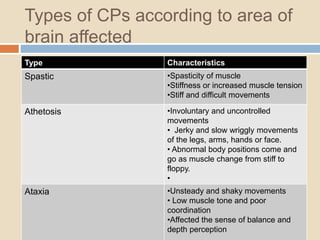
Cerebral palsy is a neurological disorder caused by damage to the brain that controls body movement. It causes difficulties with muscle control and coordination of body positioning and movement. Cerebral palsy can be caused by accidents or medical conditions before, during, or after birth that damage the developing brain, such as lack of oxygen, infection, or premature birth. Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity but may include abnormal reflexes, impaired motor skills, muscle stiffness, involuntary movements, difficulties with speech, hearing, and vision. Treatment is individualized and may include therapies, medications, surgery, and assistive devices to help improve symptoms and quality of life.