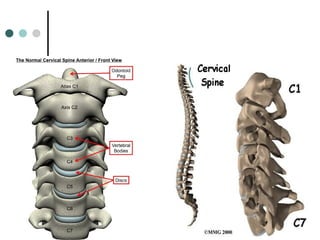
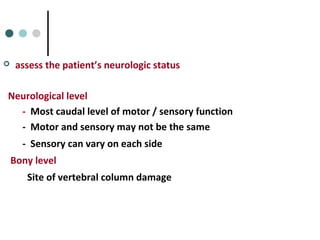
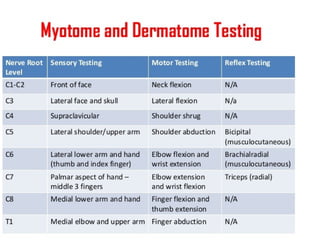
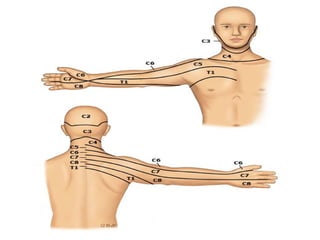
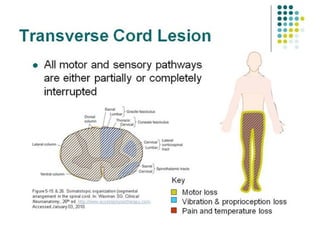
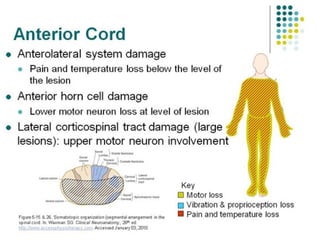
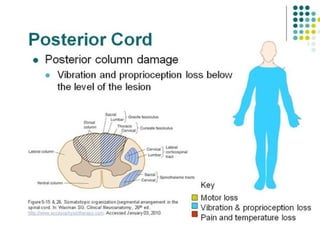
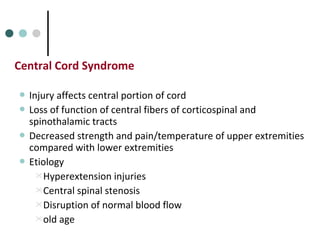
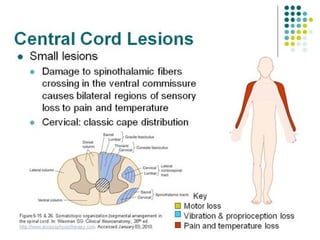
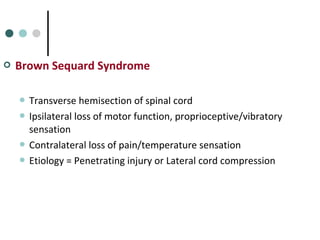
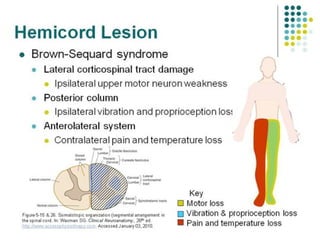
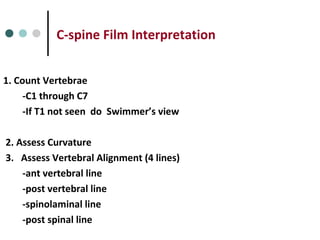
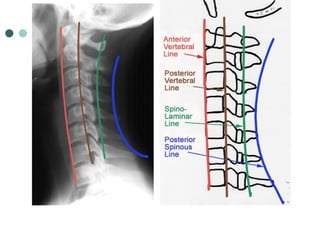
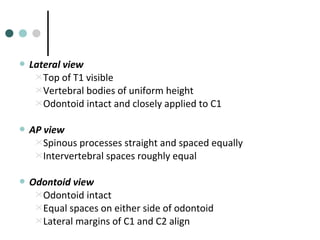
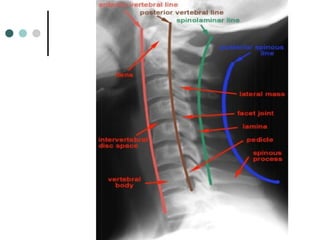
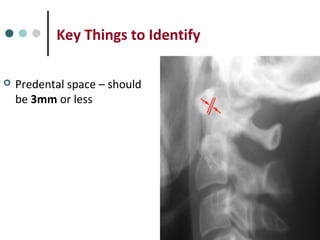
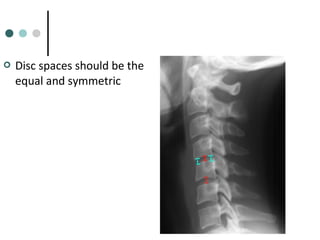
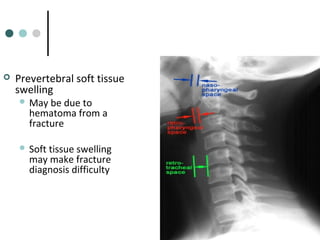
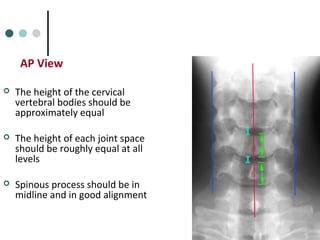
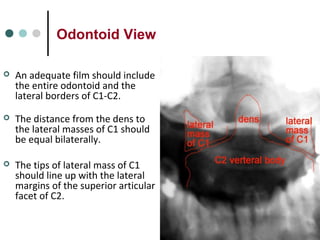
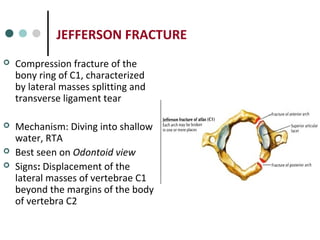
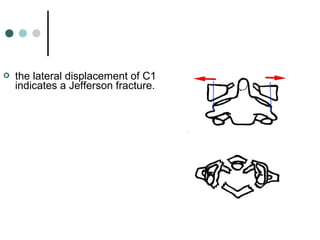
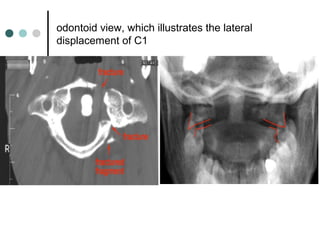
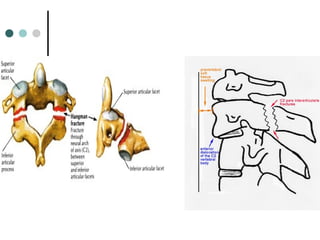
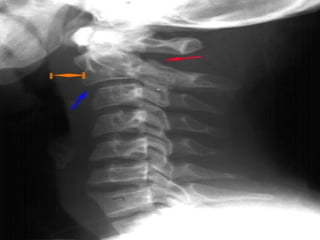
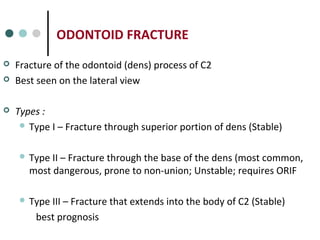
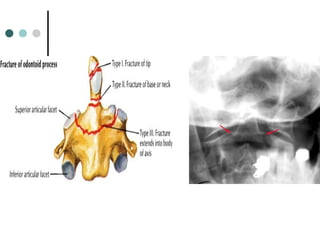
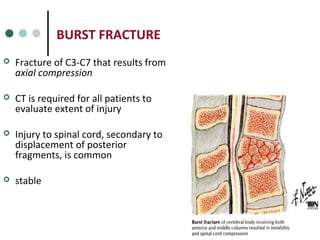
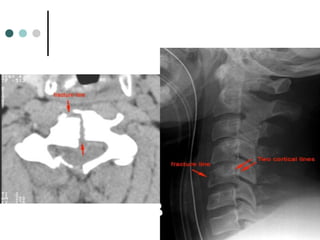
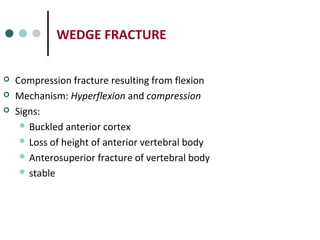
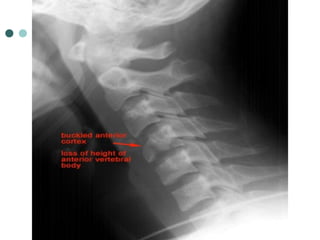
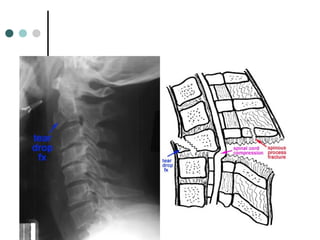
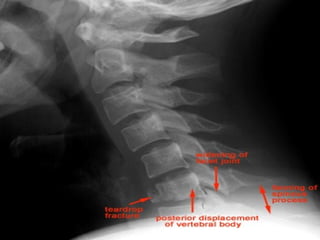
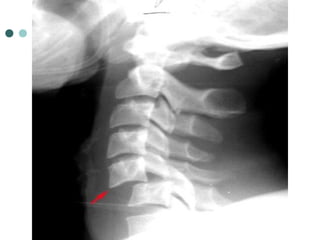
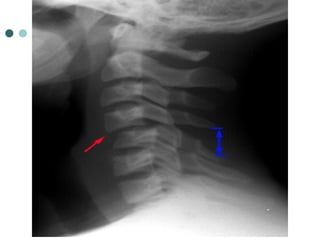
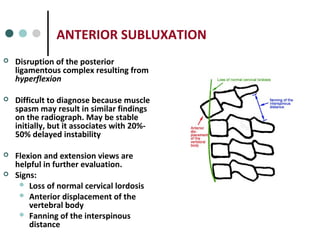
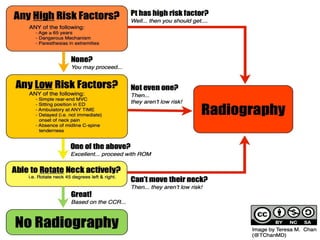
This document provides an overview of cervical trauma and cervical spine injuries. It discusses anatomy, mechanisms of injury, history and examination findings, imaging, classifications of injuries including fractures and spinal cord syndromes, and indications for surgical intervention. The key points are that cervical spine injury must be considered in polytrauma patients, manual stabilization is needed in addition to collars, and imaging such as CT and MRI can help classify fractures and rule out injuries when clinical suspicion remains.