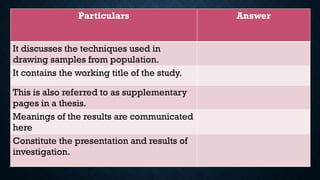
The document outlines the components and structure of a thesis in academic programs, highlighting key parts such as the introduction, methodology, results, and conclusion. It emphasizes the importance of clear titles, structured abstracts, and proper acknowledgments while providing guidance on the review of literature and methodology. Additionally, it mentions the necessity of bibliographic citation and author vitae for a comprehensive academic submission.