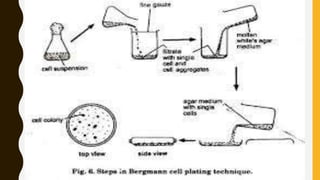
- A cell suspension culture consists of cell aggregates dispersed and growing in continuously agitated liquid media. It is initiated by transferring pieces of callus tissue to liquid medium or by mechanical or enzymatic breakdown of plant tissues.
- Suspension cultures can be grown as batch, continuous, or semi-continuous cultures. Batch cultures grow until a limiting factor stops growth, while continuous cultures are maintained at a steady state through constant influx of fresh media and outflow of spent media and cells.
- Growth in suspension cultures is measured by cell number, fresh or dry weight, and packed cell volume. Synchronous cultures with cells proceeding through growth phases simultaneously can be achieved through temperature shocks, starvation, use of inhibitors, or pl