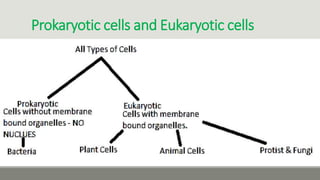
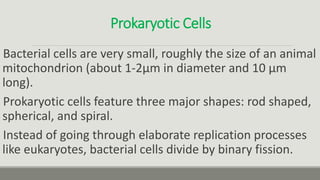
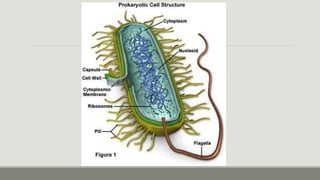
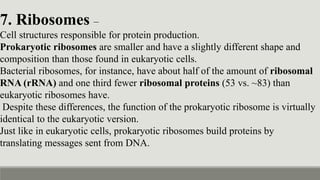
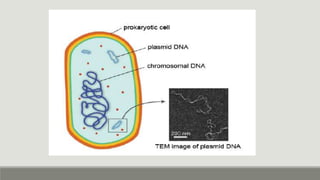
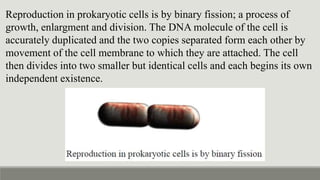
This document provides an overview of biophysics and cellular biophysics. It defines biophysics as the science investigating physical and physicochemical processes in living organisms from the submolecular to organism levels. Molecular biophysics studies macromolecules and interactions, while cellular biophysics examines the physicochemical basis of cell function and processes. The document then describes prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, noting the differences in their structures and components, including cell membranes, walls, cytoplasm, and organelles. Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound nuclei and have DNA in a nucleoid rather than chromosomes. Key cellular components of prokaryotes like bacteria are also outlined.
![Dr. S. C. JEYAKUMAR M.Sc., M.Phil., Ph.D
M.Ed., M.B.A.[HR]., M.L.I.Sc., PGDCA
BIOPHYSICS
UNIT I. CELLULAR BIOPHYSICS
1.01 WHAT IS BIOPHYSICS?
ARCHITECTURE OF PROKARYOTIC CELLS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-240314134850-5b11adba/75/1-01-WHAT-IS-BIOPHYSICS-pptx-1-2048.jpg)