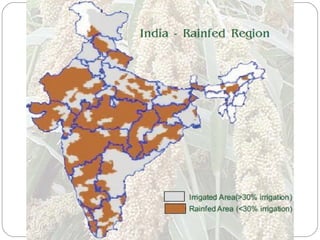
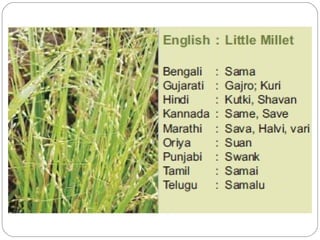
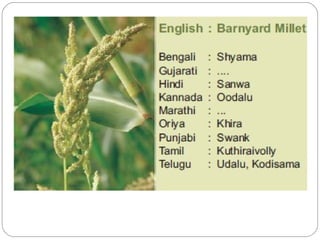
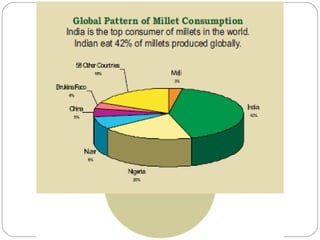
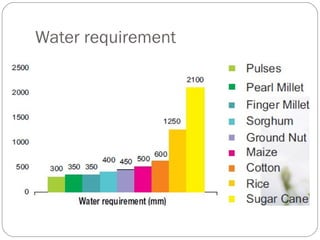
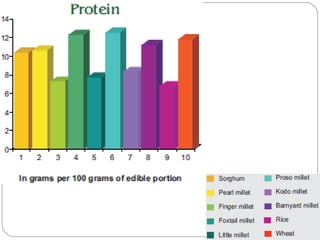
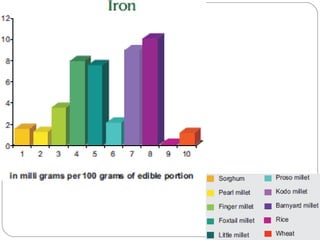
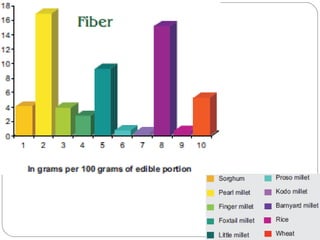
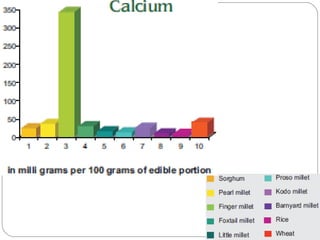
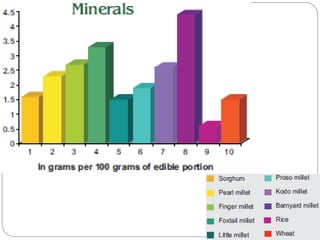
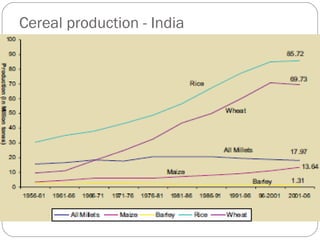
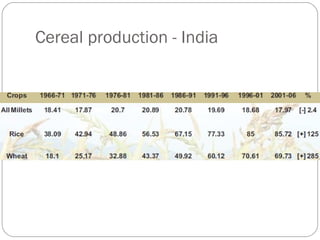
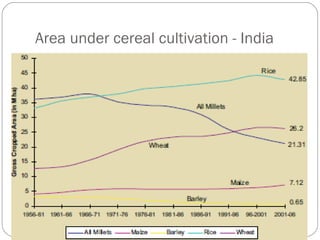
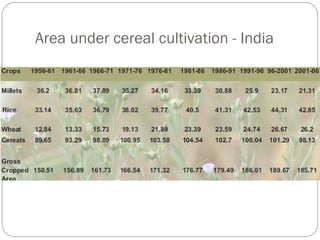
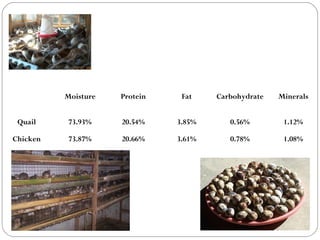
The document discusses millets, their cultivation in India, and their advantages. Millets require less water than other cereals, can grow in poor soils without fertilizers, and are pest-resistant. They allow for multiple intercropping and provide food, nutrition, fodder, fiber, and livelihood benefits. The document also briefly describes Coleus and Quails, noting their nutritional profiles and that Quails were first domesticated in Japan and later introduced to India for their high protein and rapid growth.