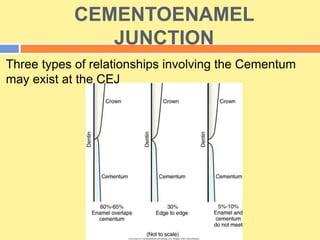
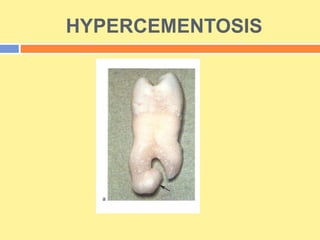
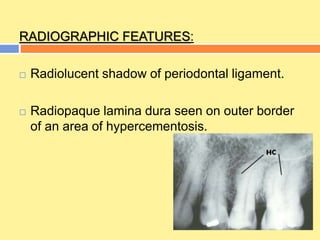
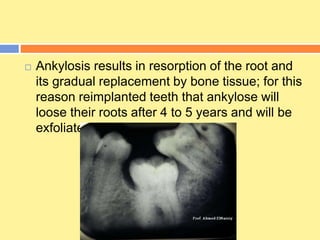
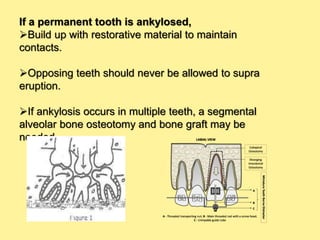
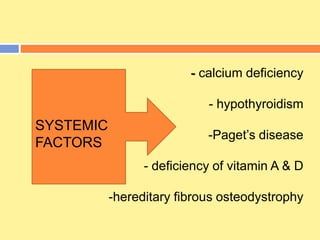
This document provides an overview of cementum, including its definition, composition, properties, classification, and clinical considerations. Some key points:
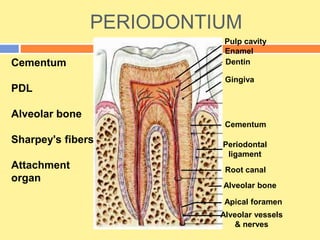
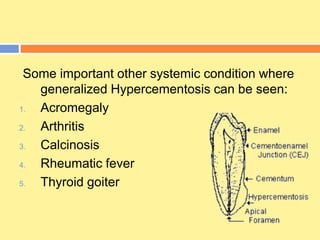
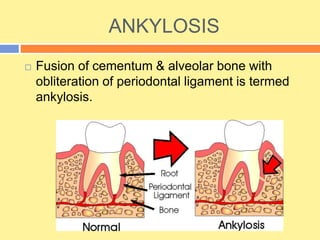
- Cementum is the calcified tissue covering tooth roots that provides attachment for periodontal ligament fibers. It begins forming at the cementoenamel junction and continues to the root apex.
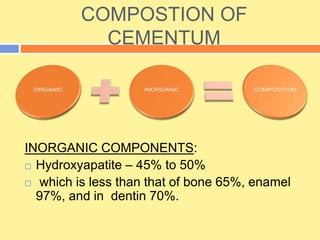
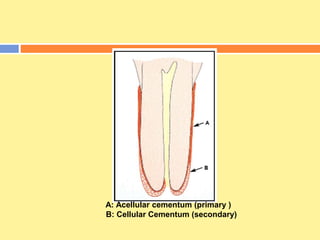
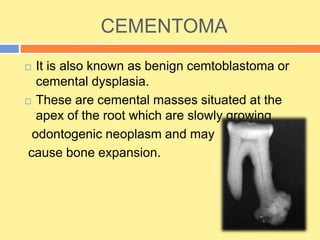
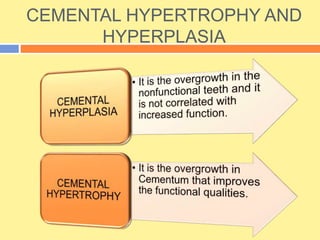
- It has both inorganic (hydroxyapatite) and organic (collagen) components. There are two types - acellular cementum which lacks cells and makes up the cervical third of roots, and cellular cementum which contains cementocytes and forms after tooth eruption.
- Cementum thickness increases with age, especially in the apical third and furc