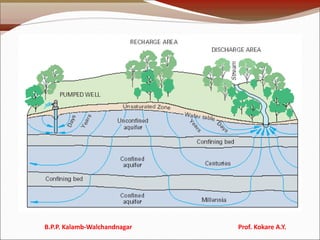
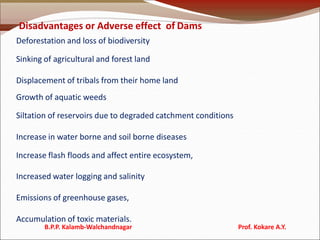
The document discusses natural resources, categorizing them into renewable and non-renewable types, and highlights the benefits of forests and the consequences of deforestation. It also addresses water resources, describing the impact of floods and droughts, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of dams. Additionally, it covers mineral and food resources, focusing on environmental effects, food security issues, and the consequences of modern agricultural practices.