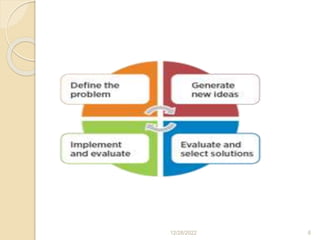
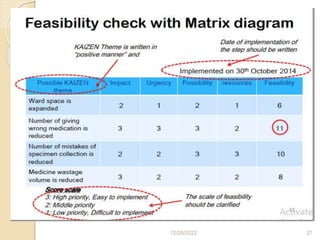
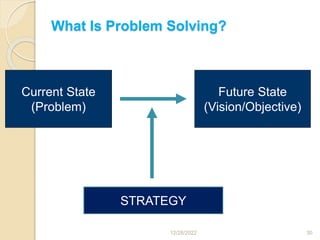
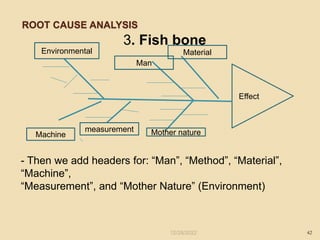
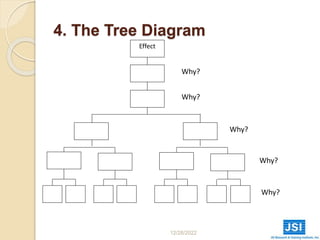
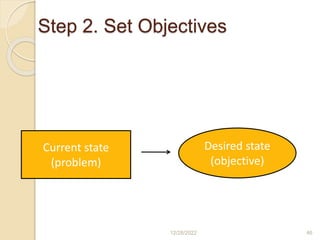
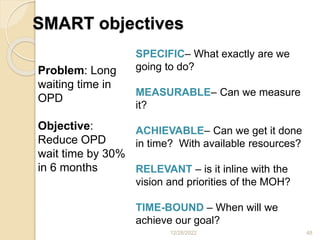
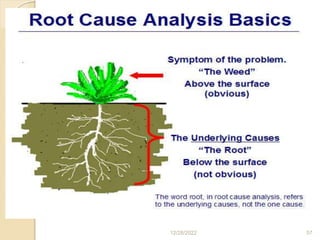
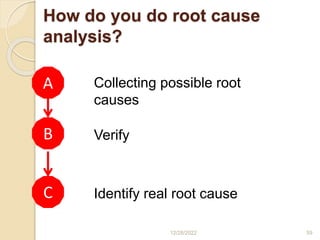
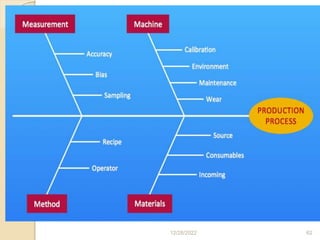
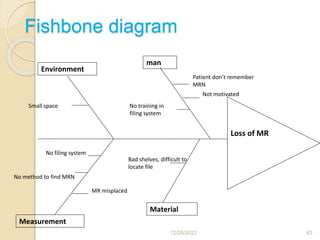
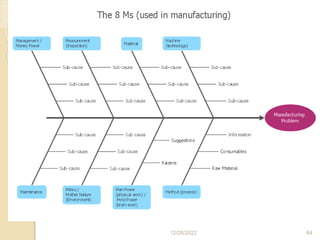
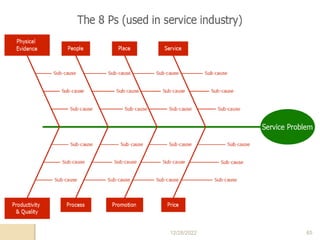
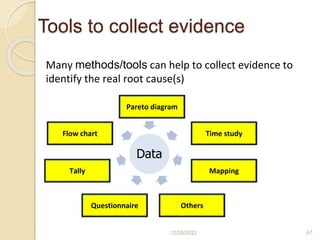
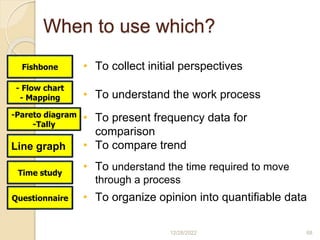
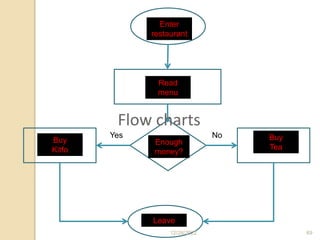
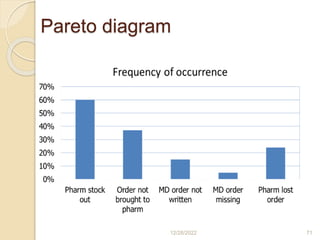
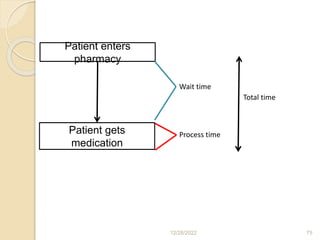
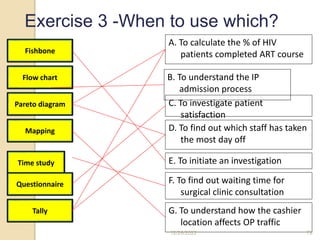
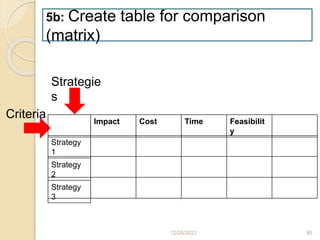
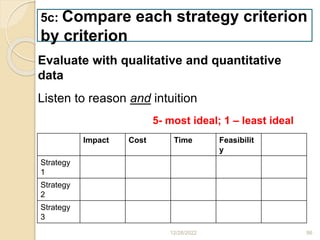
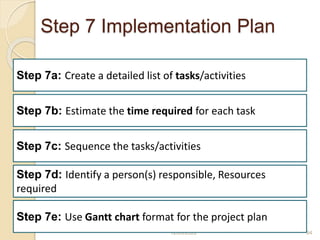
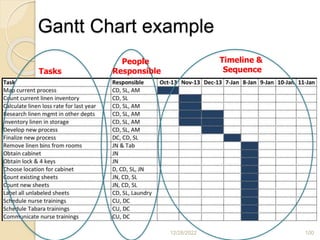
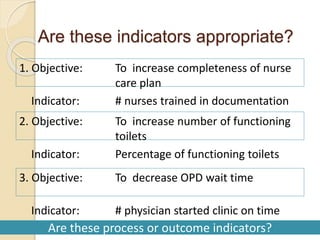
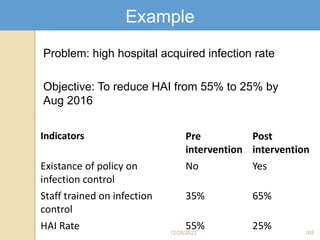
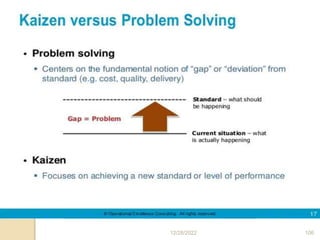
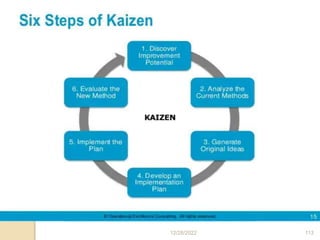
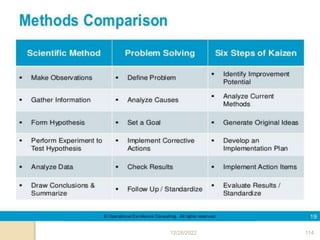
This document provides guidance on problem solving techniques and tools for health extension workers. It discusses defining problems, measuring their magnitude, generating alternative solutions, and setting objectives. Key steps in the problem solving process include identifying and prioritizing problems, analyzing causes, examining countermeasures, and assessing solutions. Tools that can be used include fishbone diagrams, brainstorming, line graphs and tree diagrams to help analyze problems and their root causes in a systematic way. The overall goal is to implement measurable solutions to identified challenges in healthcare.