Huzaifa Ismail presented on the production technology of castor bean. Some key points:
- Castor bean is native to East Africa and has been grown in India and Egypt for its oil and seeds. It is drought resistant and grown in dry areas.
- It is mainly grown in Sindh and districts of Punjab like Multan and Bahawalpur. Seed bed preparation involves deep plowing and soil is kept moist.
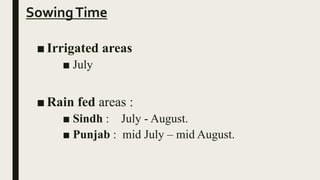
- Sowing is done in July-August through dibbling, drilling or keera methods. Fertilizers, irrigation, weeding and insect control are important management practices.
- Harvesting begins 90-120 days after sowing through multiple pickings