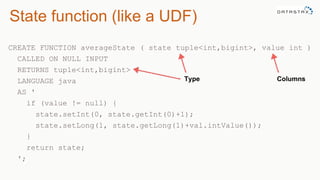
The document discusses the new features of Cassandra versions 2.2 and 3.0, highlighting the introduction of JSON support, user-defined functions, aggregates, and a new storage engine for improved efficiency. It includes various examples of data modeling, such as creating tables and using materialized views, along with details on handling customer event data and utilizing aggregates. The document emphasizes the balance between denormalization for scalability and performance, while also providing resources for further exploration of Cassandra capabilities.




![Hello JSON
• create TABLE user (username text primary key,
first_name text , last_name text , emails set<text> ,
country text);
• INSERT INTO user JSON '{"username": "chbatey",
"first_name":"Christopher", "last_name": "Batey",
“emails":["christopher.batey@datastax.com"]}';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandra-2-150916230417-lva1-app6891/85/Cassandra-2-2-3-0-7-320.jpg)