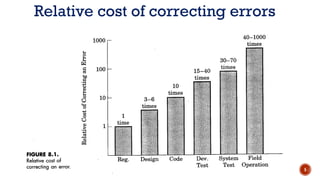
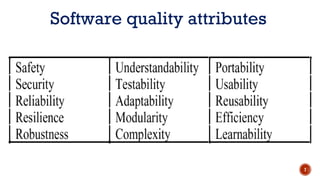
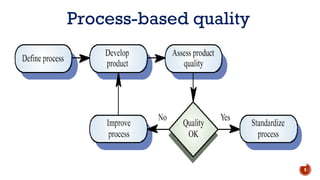
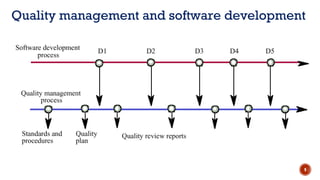
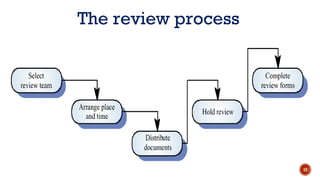
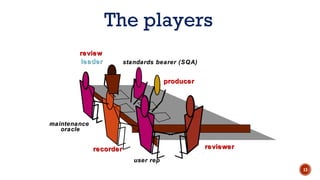
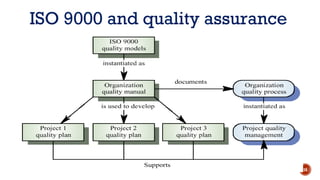
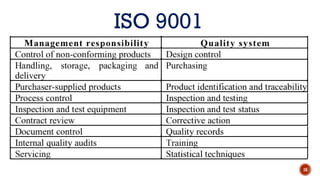
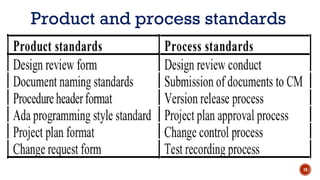
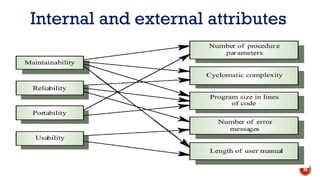
The document discusses software quality and quality assurance concepts, emphasizing the importance of meeting specified requirements and customer expectations. It outlines key aspects like quality planning, control, and costs, as well as the role of formal technical reviews in improving software quality. Additionally, it touches on ISO 9000 and ISO 9001 certifications as standards for quality management applicable to various organizations.