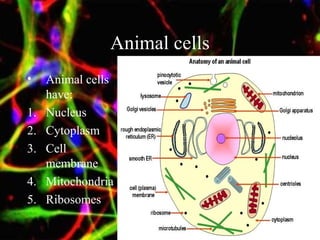
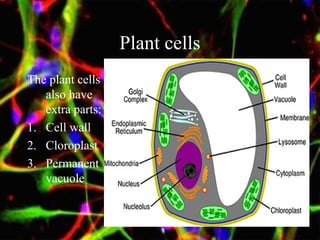
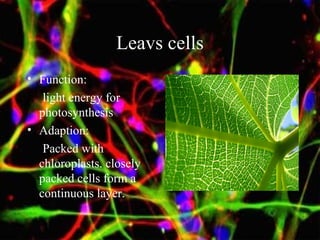
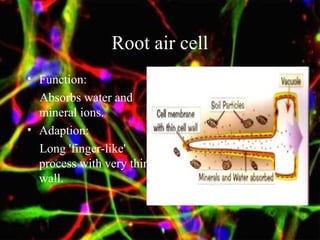
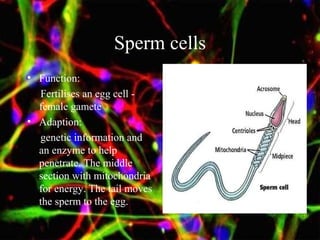
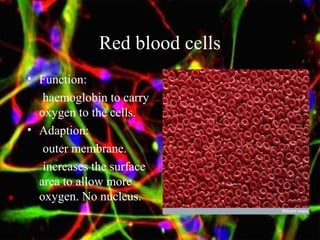
The document discusses different types of cells, including their structures, functions, and adaptations. It describes prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and provides details about specific cell types like animal cells, plant cells, leaf cells, root hair cells, sperm cells, and red blood cells. It also explains the cellular processes of diffusion and osmosis.