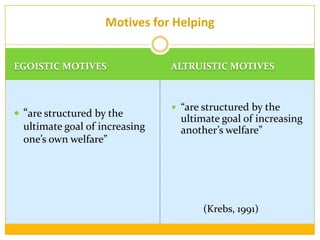
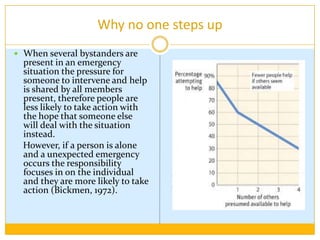
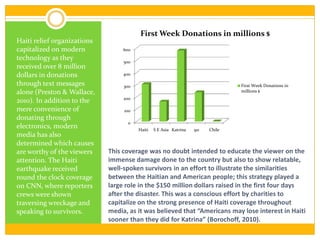
This document discusses prosocial behavior, which is defined as acts that benefit others. It explores various motivations for helping behavior, including egoistic motives aimed at increasing one's own welfare and altruistic motives aimed at helping others. Some key points discussed include evolutionary reasons for helping relatives due to kin selection, the empathy-altruism hypothesis which links seeing others in distress to a desire to help, and situational factors like the bystander effect that influence whether people help strangers. The role of media and celebrity endorsements in drawing attention and donations to causes like disaster relief is also examined.