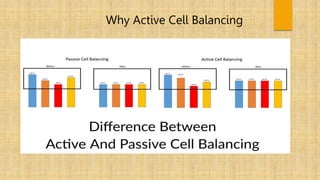
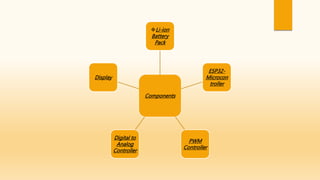
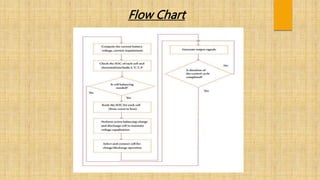
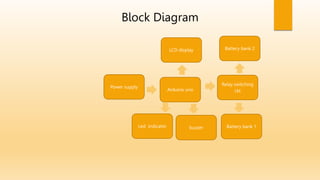
This document discusses cell balancing techniques for electric vehicle batteries. It begins with an abstract stating that battery life can be improved by equalizing the energy levels of individual cells through either passive or active cell balancing. The introduction explains that manufacturing inconsistencies can cause cell voltage and state of charge imbalances over time, degrading the battery life and creating safety issues. Active cell balancing is discussed as transferring energy from higher voltage cells to lower voltage cells. The conclusion states that the presented system is able to actively balance 16 battery cells by monitoring voltages and transferring energy between cells using a microcontroller and relays.