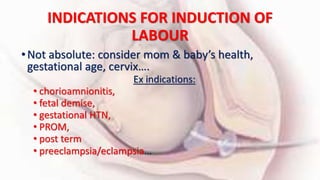
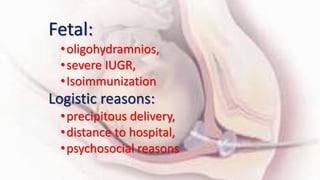
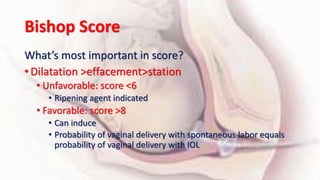
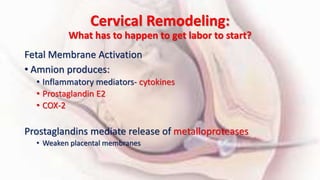
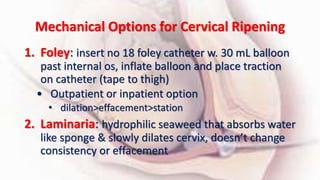
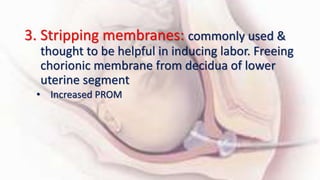
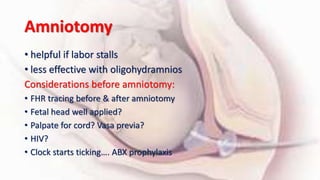
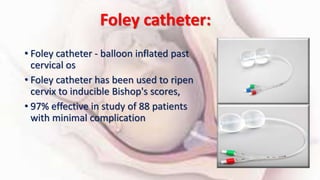
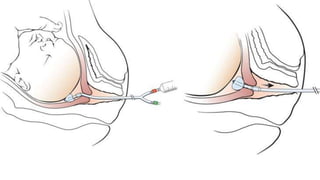
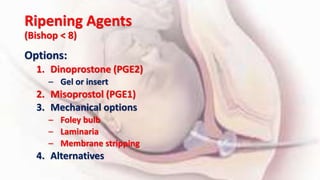
1) Cervical ripening is used to induce labor when the cervix is unfavorable (Bishop score <6) and involves using agents like prostaglandins, misoprostol, or mechanical methods to soften and dilate the cervix.
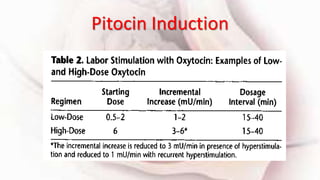
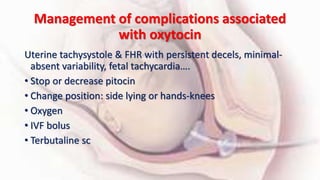
2) Oxytocin is commonly used for labor induction when the cervix is favorable but careful monitoring is needed due to risks of uterine tachysystole and changes in the fetal heart rate.
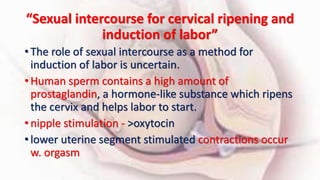
3) While prostaglandins are more effective cervical ripening agents compared to oxytocin alone, all methods have risks and more research is still needed to evaluate some traditional induction methods.