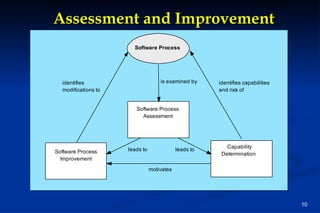
The document discusses software engineering processes and process frameworks. It describes common framework activities like requirements analysis, design, coding, testing and deployment. It also discusses umbrella activities, process models, the CMMI process model, process patterns, process assessment methods, and process improvement approaches like the Personal Software Process and Team Software Process which emphasize measurement and continuous improvement. The primary goal of any software process discussed is to deliver high quality software on time through effective requirements analysis, design, coding, testing and reducing rework.