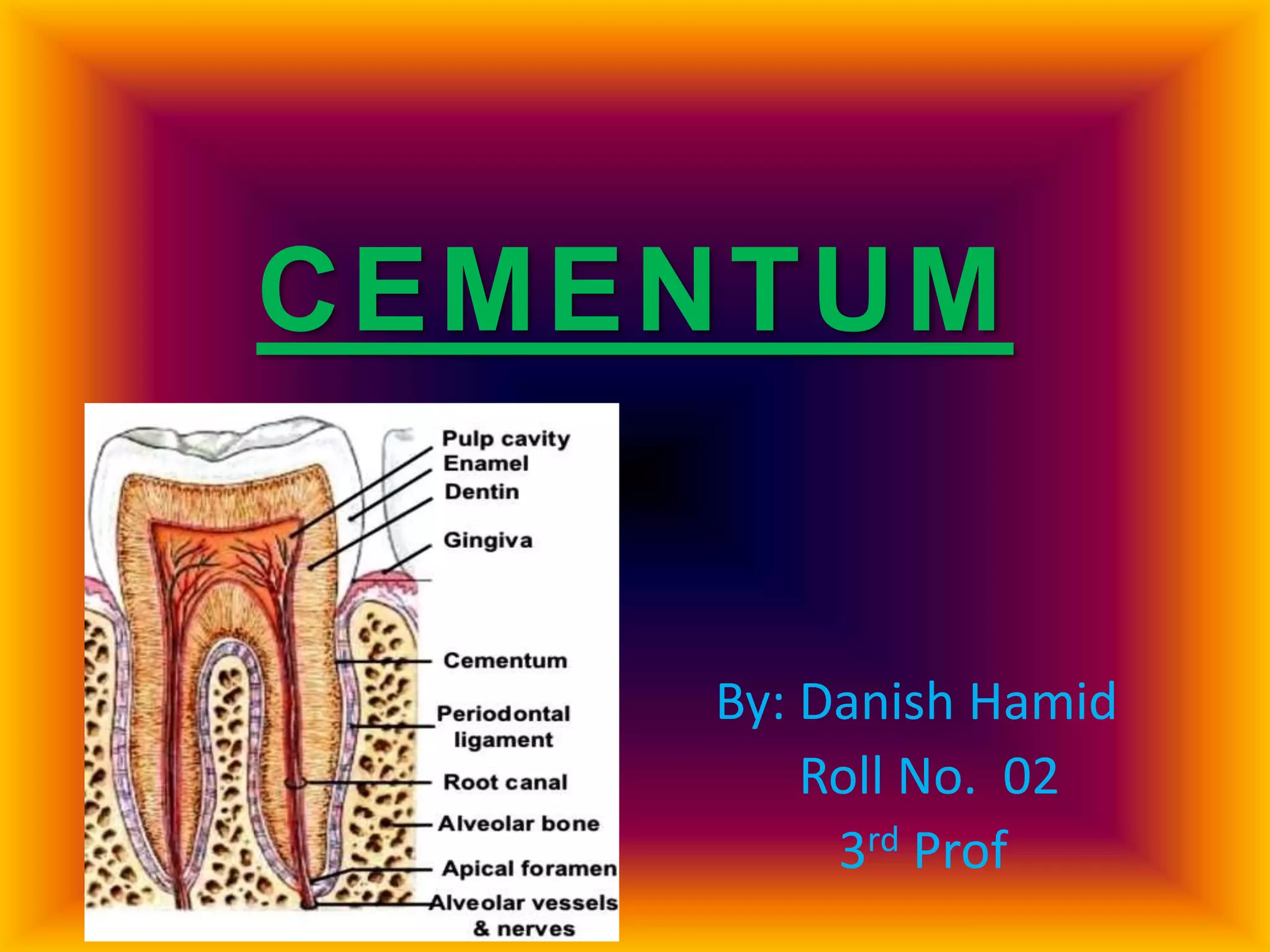
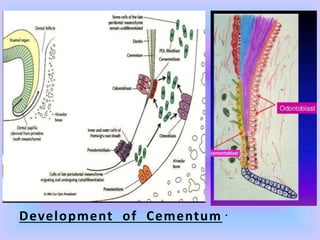
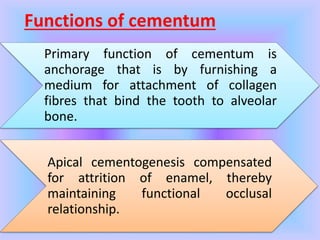
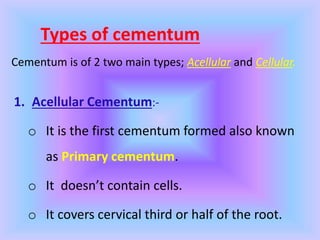
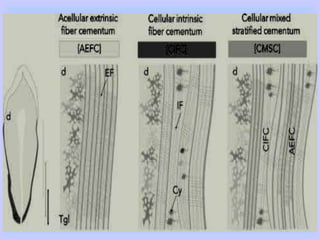
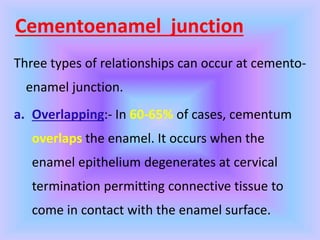
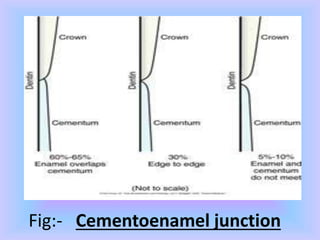
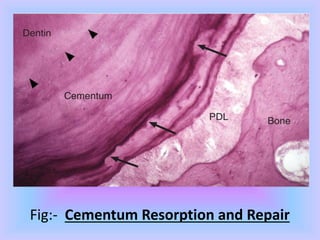
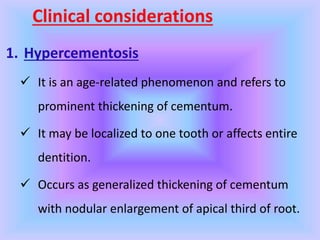
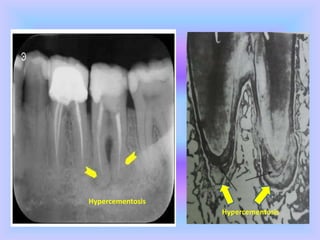
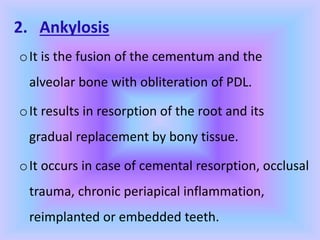
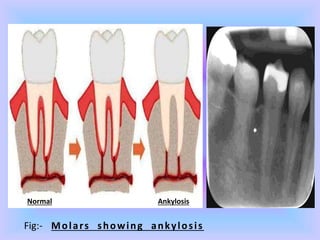
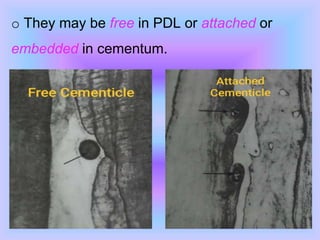
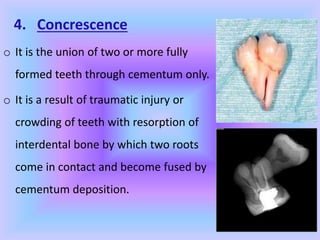
The document provides comprehensive information about cementum, a calcified tissue covering the roots of teeth, including its physical characteristics, chemical composition, development, functions, types, and clinical considerations. It distinguishes between acellular and cellular cementum and details various classifications and pathologies such as hypercementosis and ankylosis. Additionally, it covers the cementoenamel junction and details the processes of cementum resorption and repair.