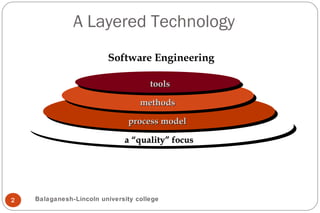
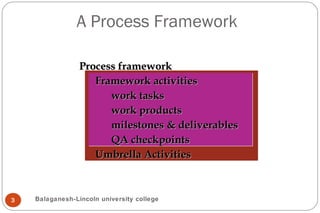
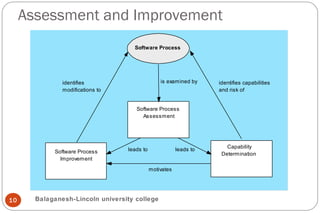
This document discusses software engineering processes. It describes a process framework that includes framework activities like communication, planning, modeling, and testing. It also includes umbrella activities like project management, quality assurance, and configuration management. The document states that the framework activities will always be applied to projects but the tasks may vary depending on the project type and characteristics. It also discusses process models like CMMI, process patterns, and process assessment and improvement methods. Finally, it covers personal and team software processes.