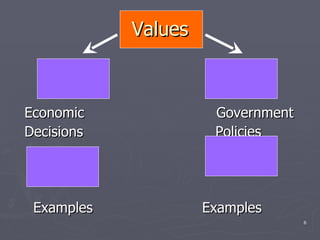
The document discusses cultural conformity and adaptation. It identifies traditional American values such as personal achievement, individualism, work, morality, and efficiency according to sociologist Robin Williams. It also discusses how younger Americans' values may differ from their parents' values regarding issues of concern. The document also outlines six sources of social change: values and beliefs, technology, population changes, diffusion of ideas, physical environment, and wars/conquests. It provides examples of how schools and societies resist change through ethnocentrism, cultural lag, and vested interests seeking to maintain the status quo.