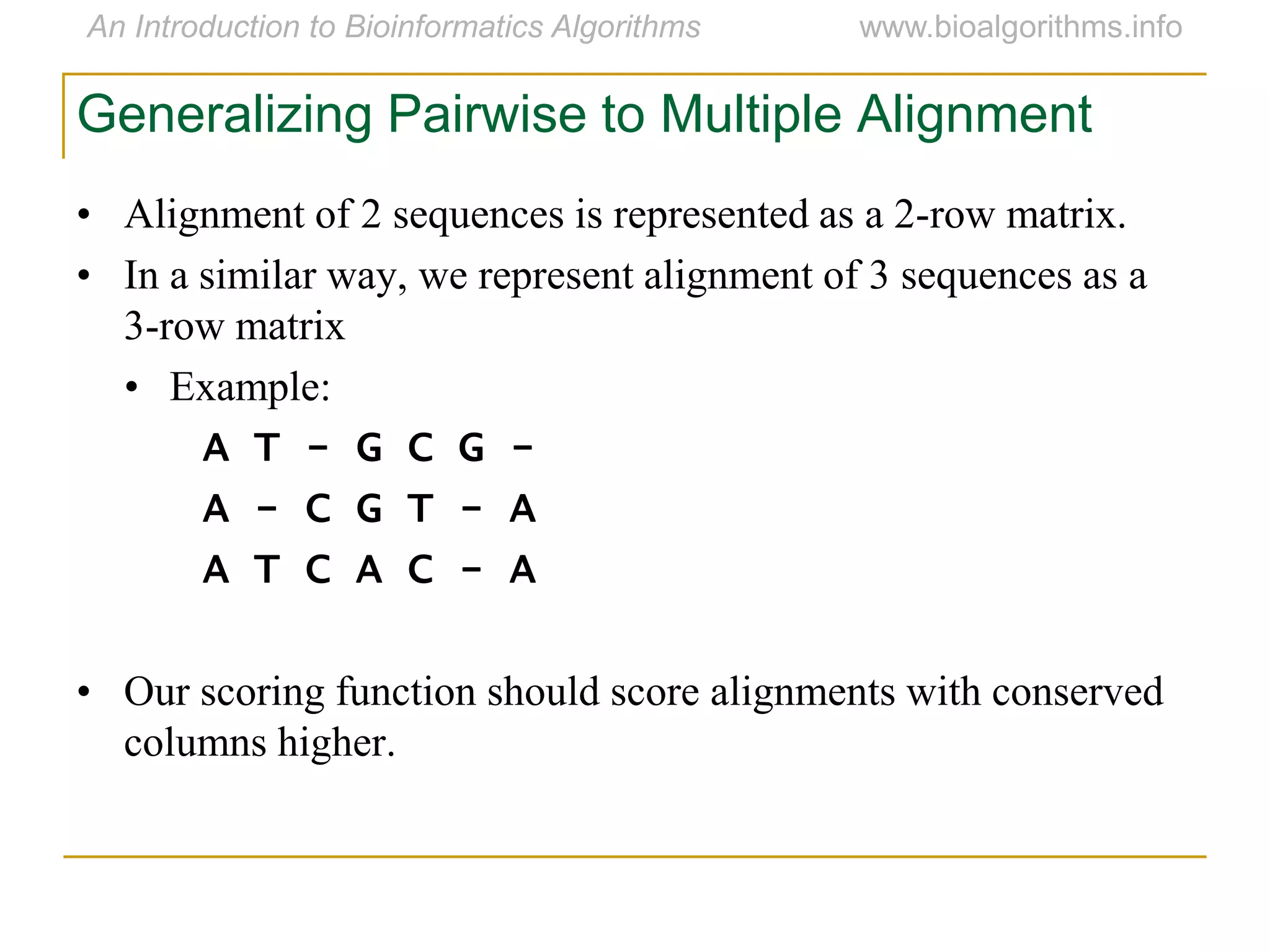
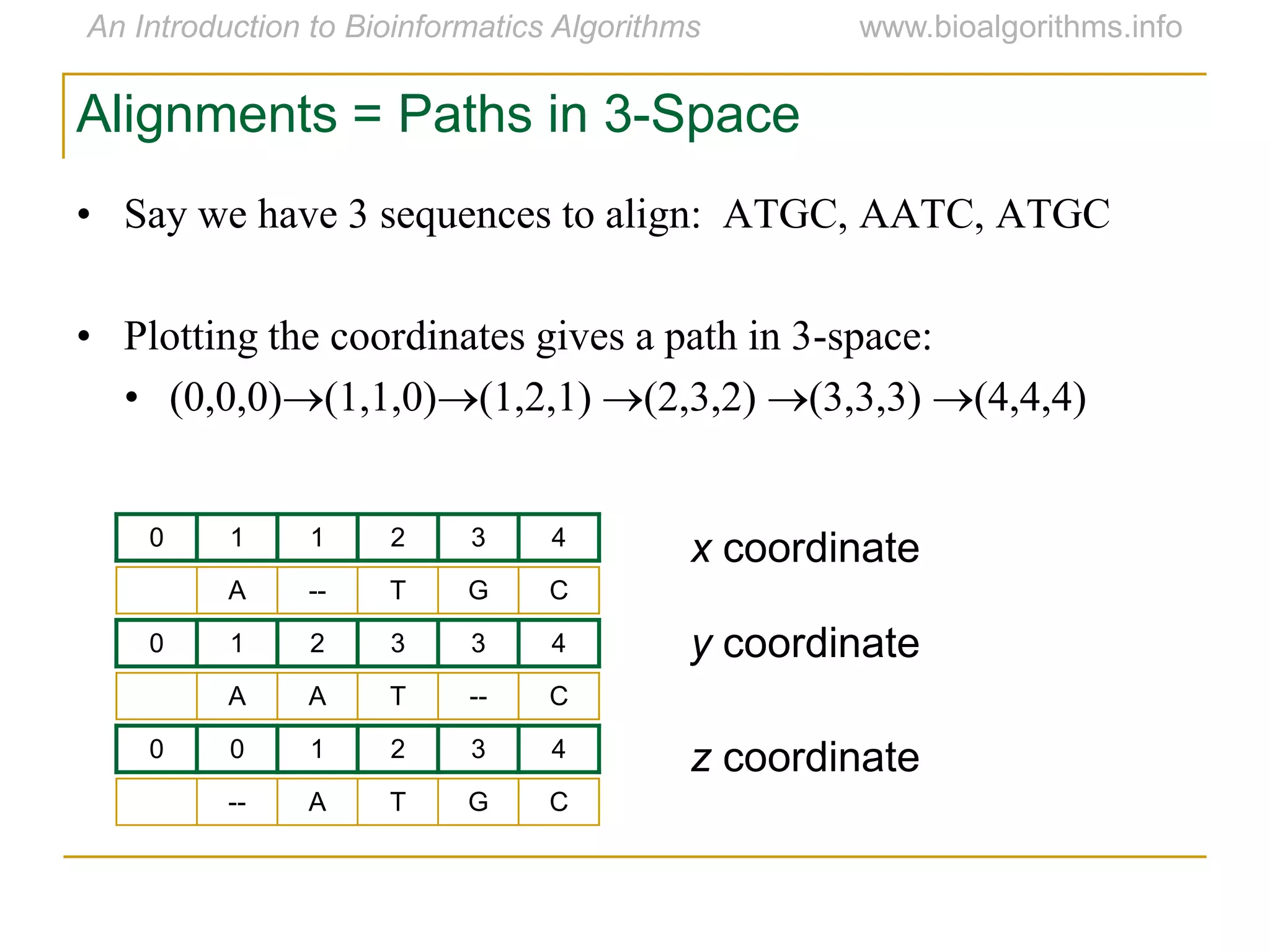
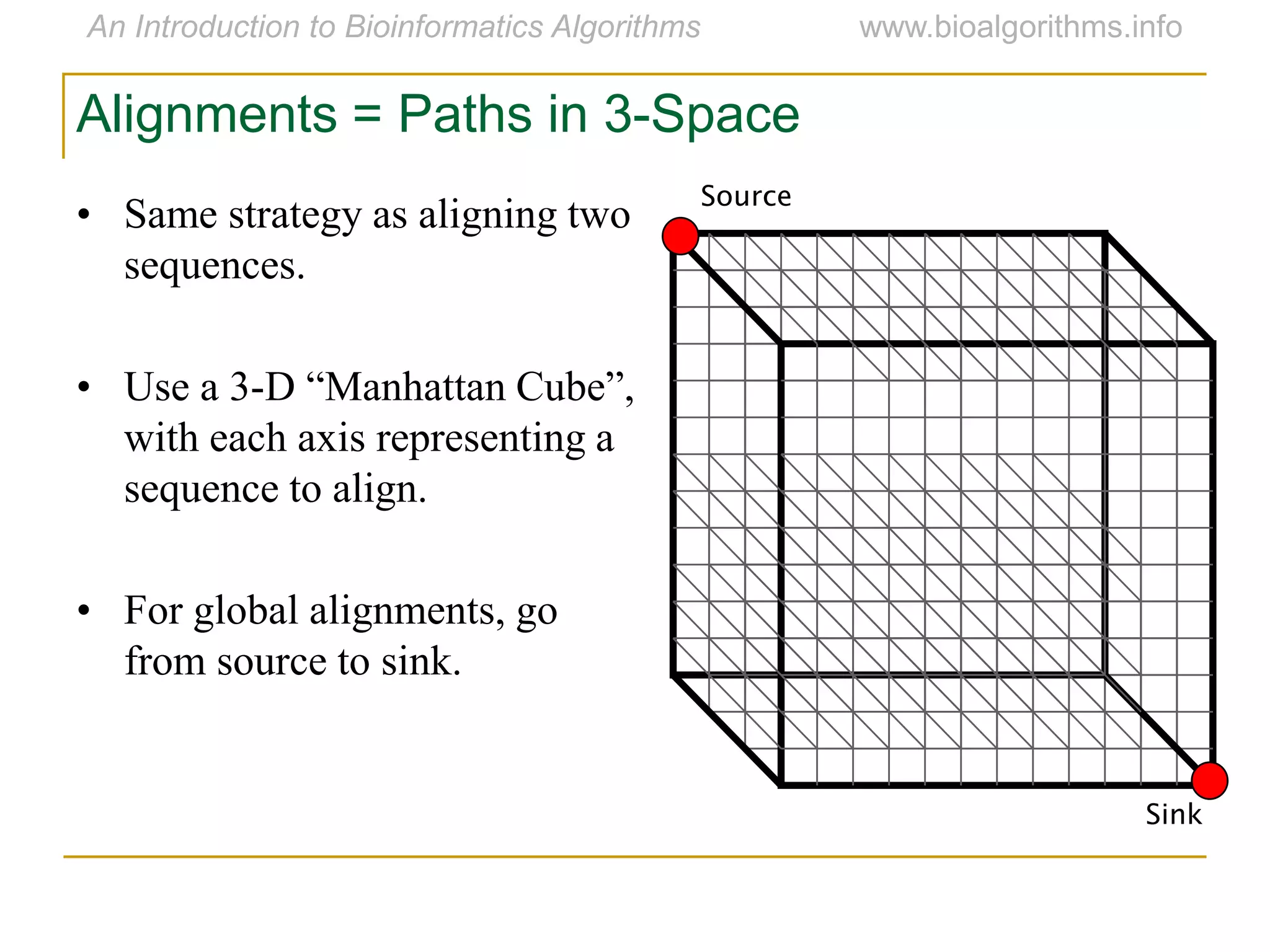
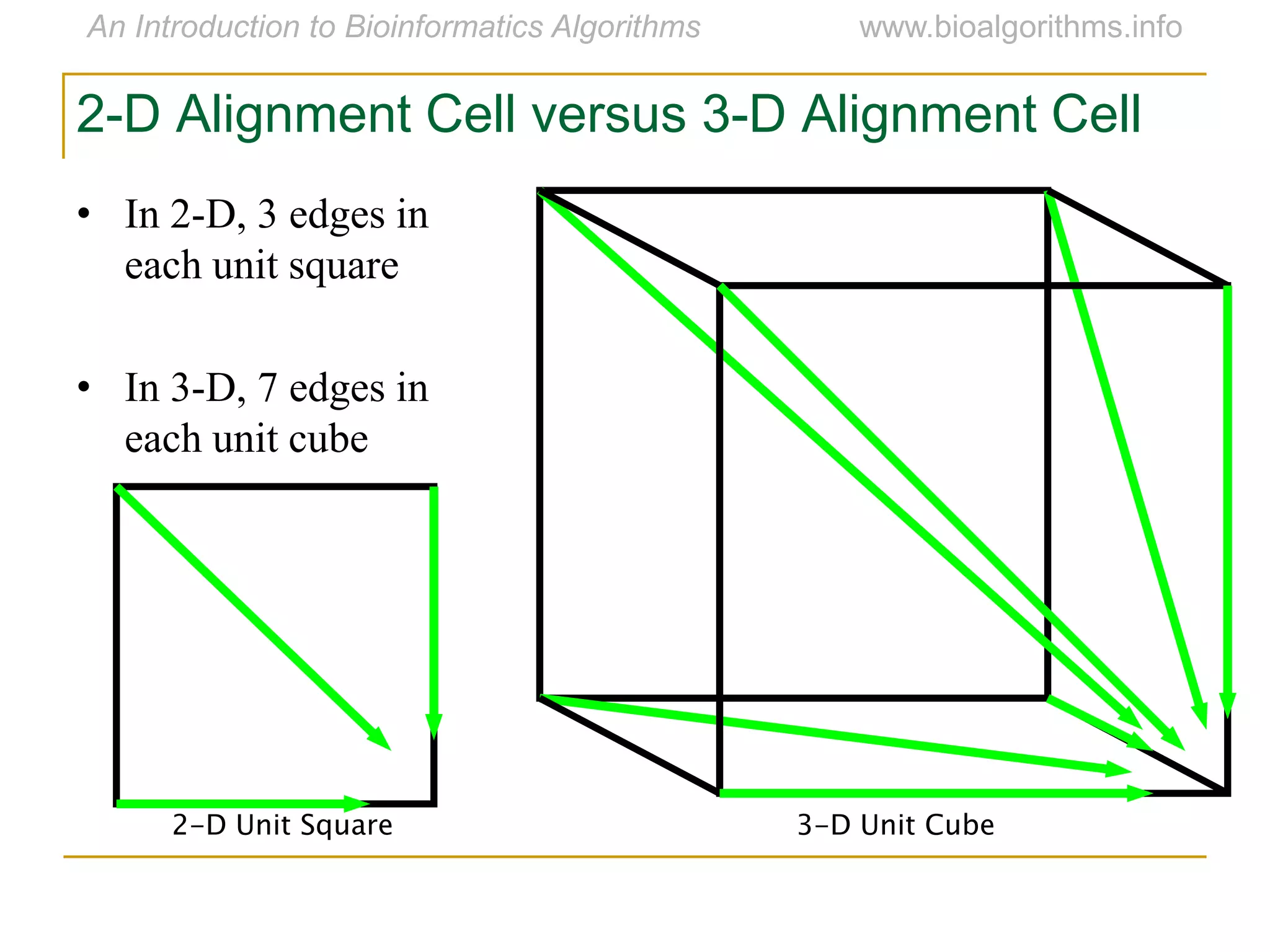
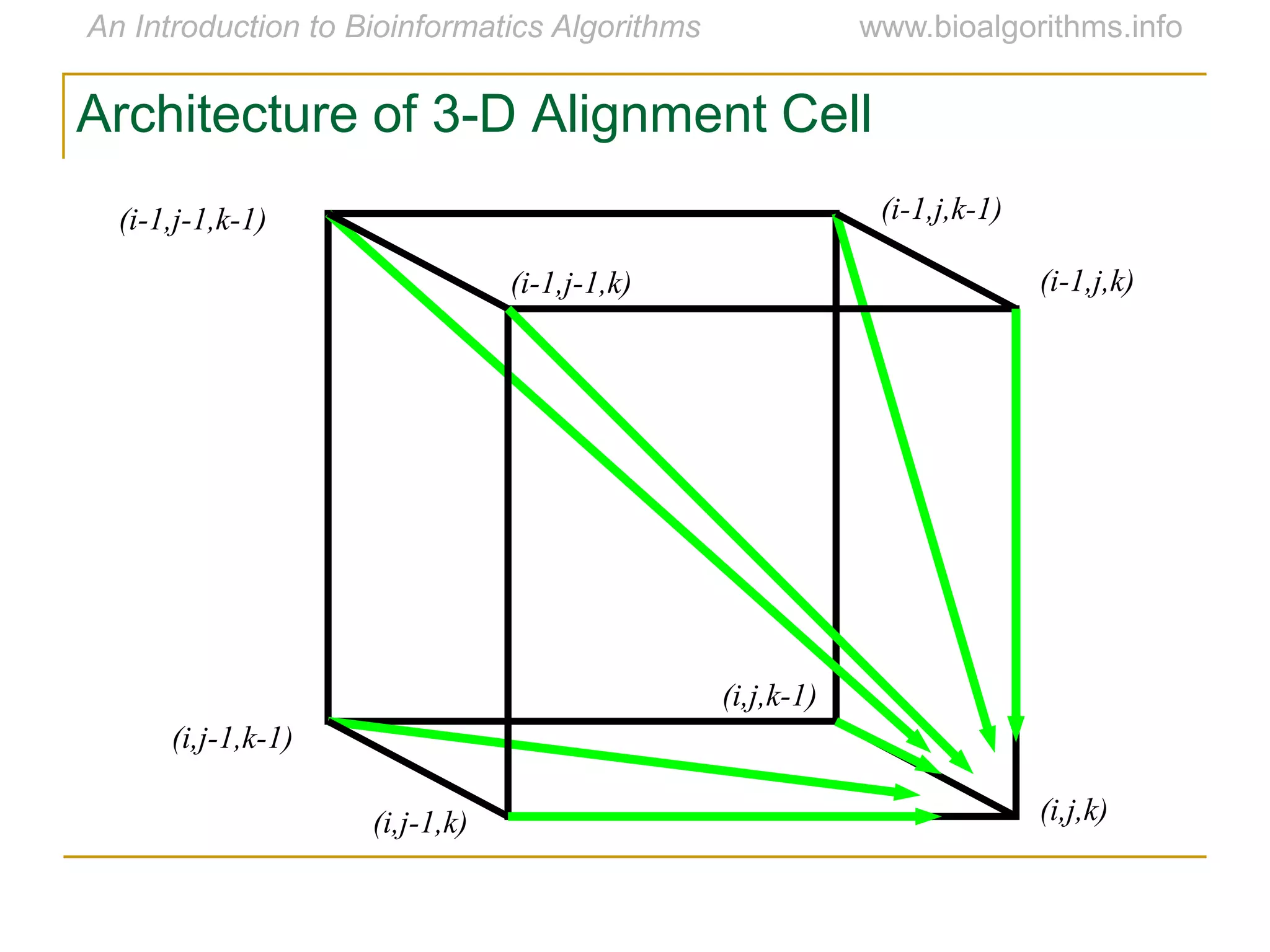
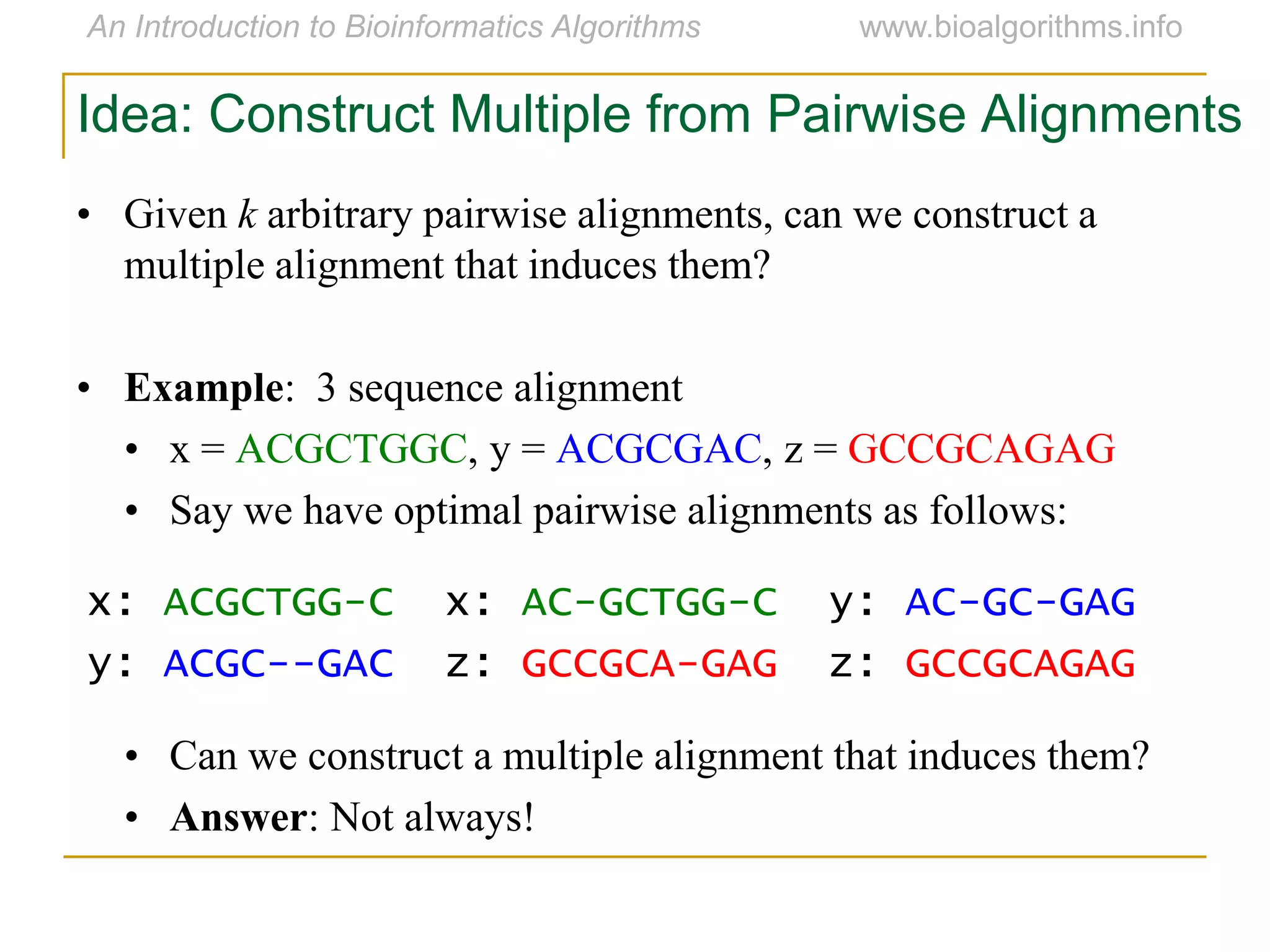
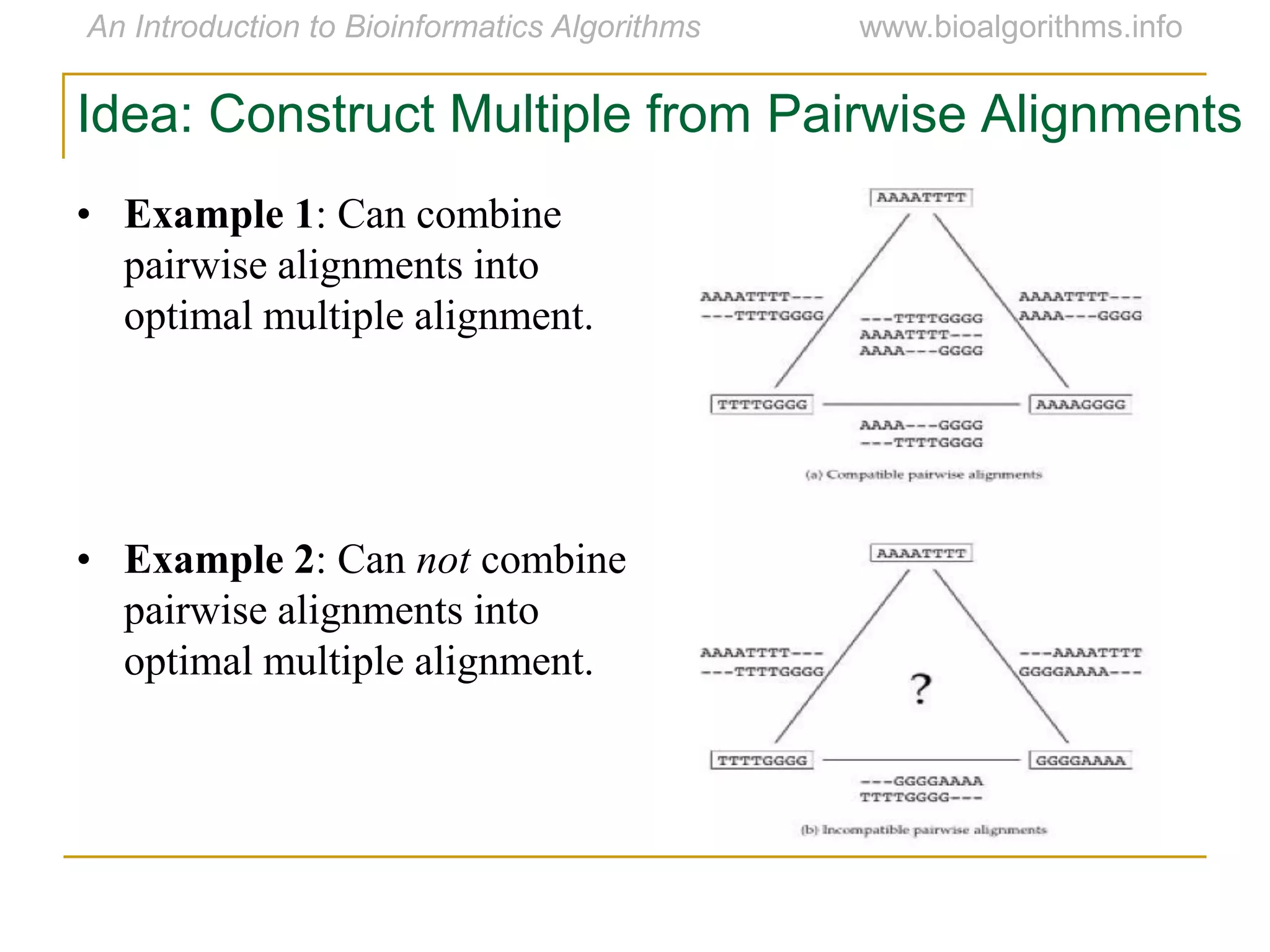
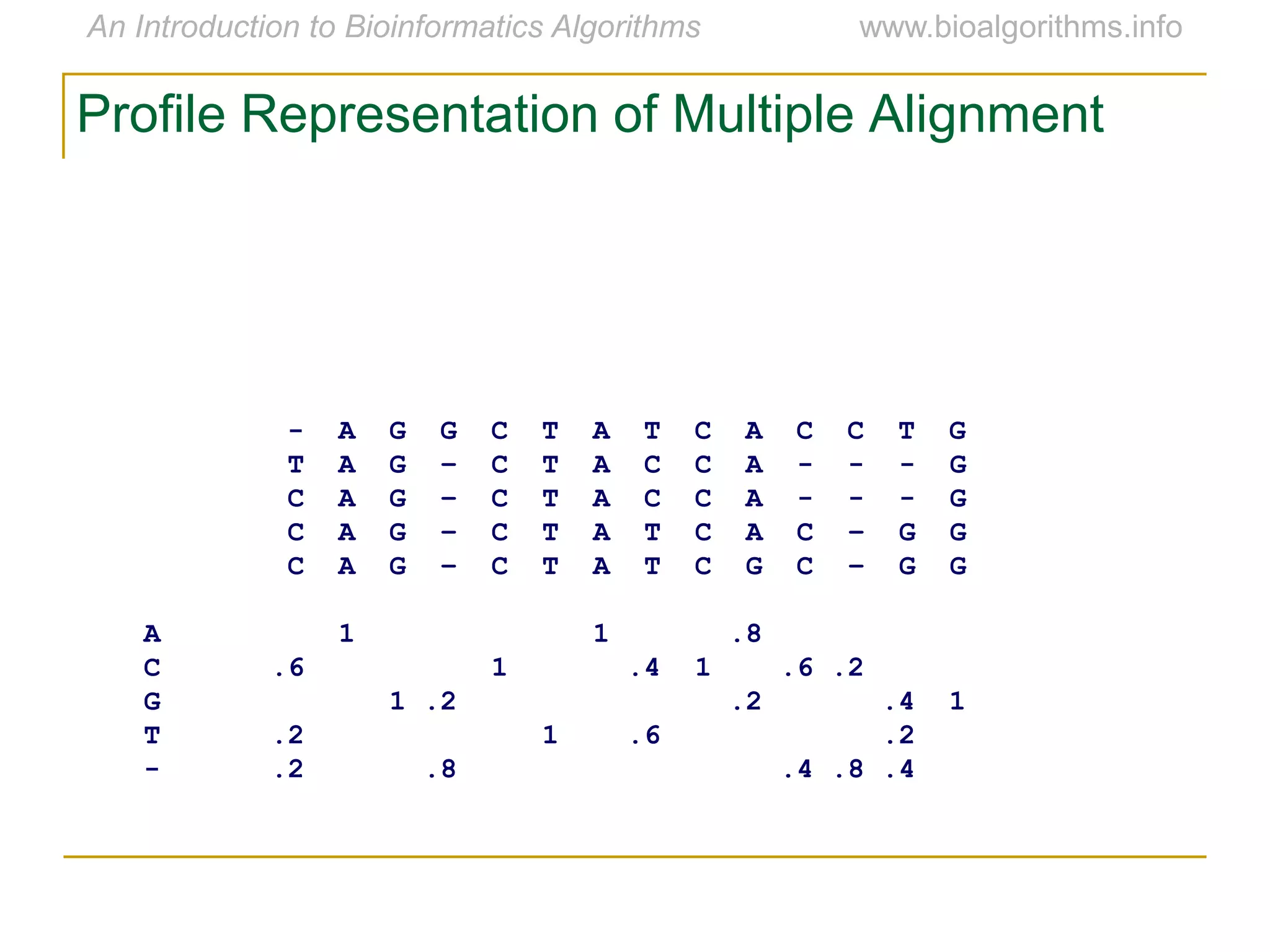
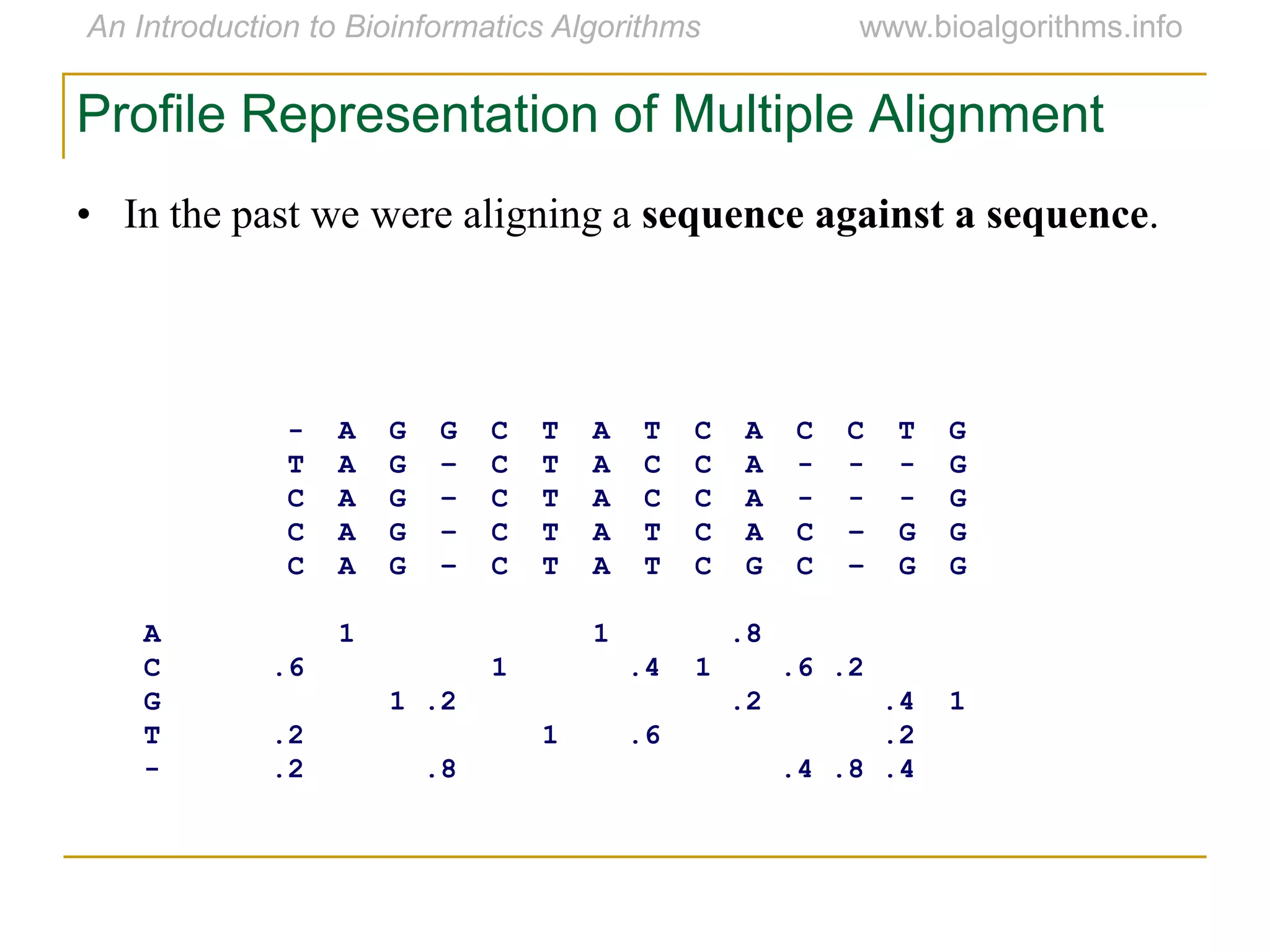
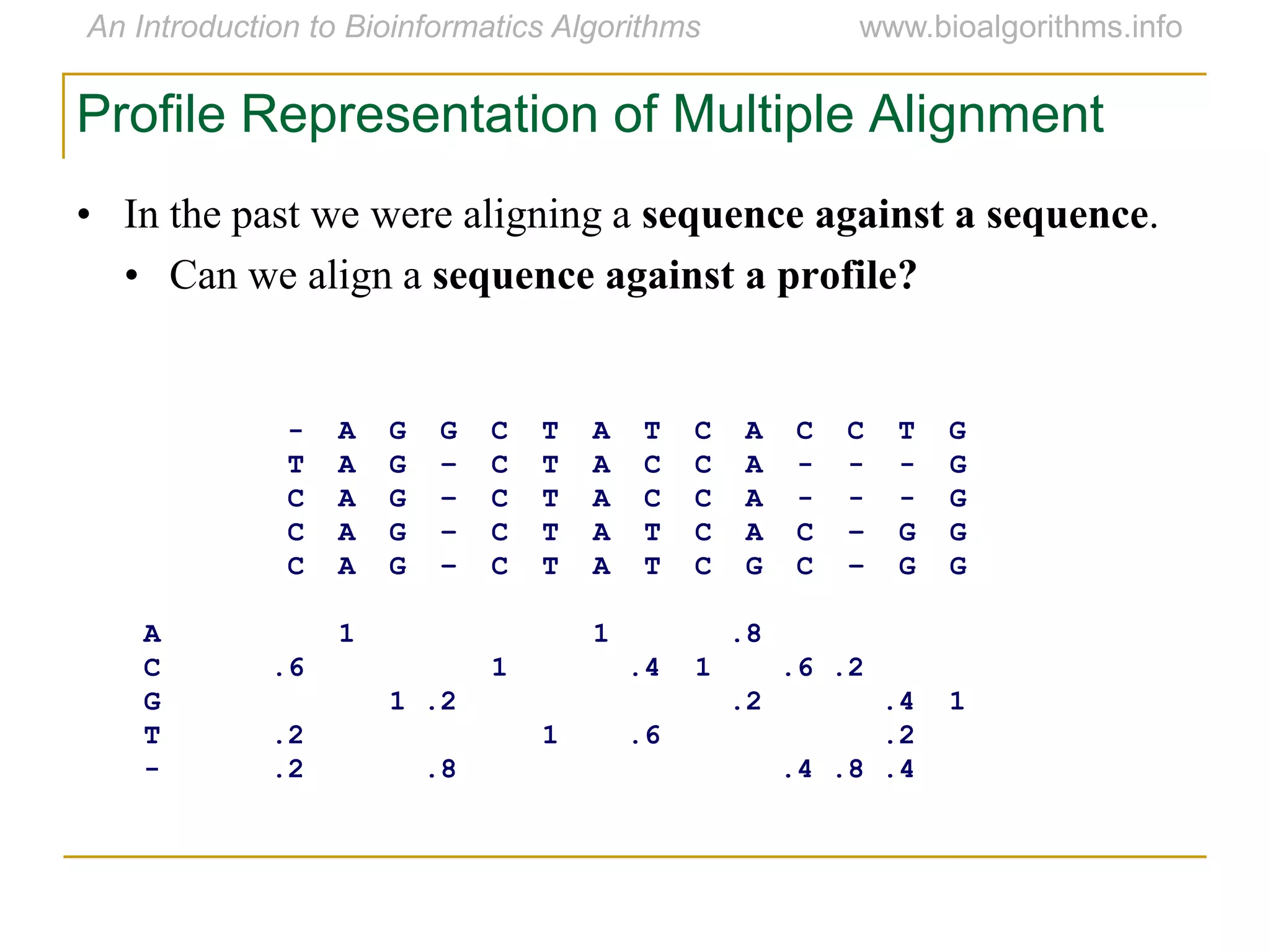
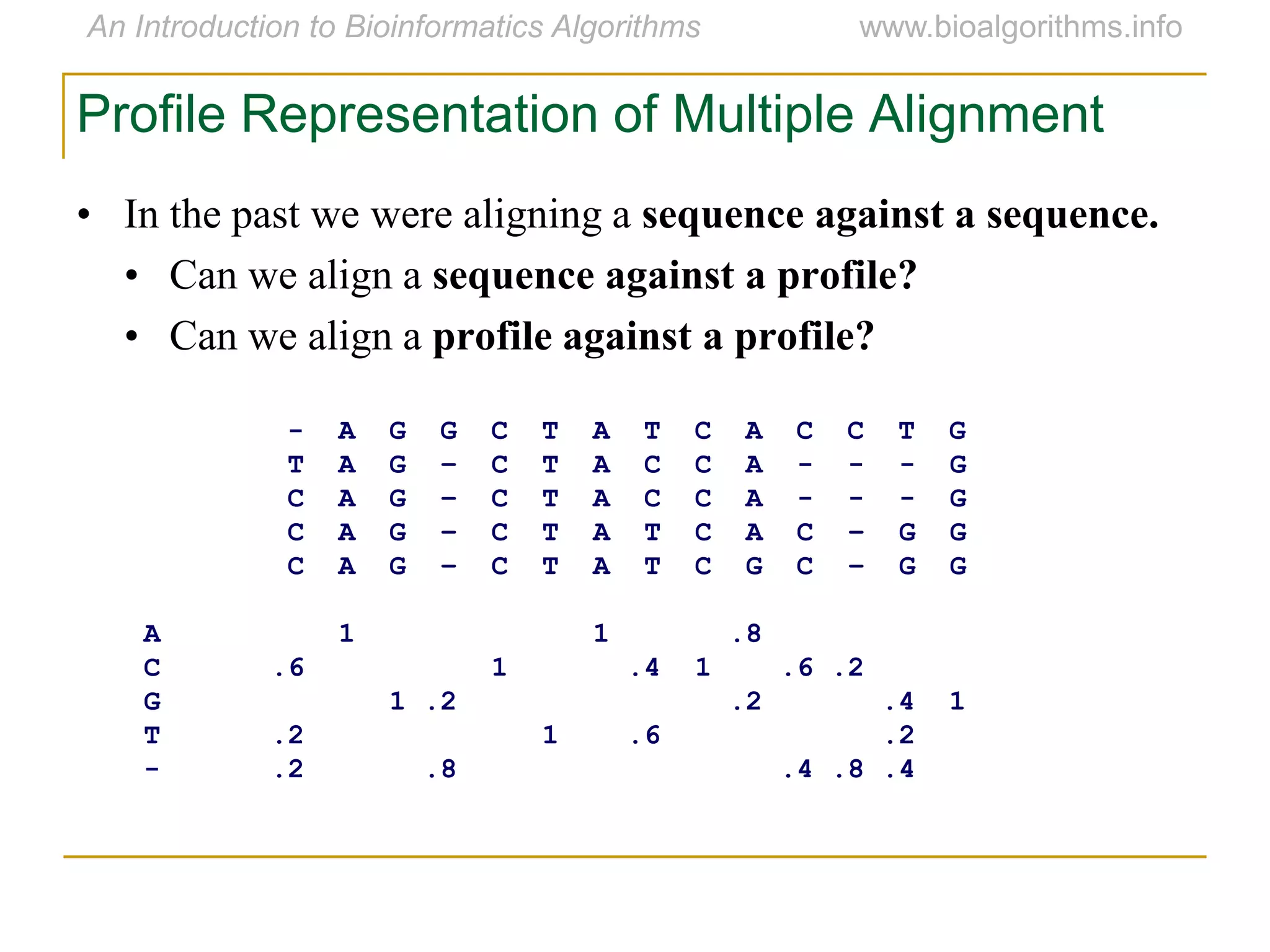
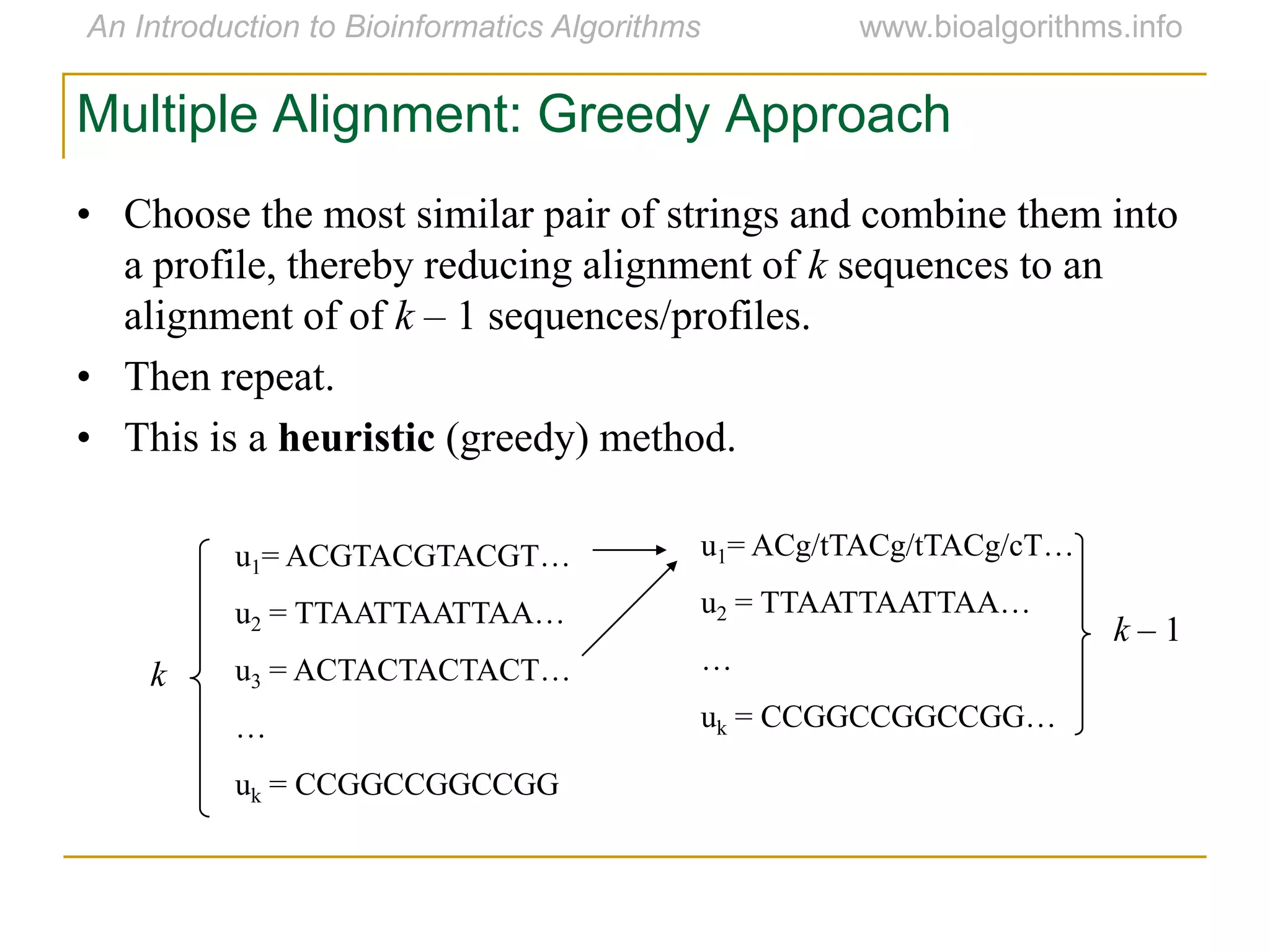
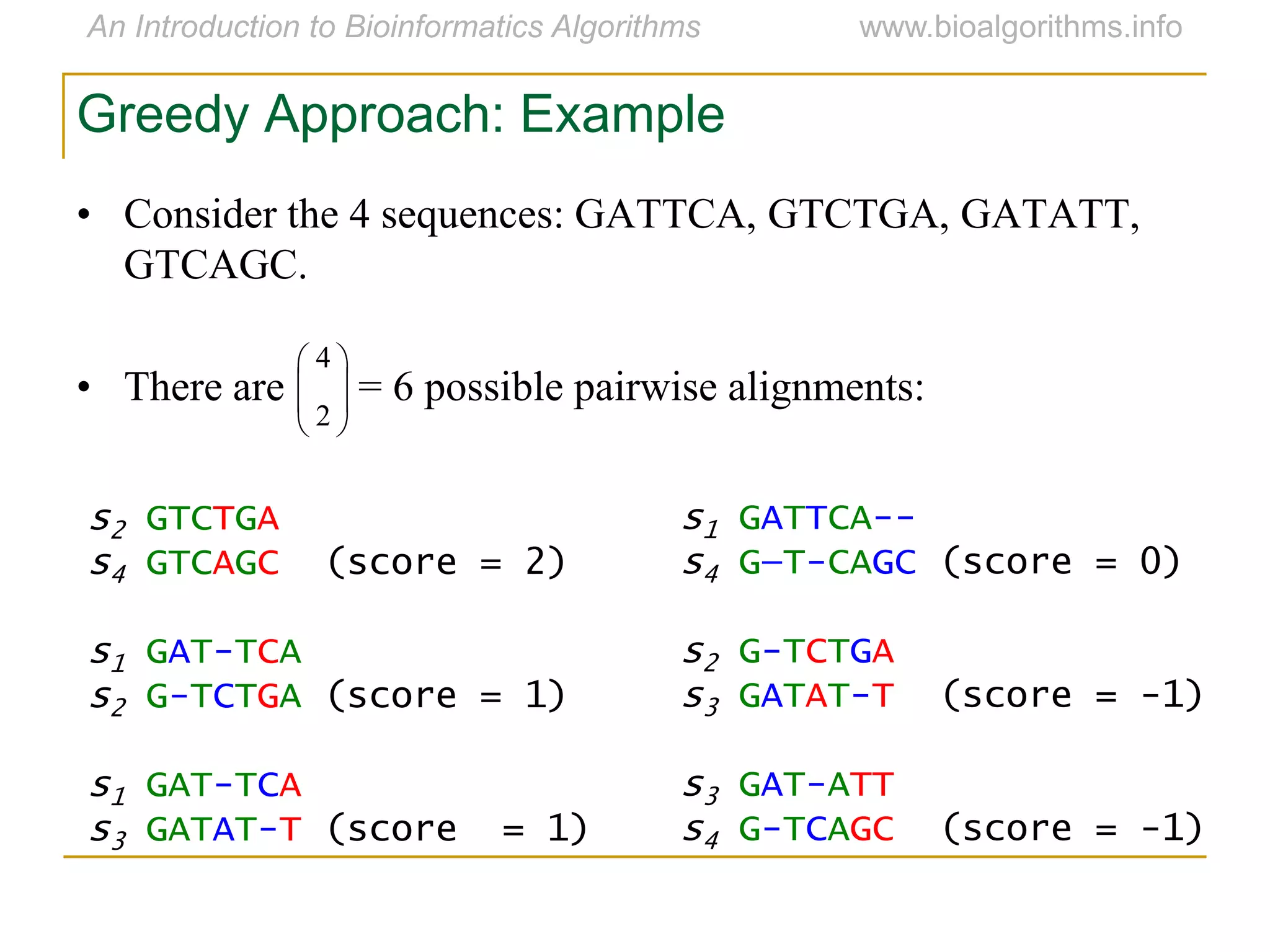
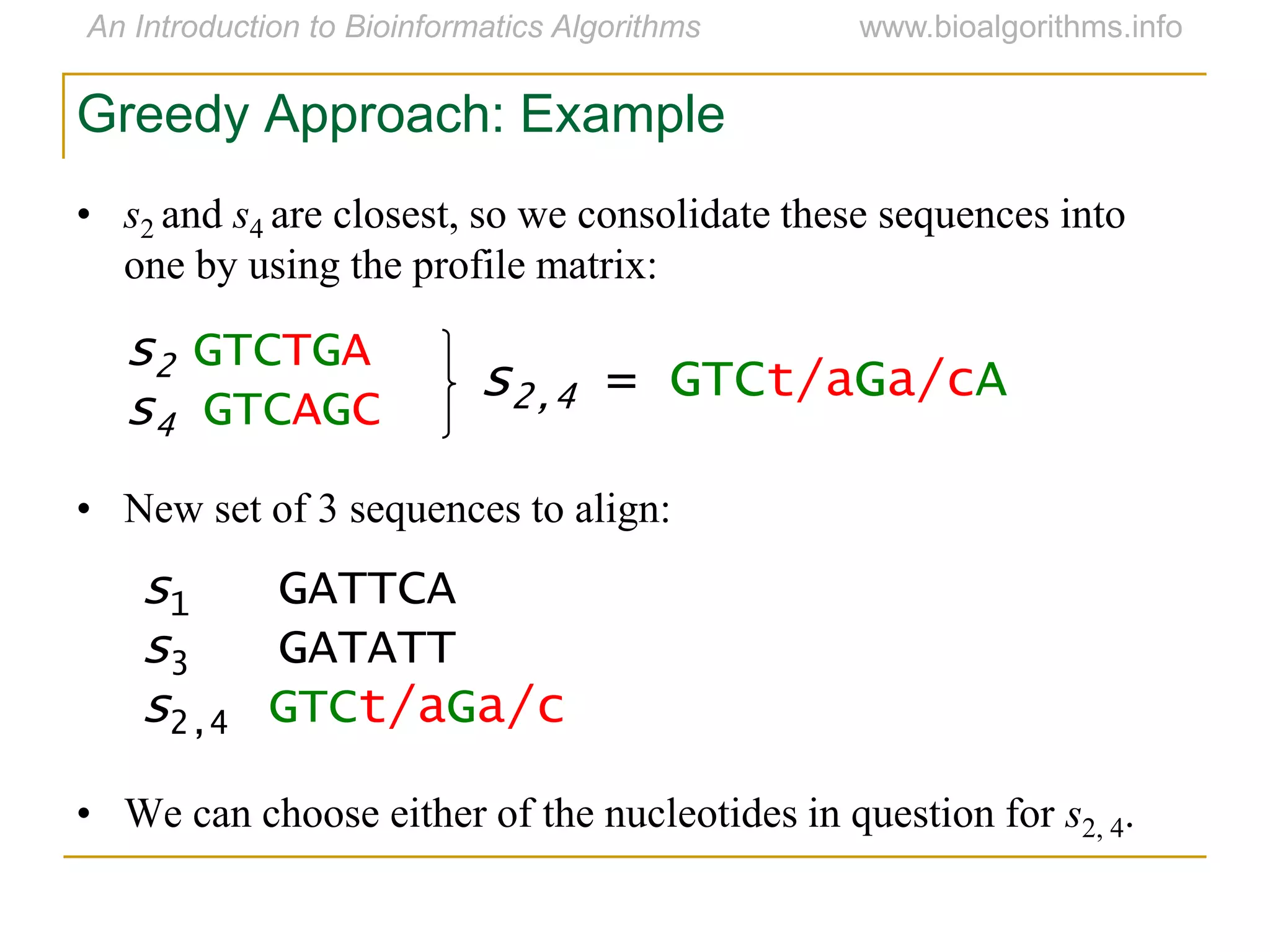
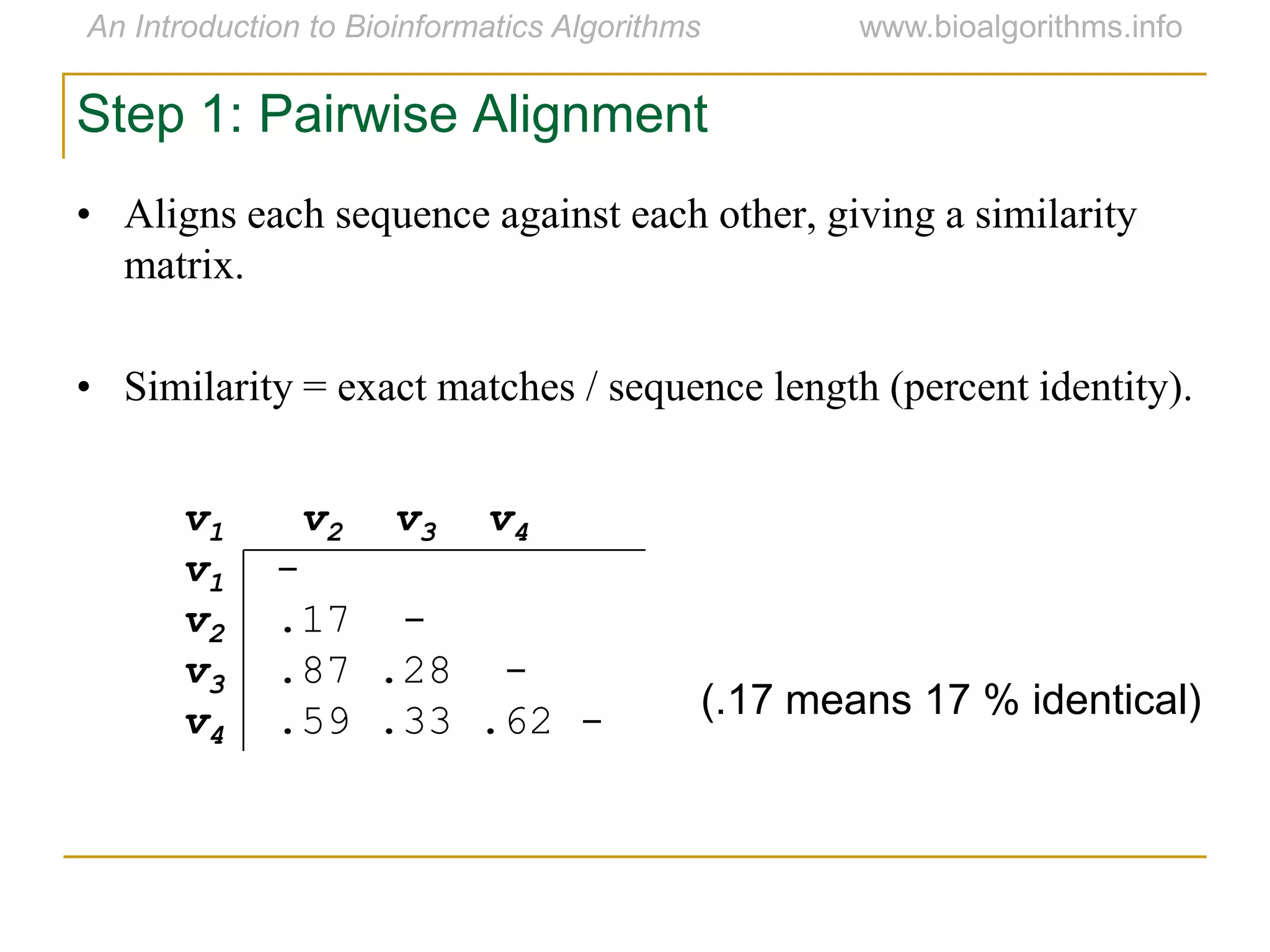
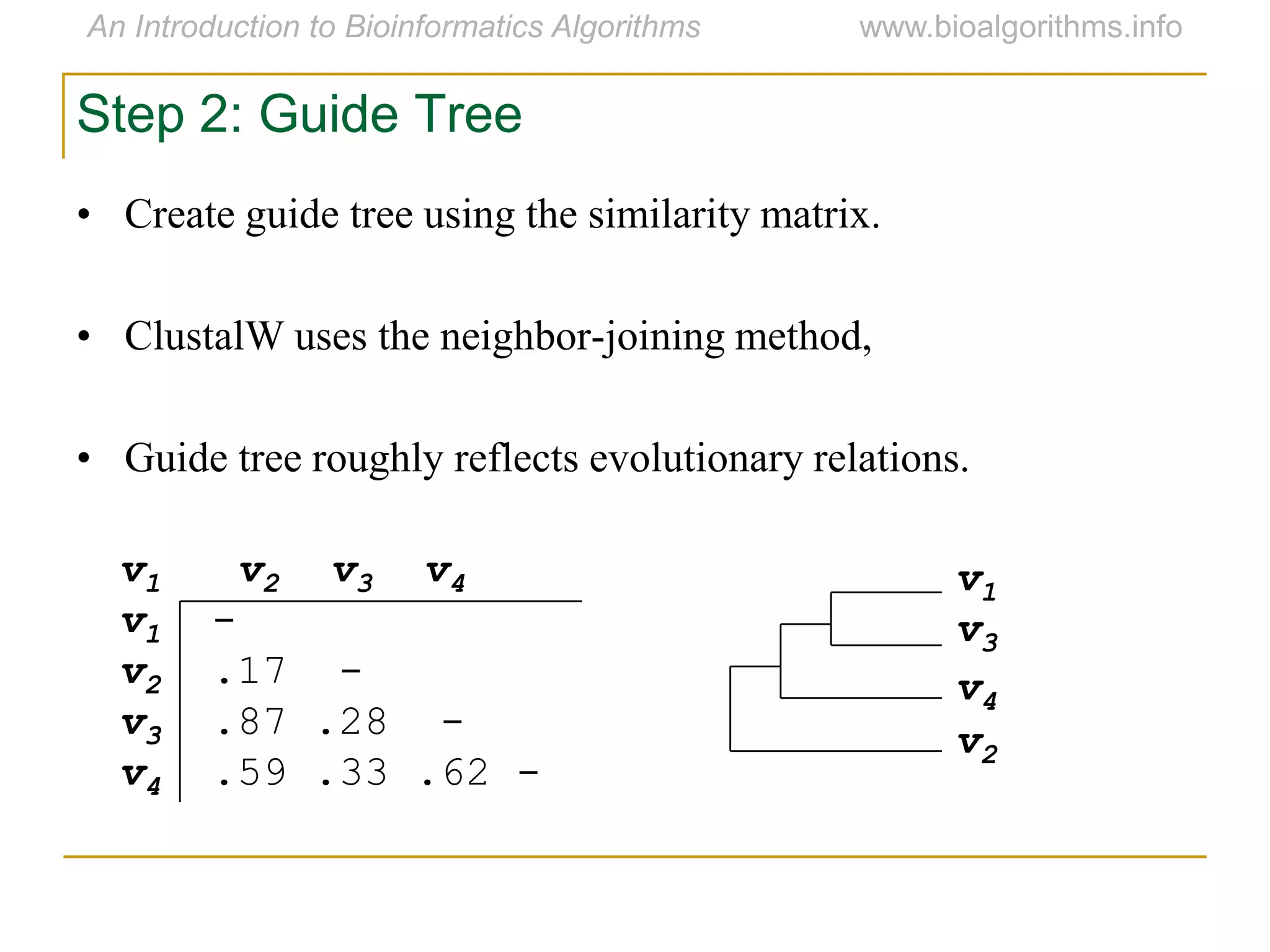
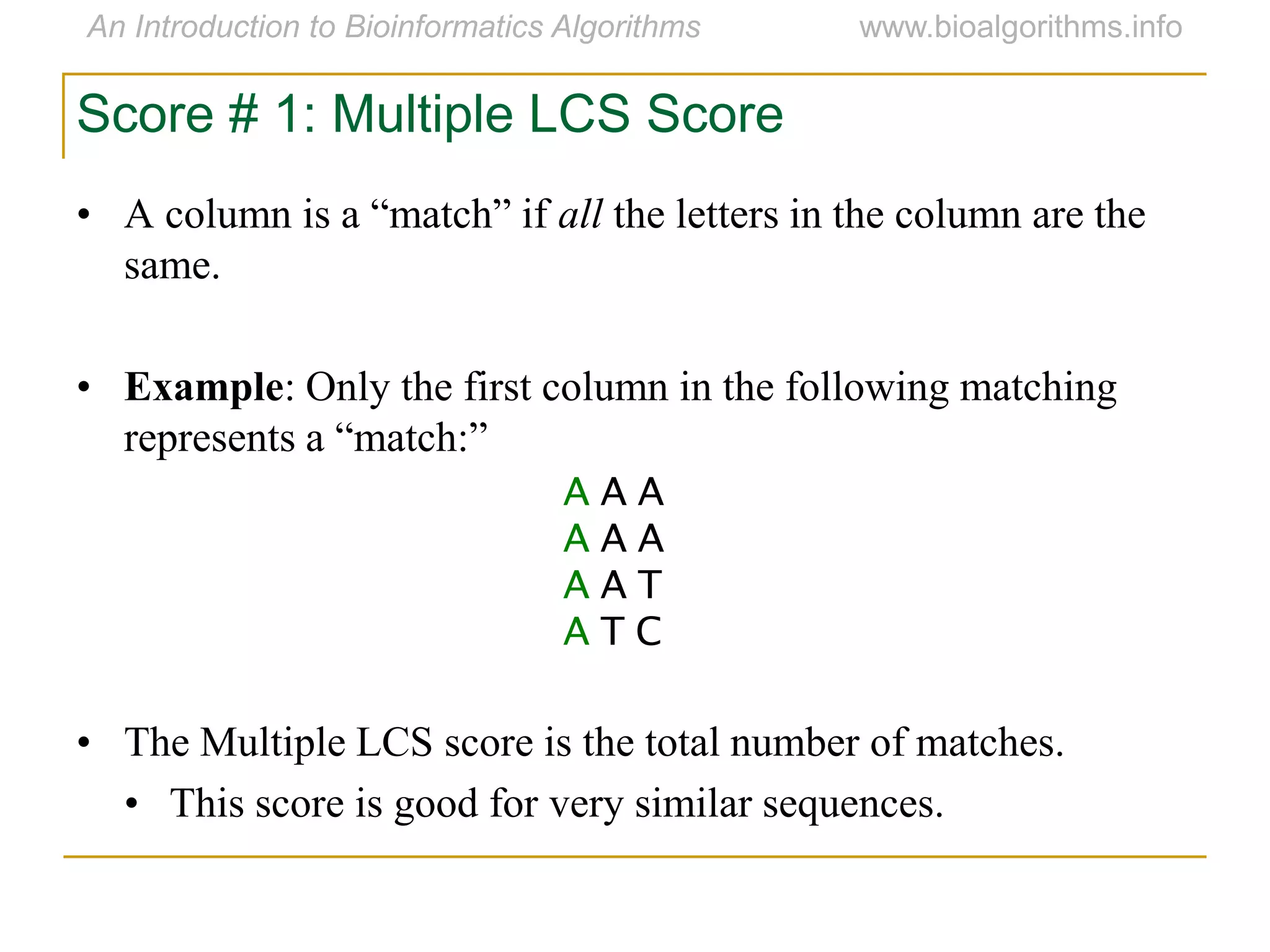
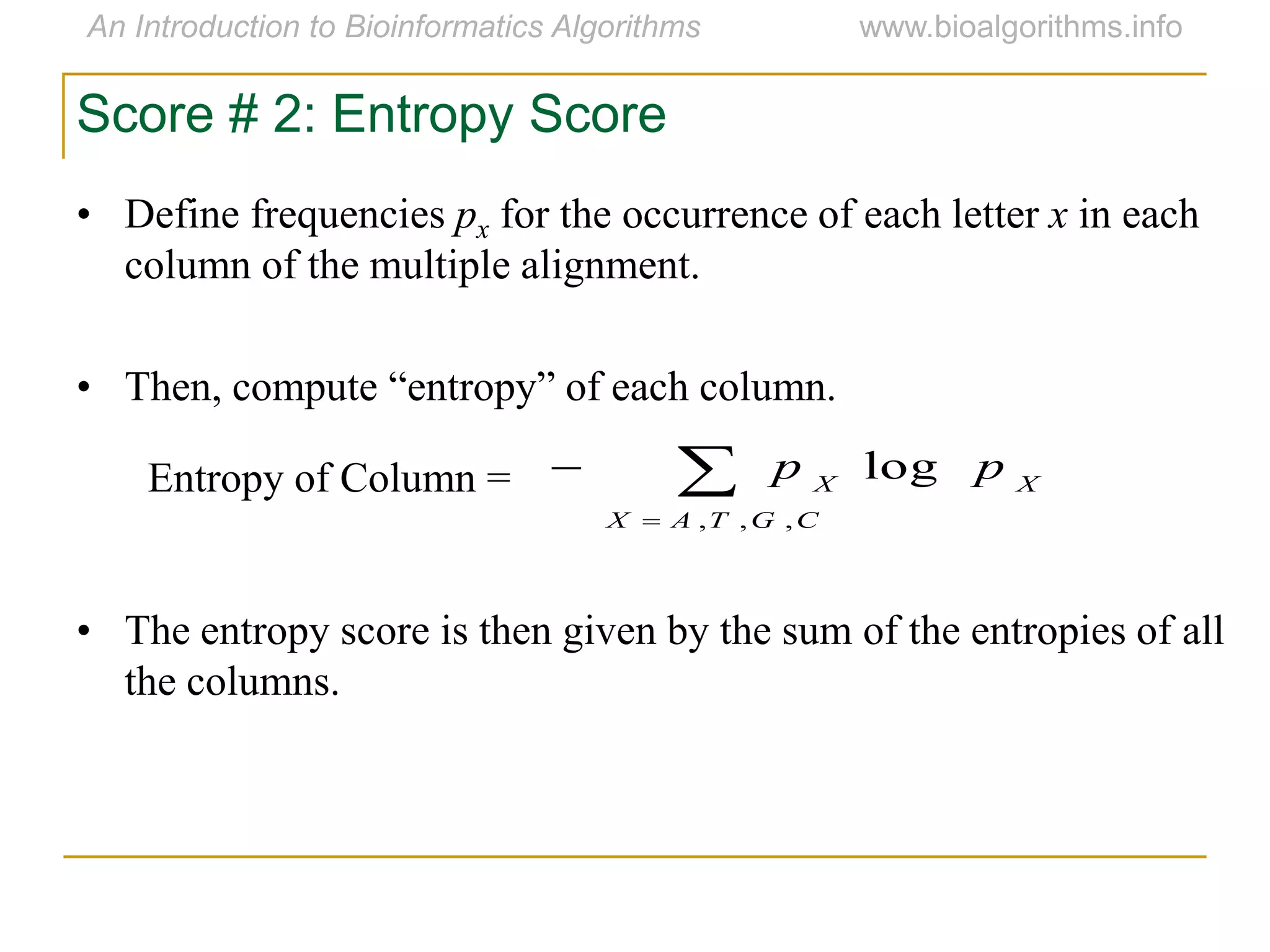
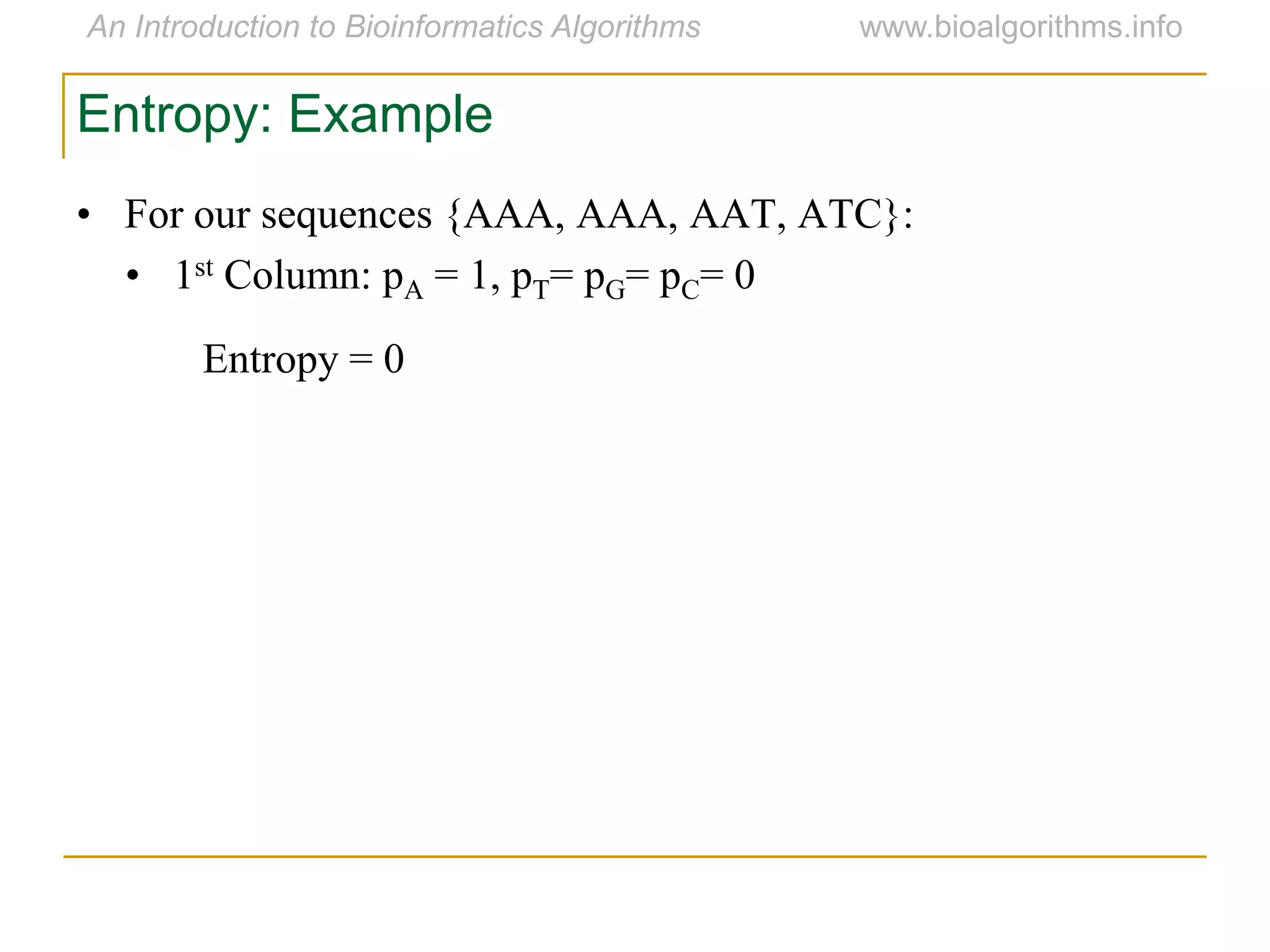
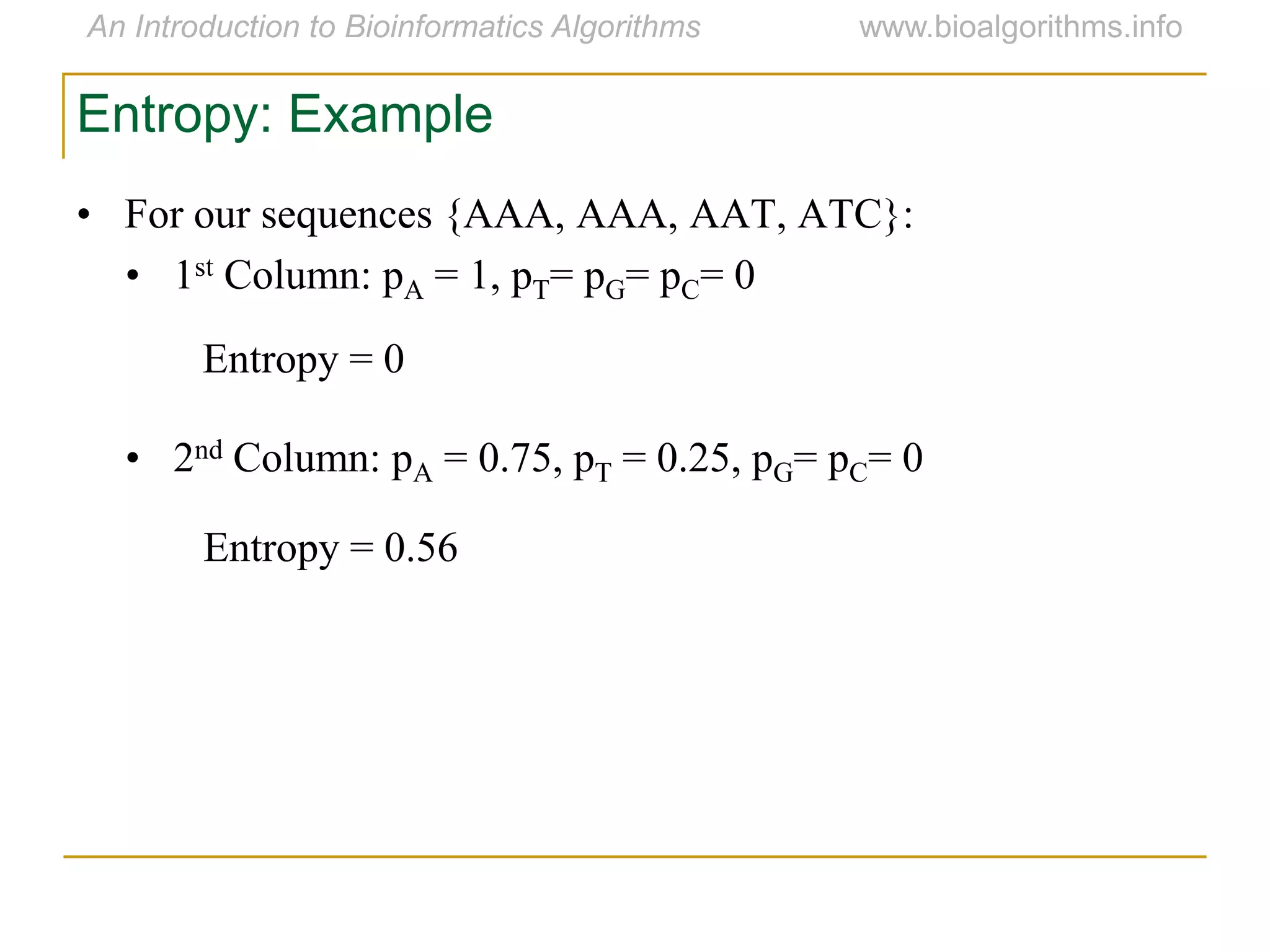
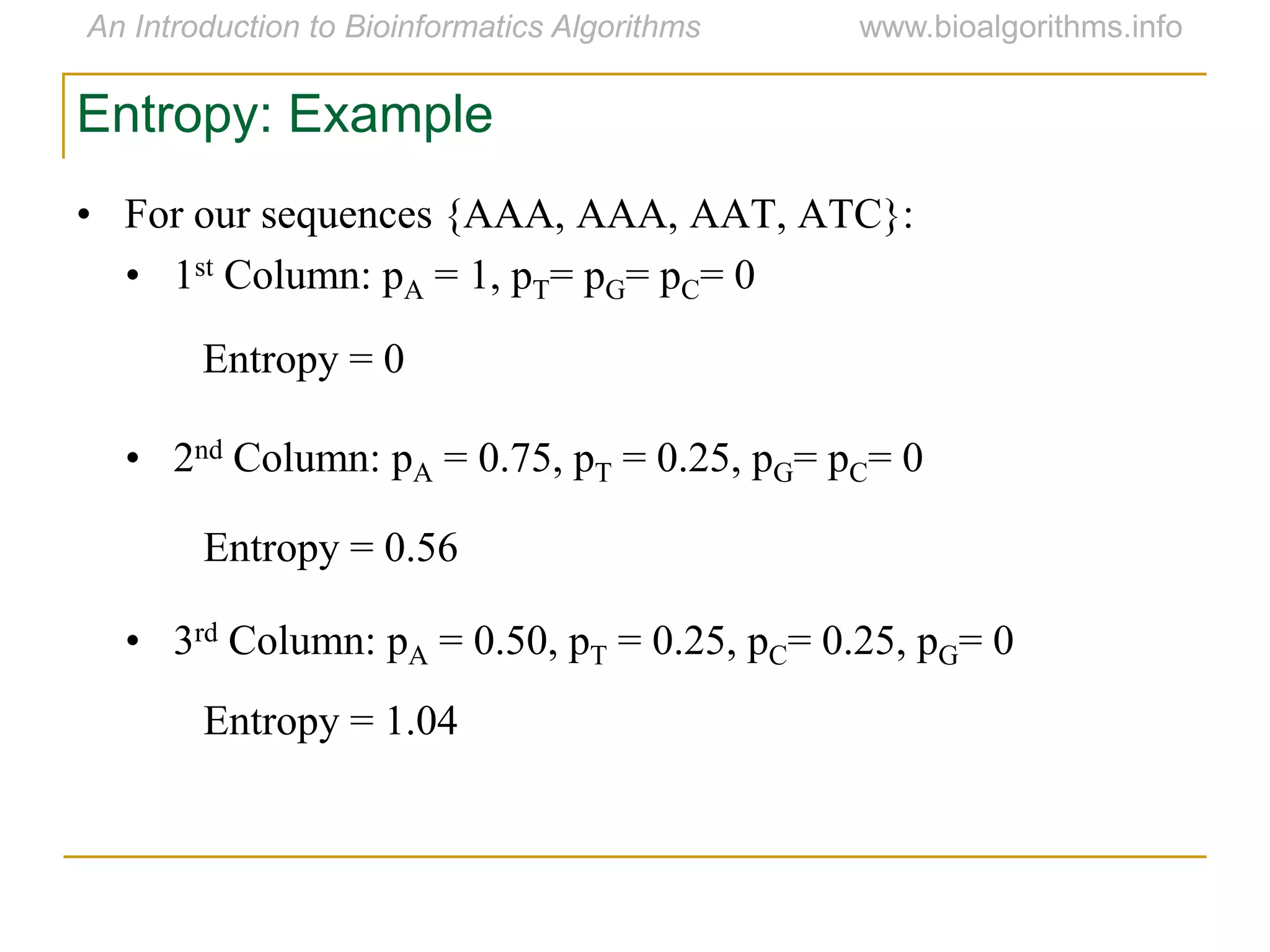
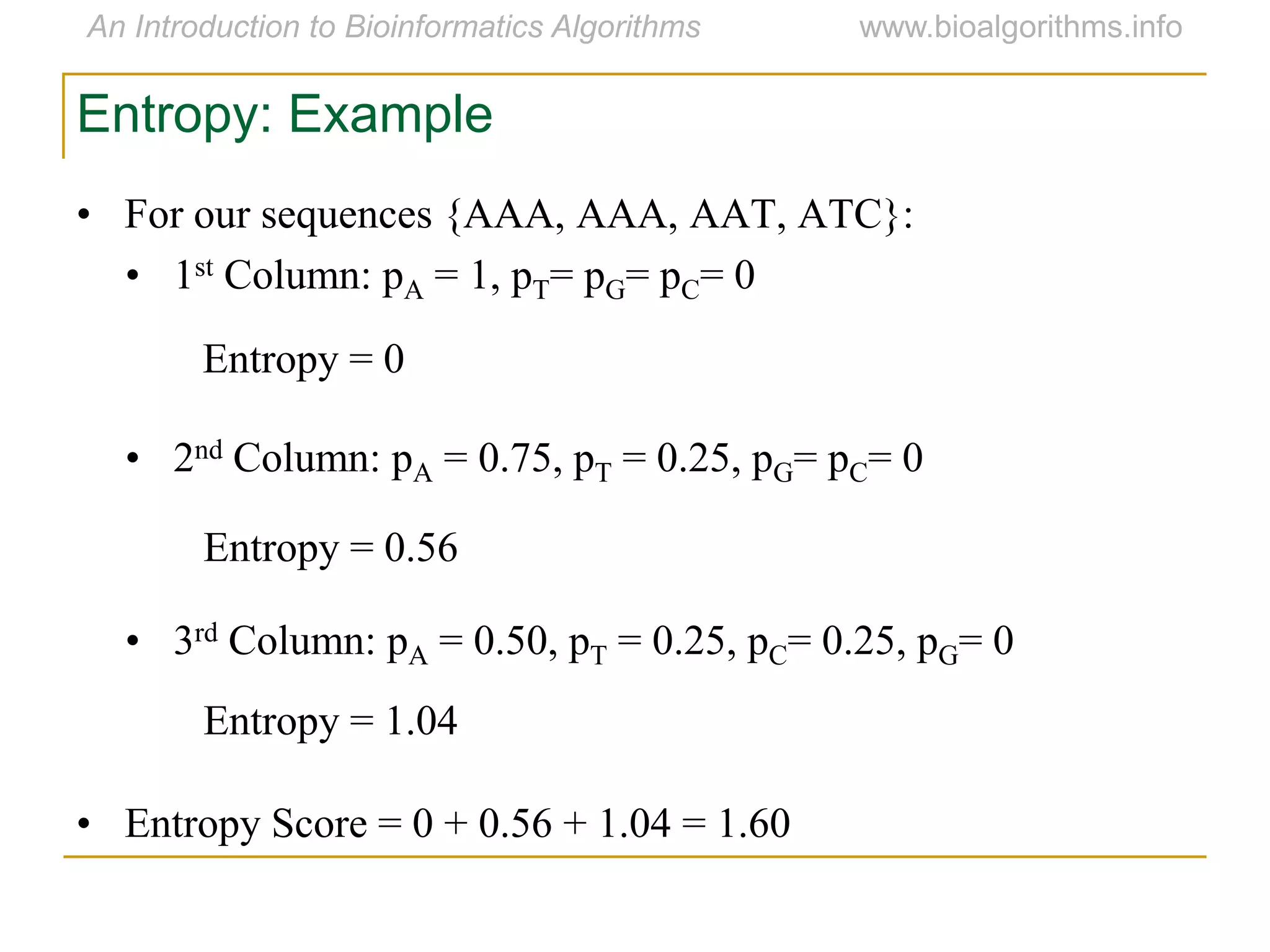
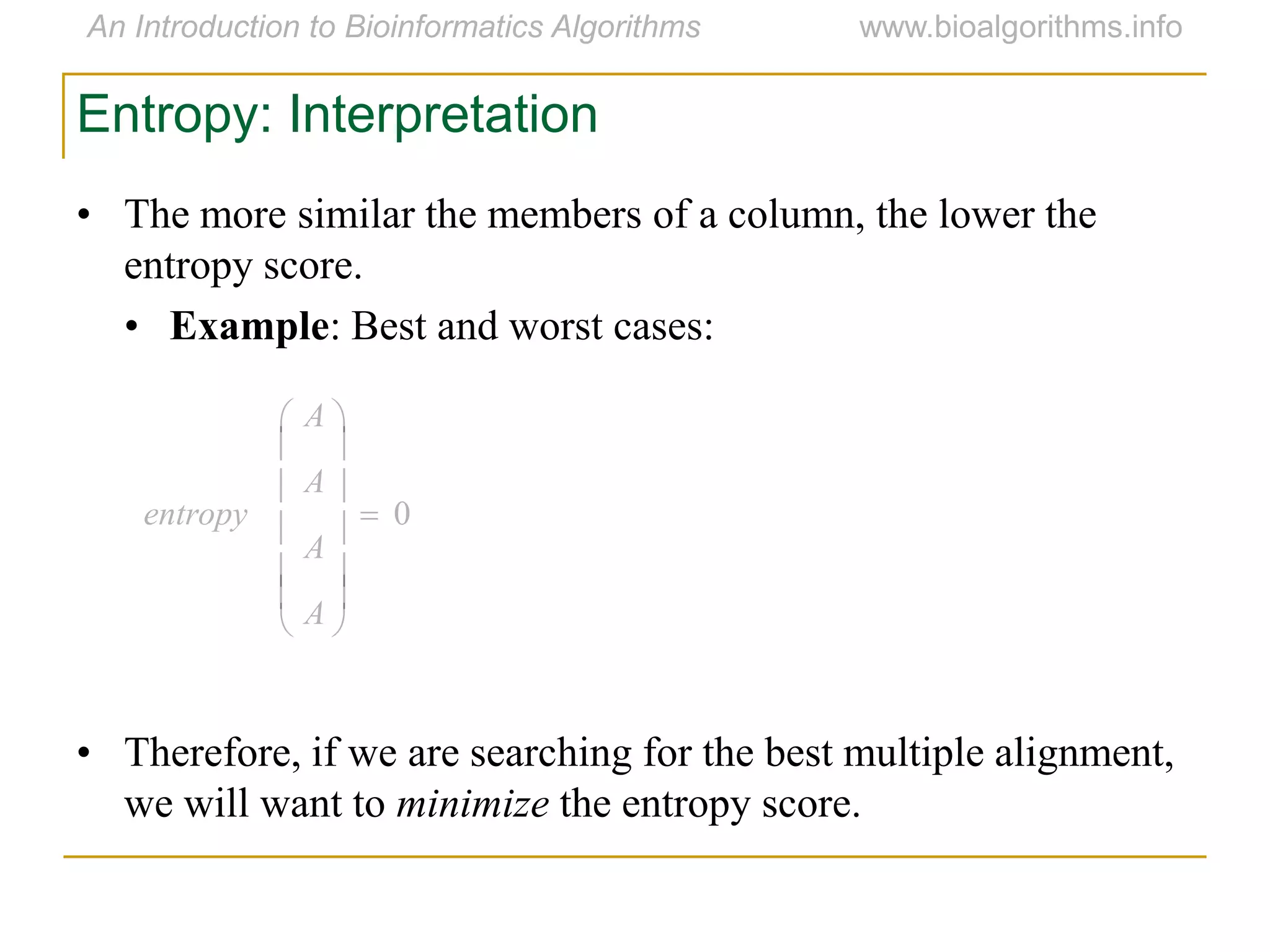
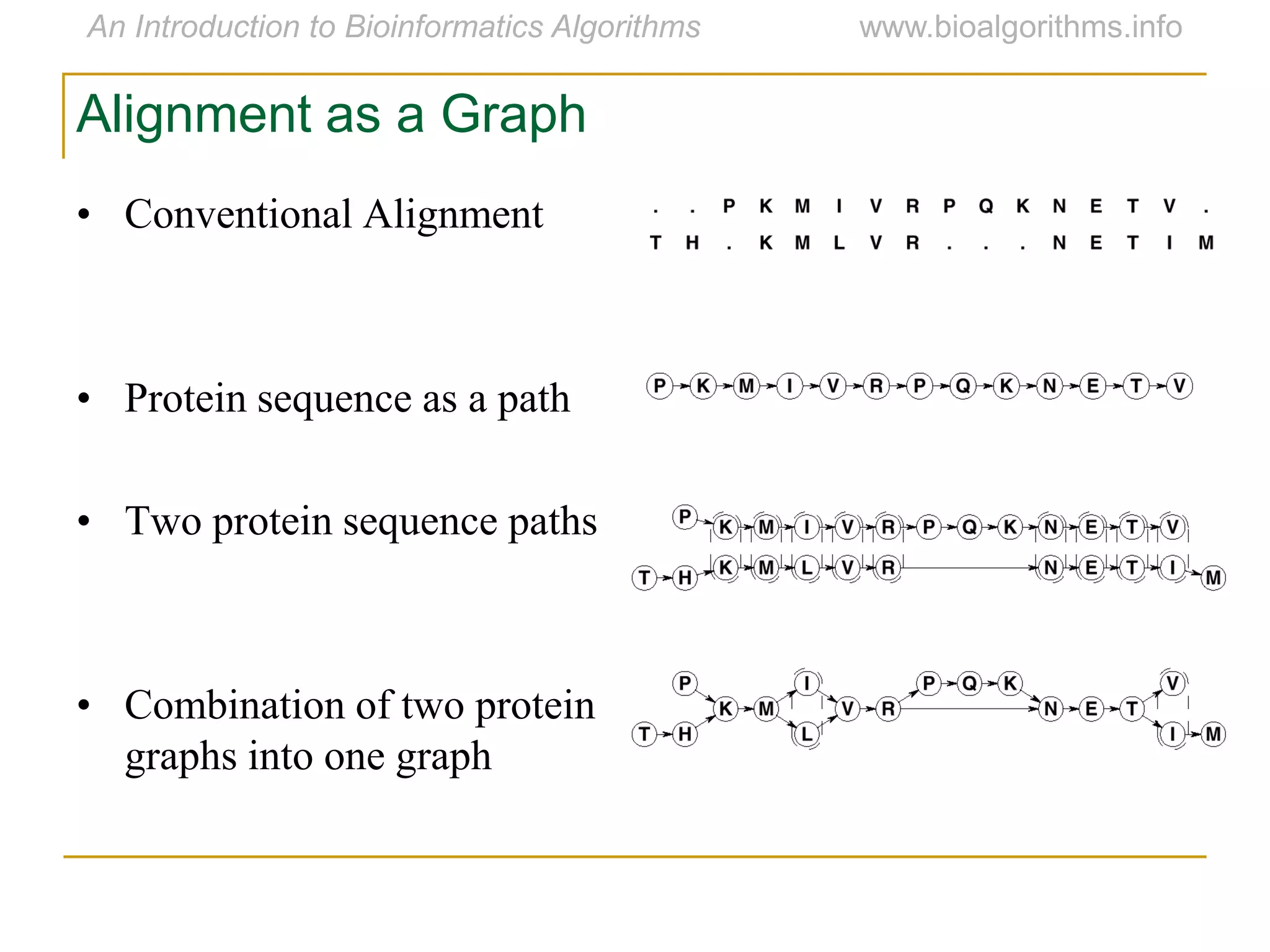
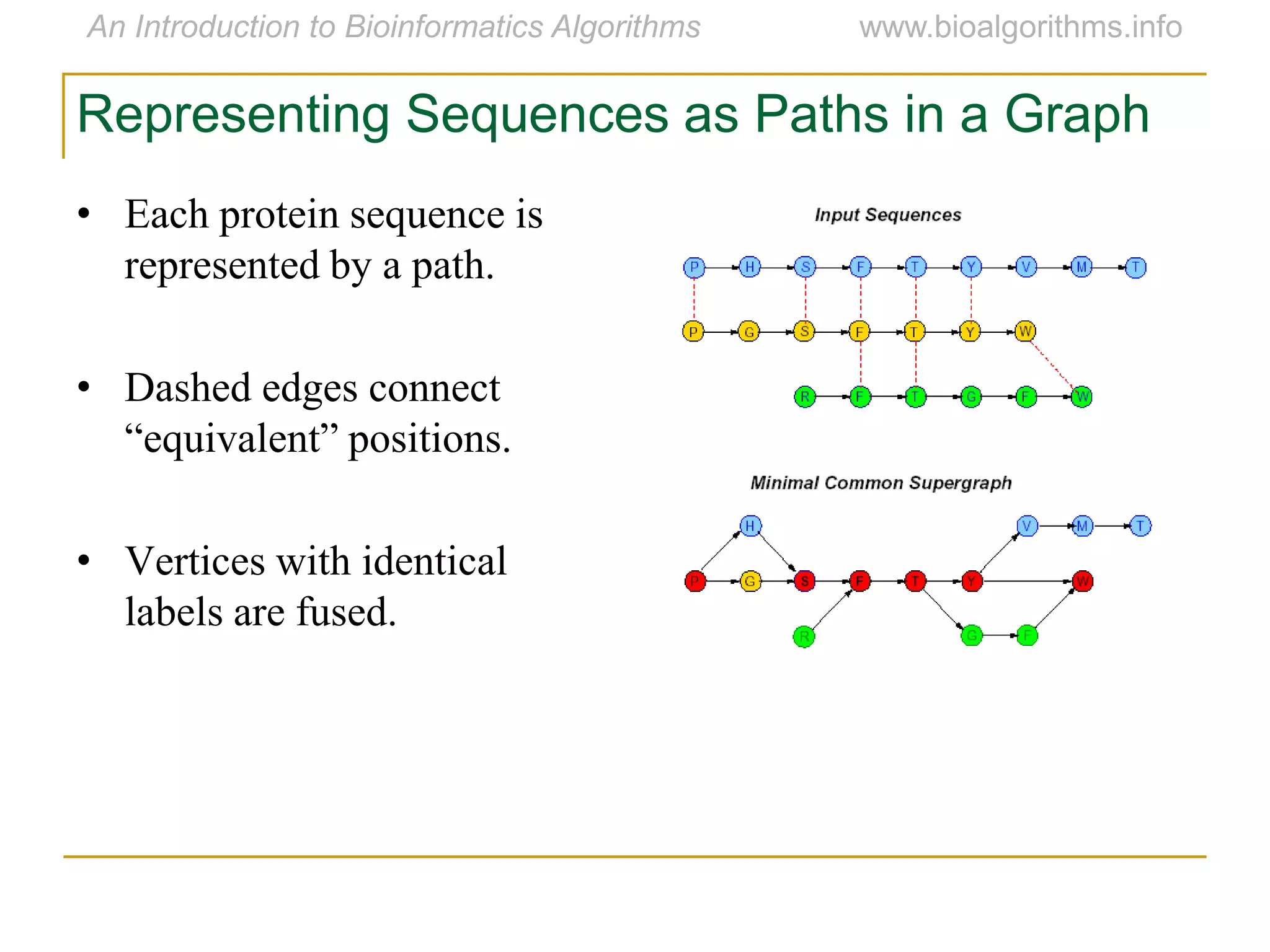
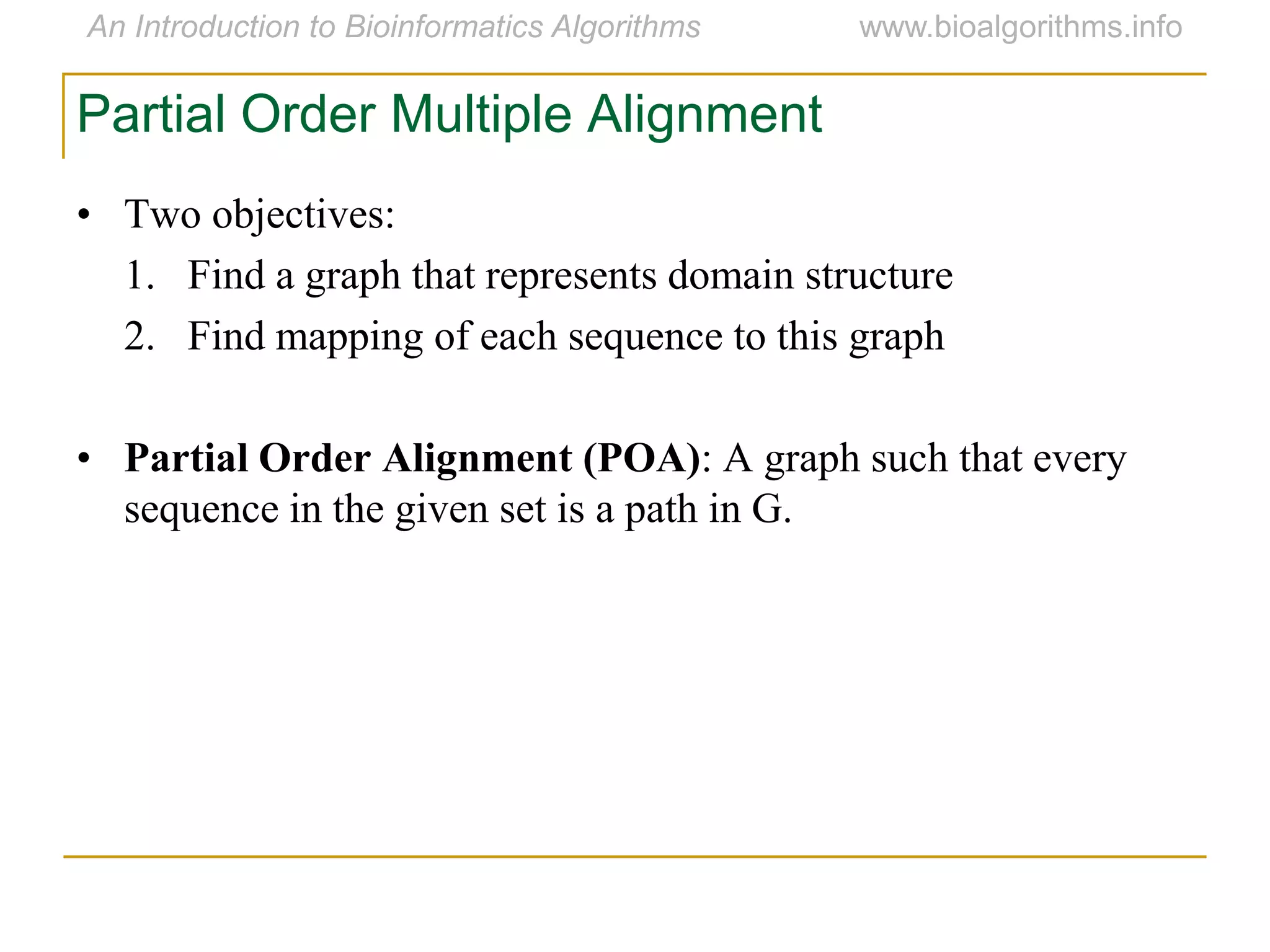
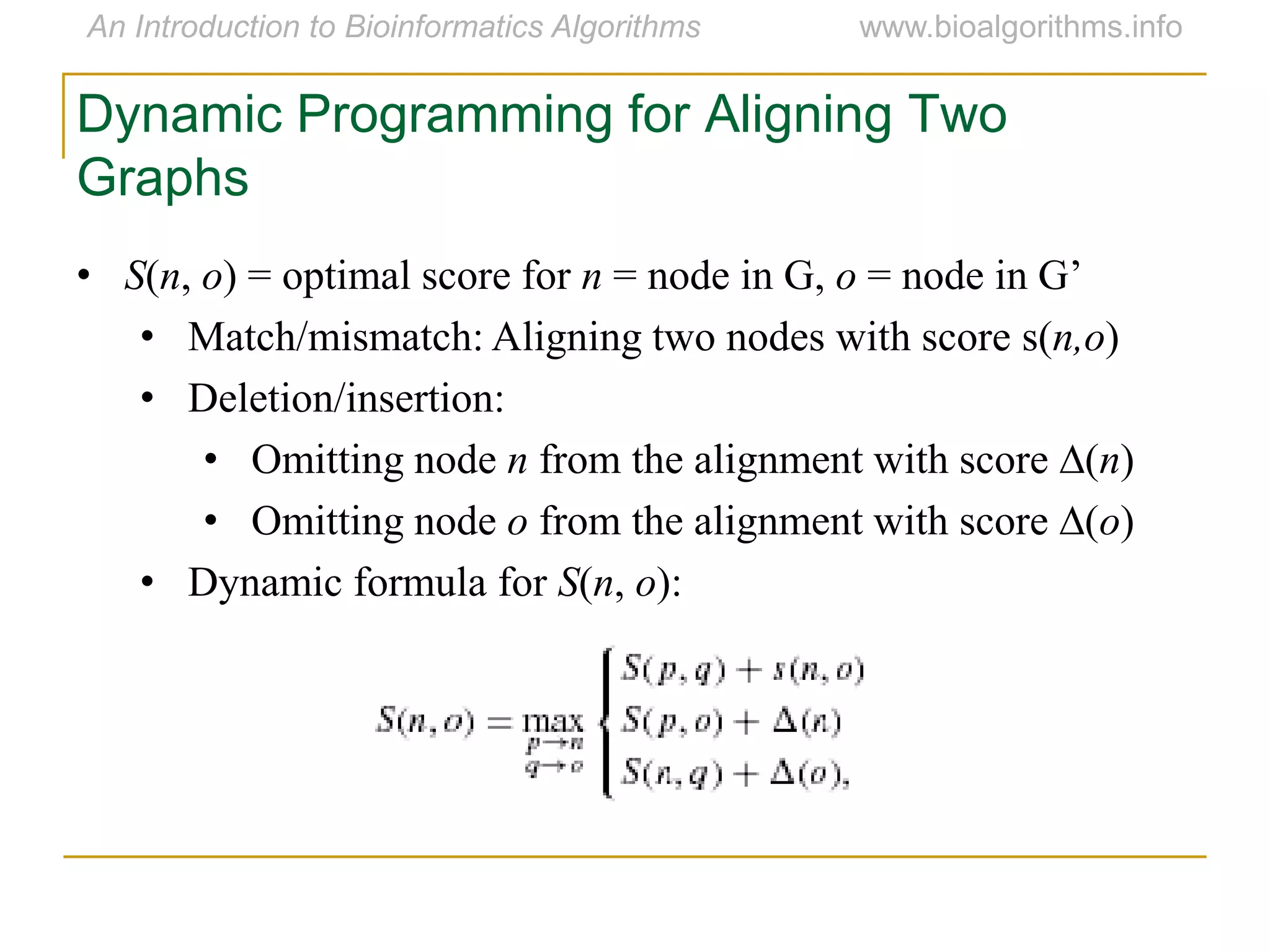
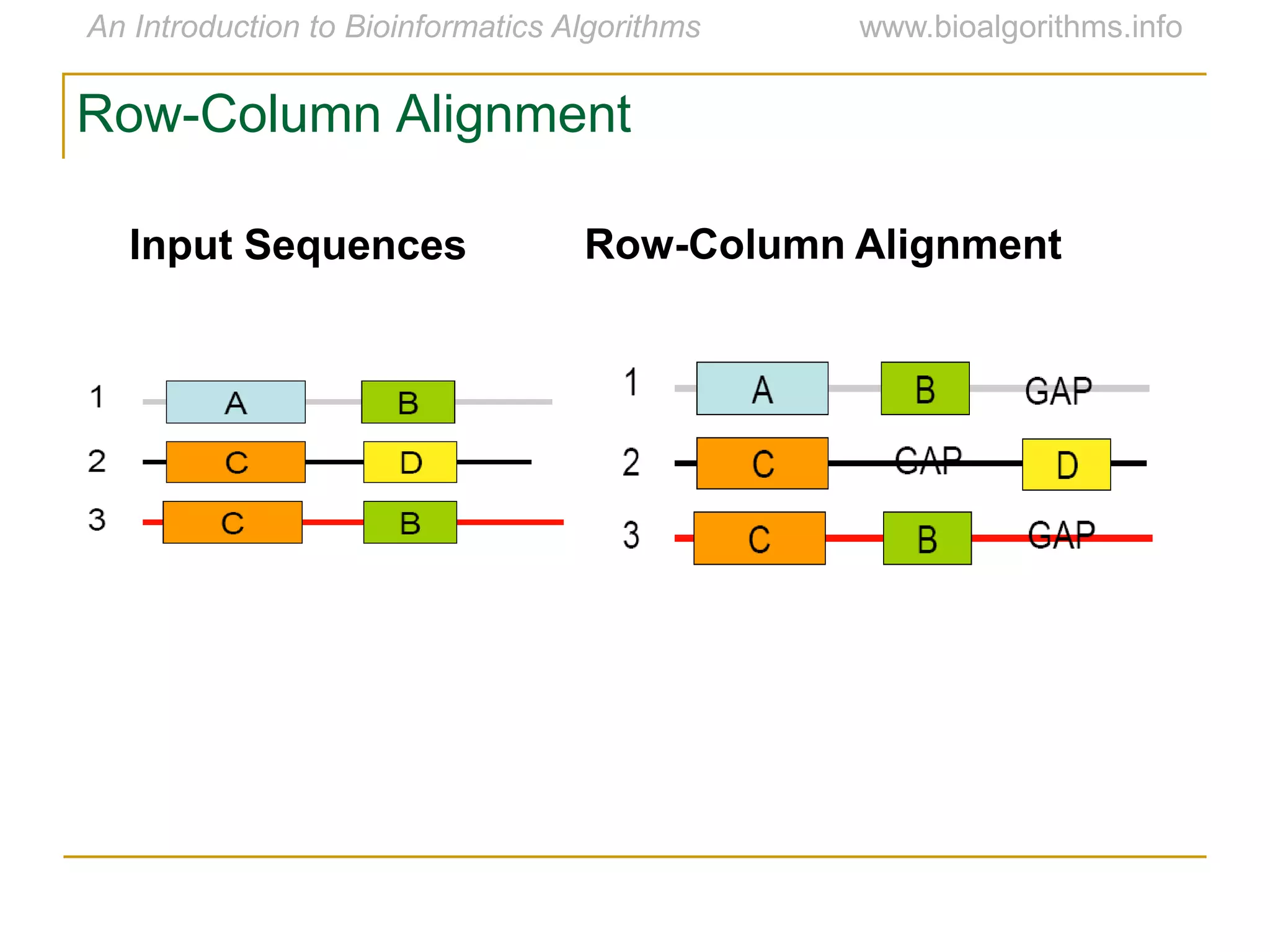
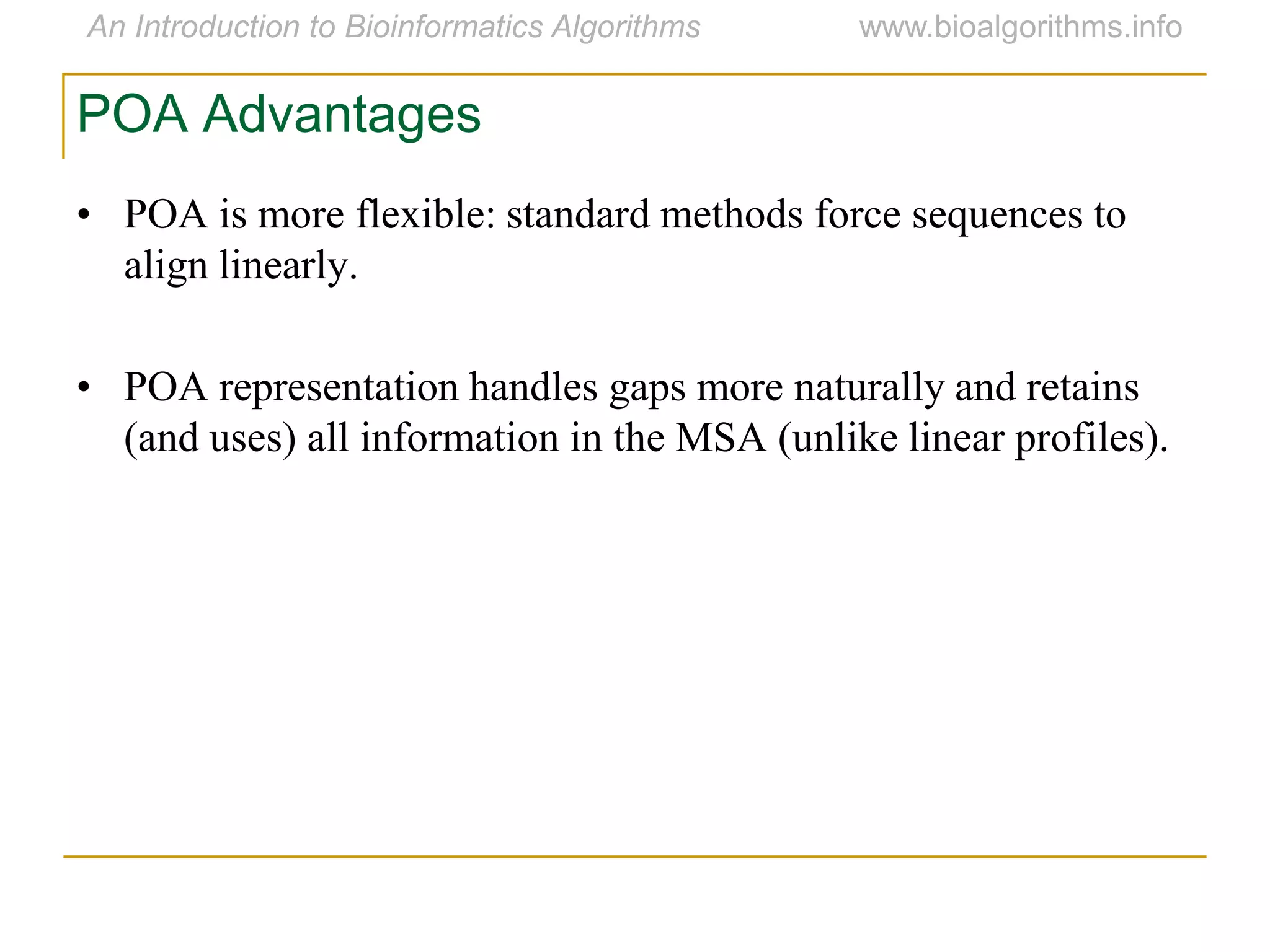
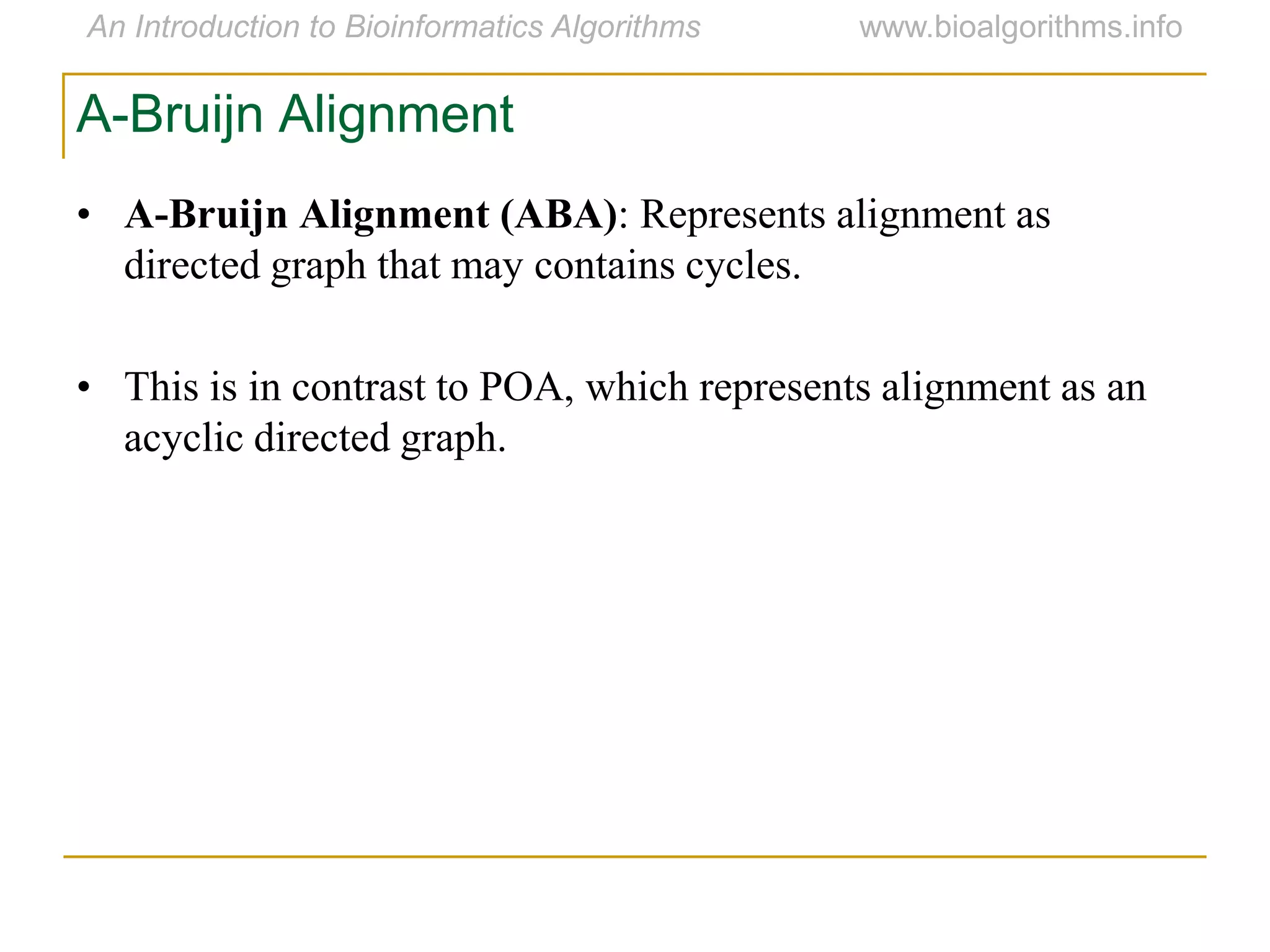
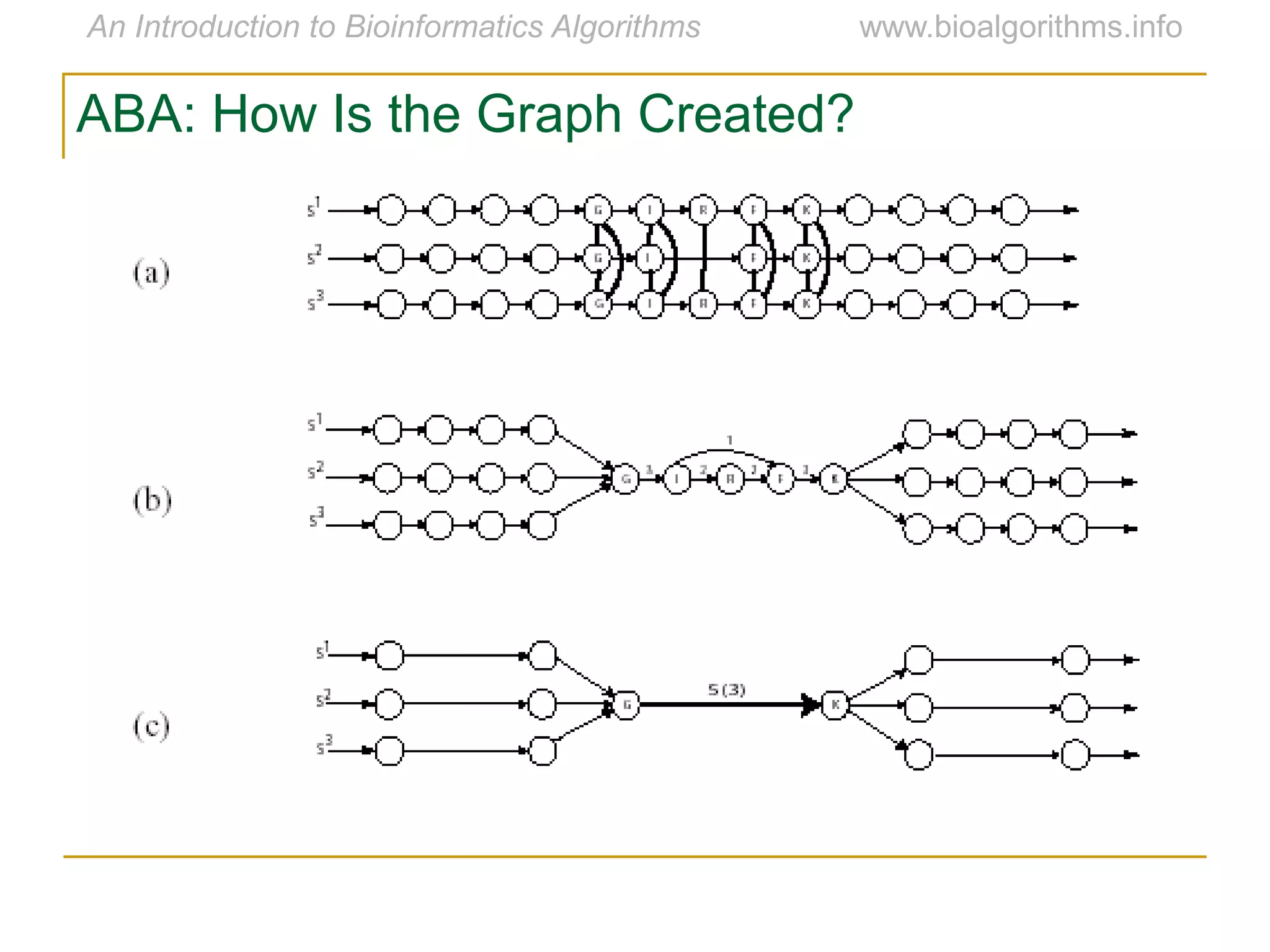
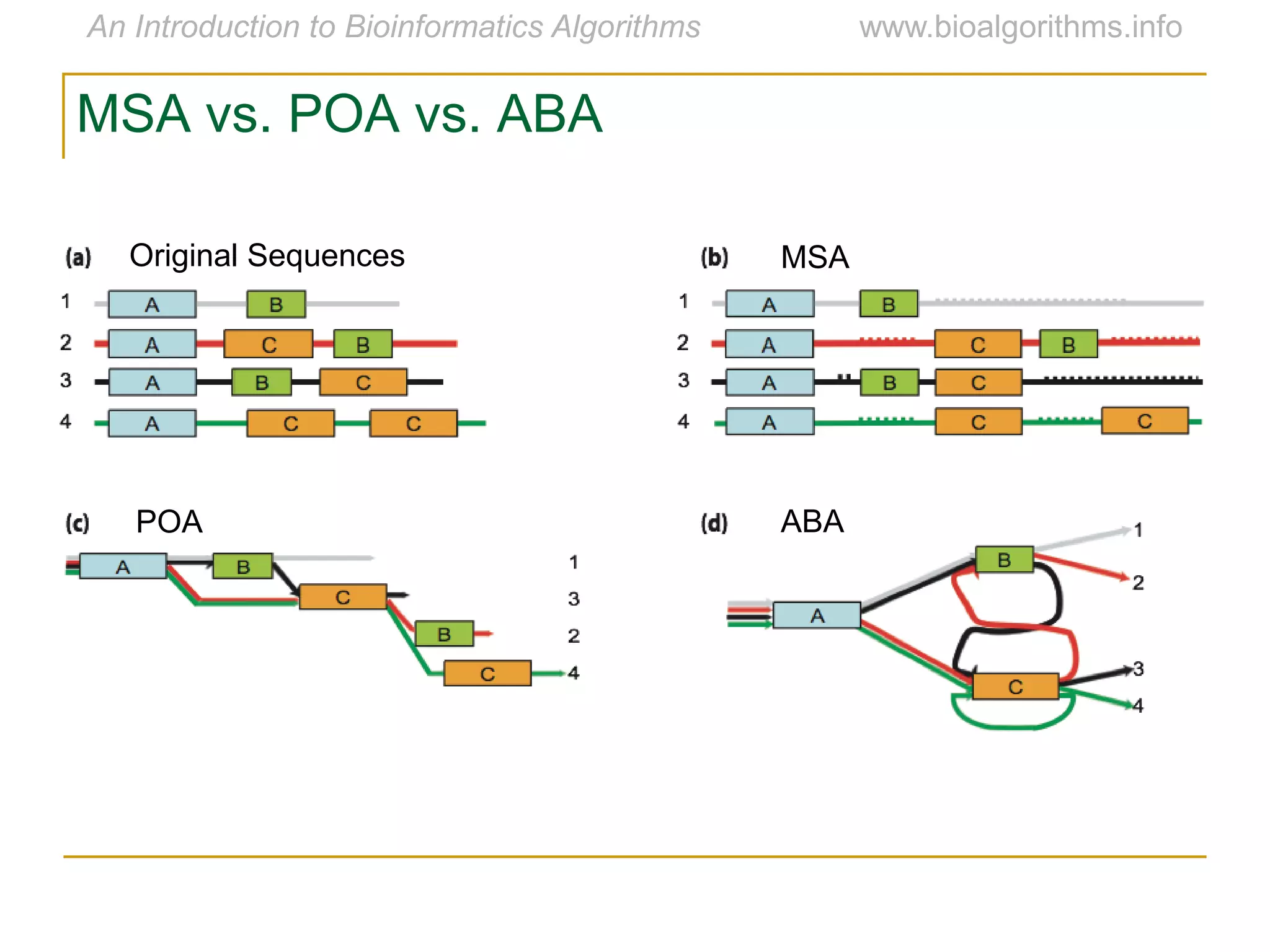
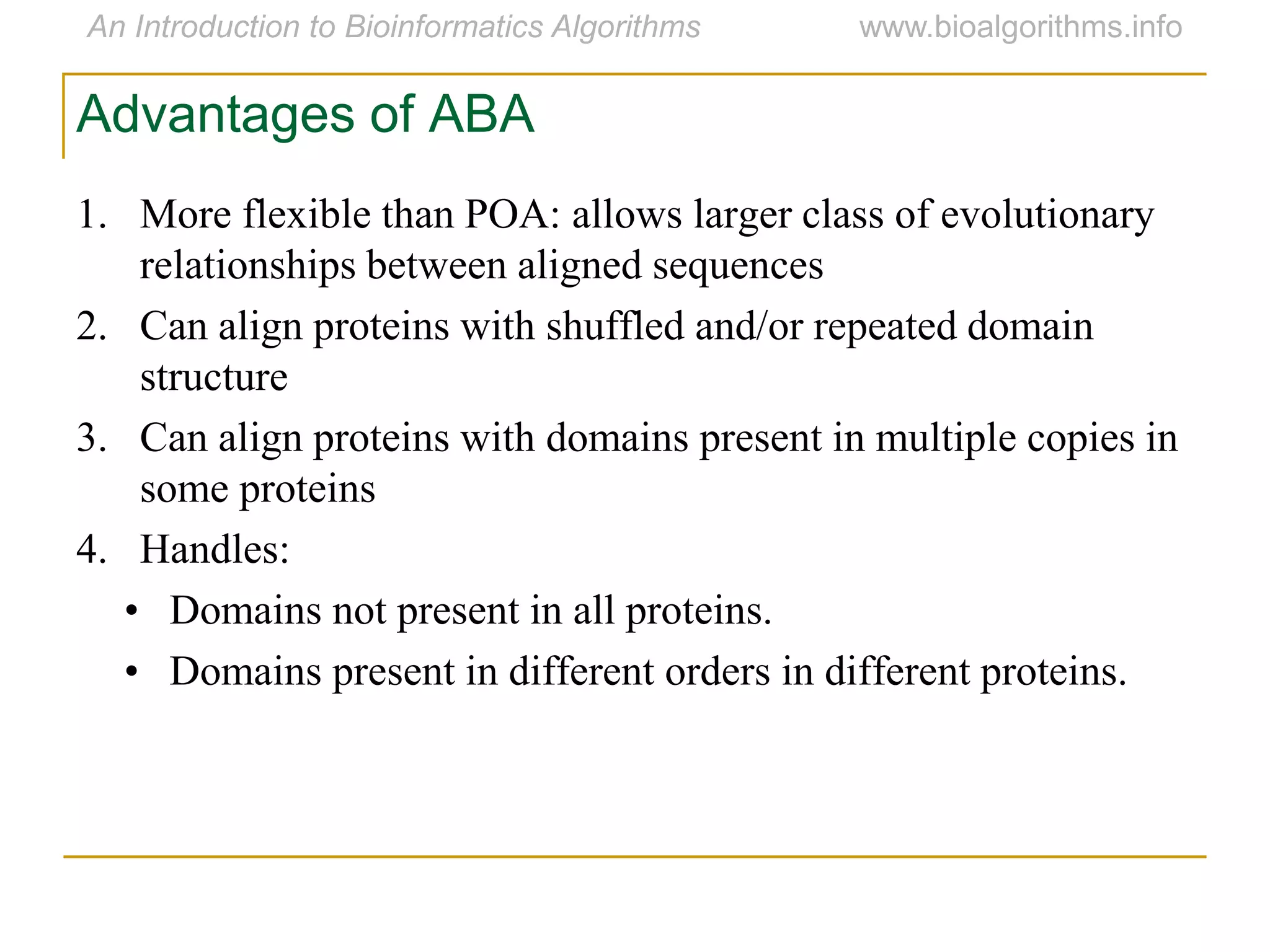
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) involves aligning more than two biological sequences, such as DNA, RNA, or protein sequences. There are several approaches to MSA, including progressive alignment and greedy algorithms. Progressive alignment works by first constructing pairwise alignments between the most similar sequences and then adding other sequences in order of similarity. This is guided by a phylogenetic tree. Greedy algorithms iteratively combine the most similar pair of sequences or profiles into a new sequence/profile to reduce the alignment problem size. Scoring MSA involves quantifying how well-conserved each column is, such as through matches, entropy, or sum-of-pairs scores.