Embed presentation
Download to read offline

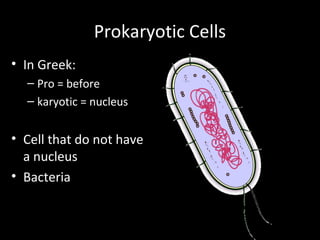


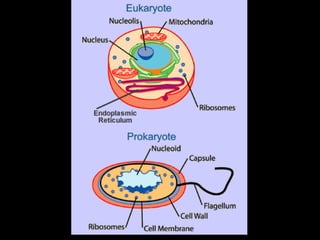
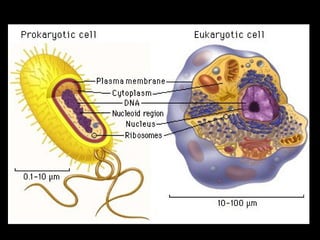

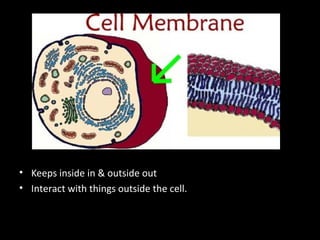
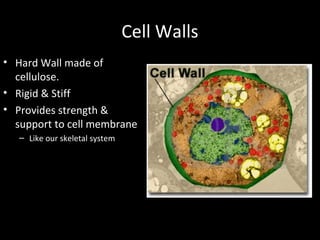
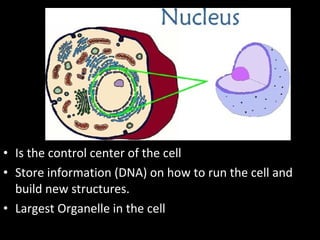
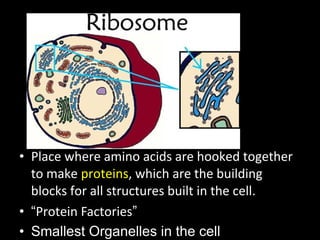
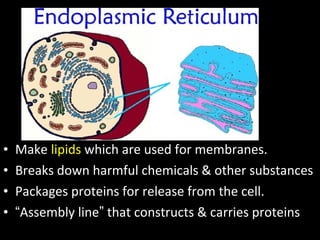
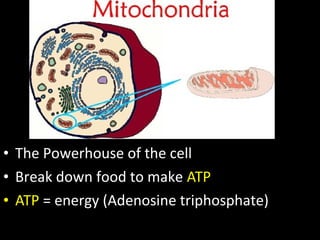
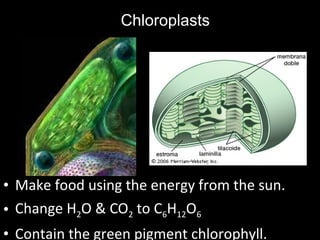
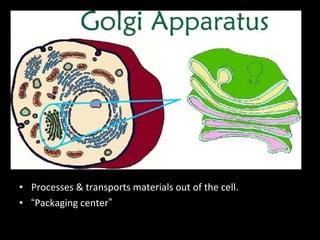
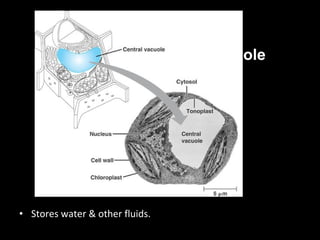
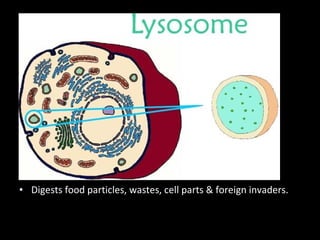
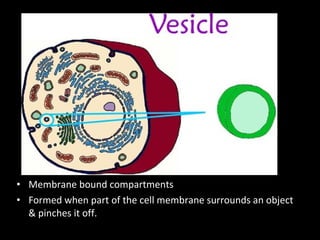

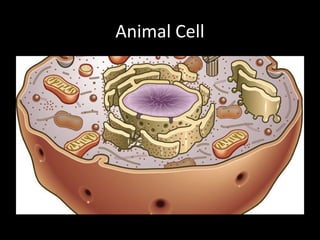
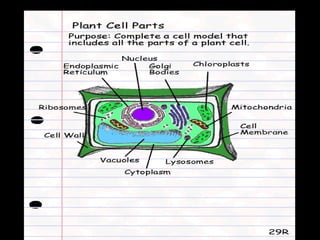
This document summarizes the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as the main organelles found within eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The main organelles described are the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and cell walls.




















