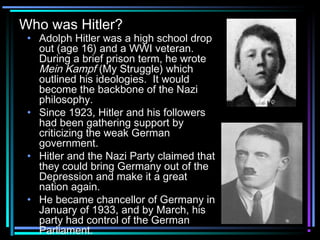
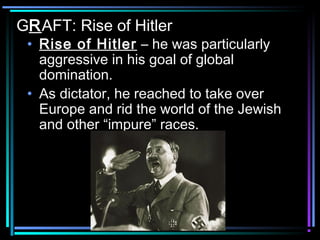
Adolf Hitler rose to power in Germany after capitalizing on resentment over the weak Weimar government and Great Depression. He became chancellor in 1933 and established a Nazi dictatorship. Initially improving the economy, Hitler rapidly instituted racist policies, stripping Jews of rights and encouraging attacks. By 1939, seeking to expand German territory and pursue racial ideology, Hitler had invaded Poland, starting World War II after Western democracies failed to counter German and Italian aggression through appeasement or an ineffective League of Nations.