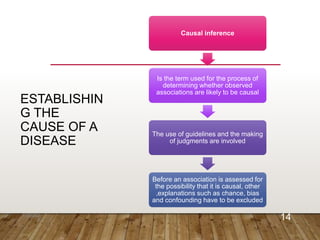
This document discusses causation and causal inference in epidemiology. It outlines concepts of single and multiple causes of disease. The Bradford Hill criteria are presented as guidelines for making causal inferences, including strengths like temporal relationship, plausibility, consistency, and dose-response relationship. Finally, it emphasizes that no single criterion proves causation but evaluating the totality of evidence using these guidelines can help strengthen causal judgments.