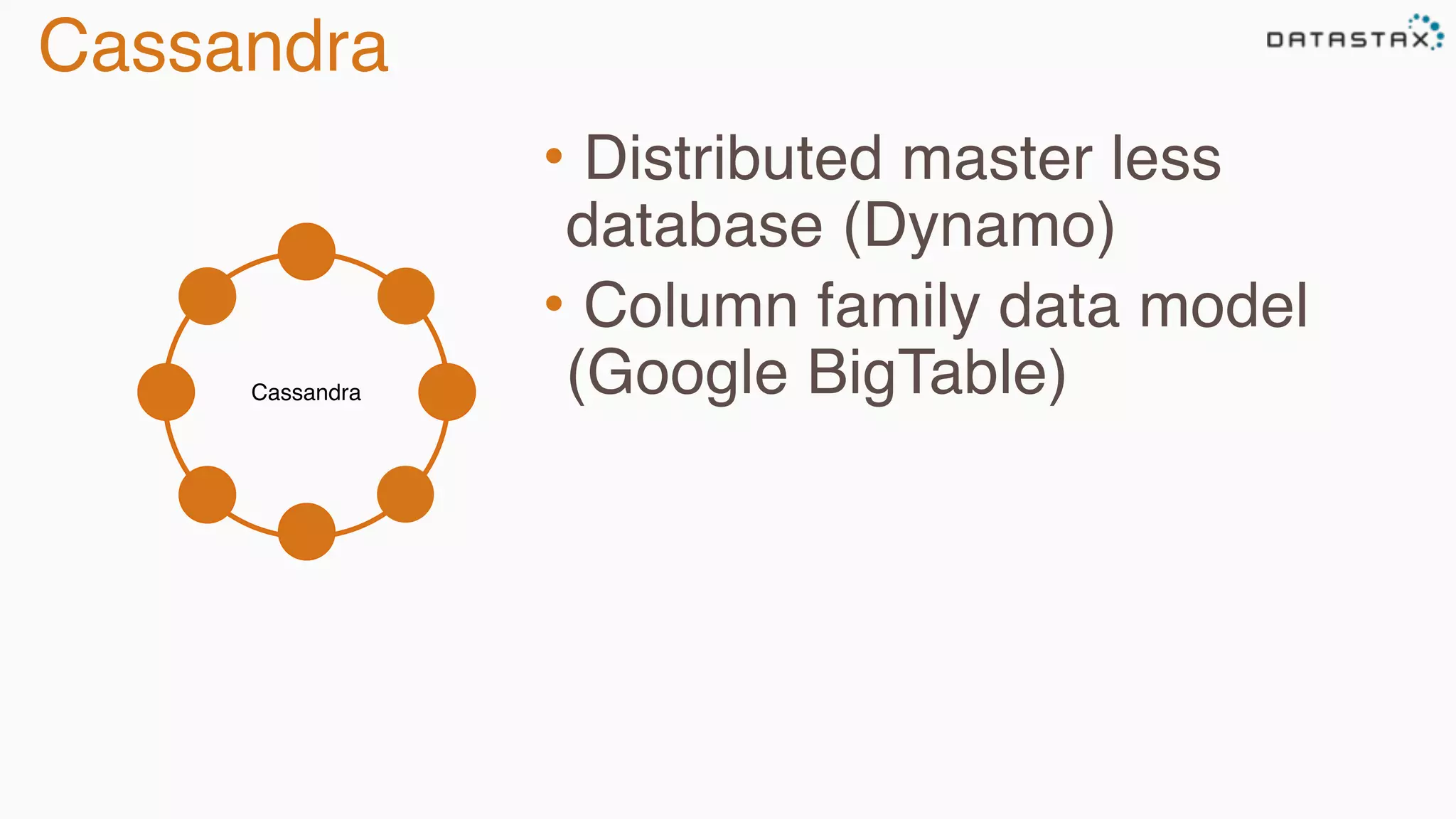
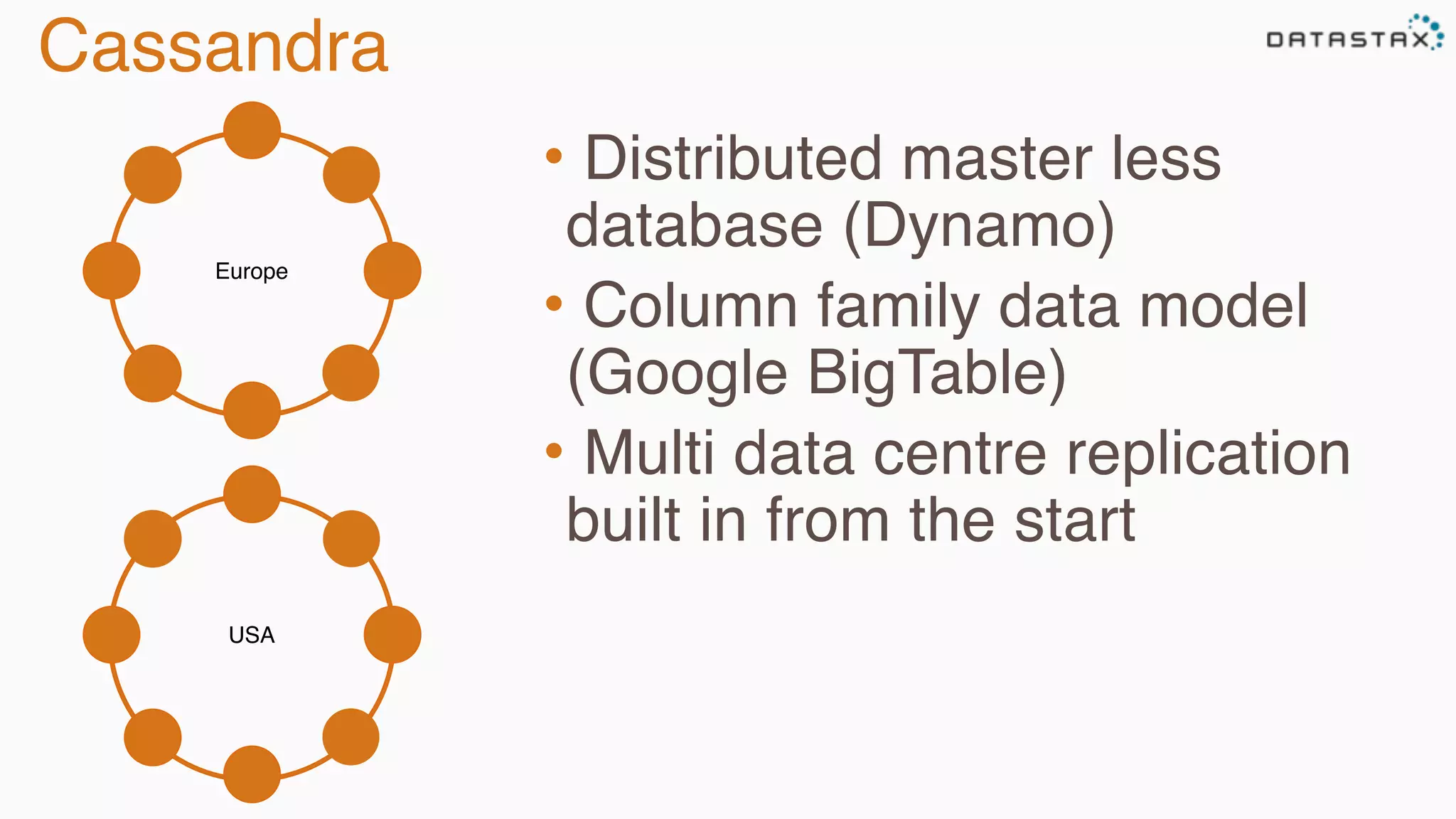
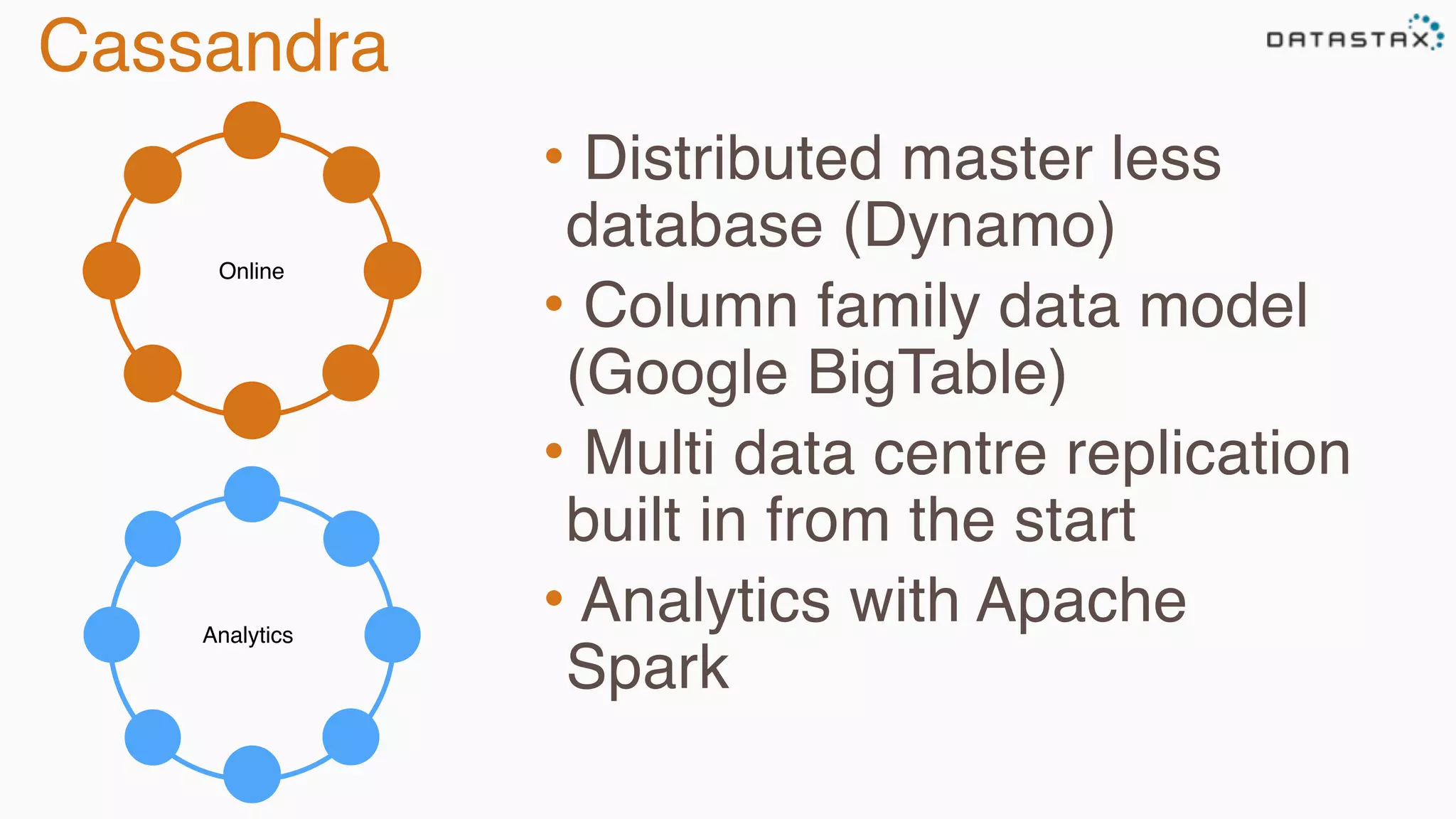
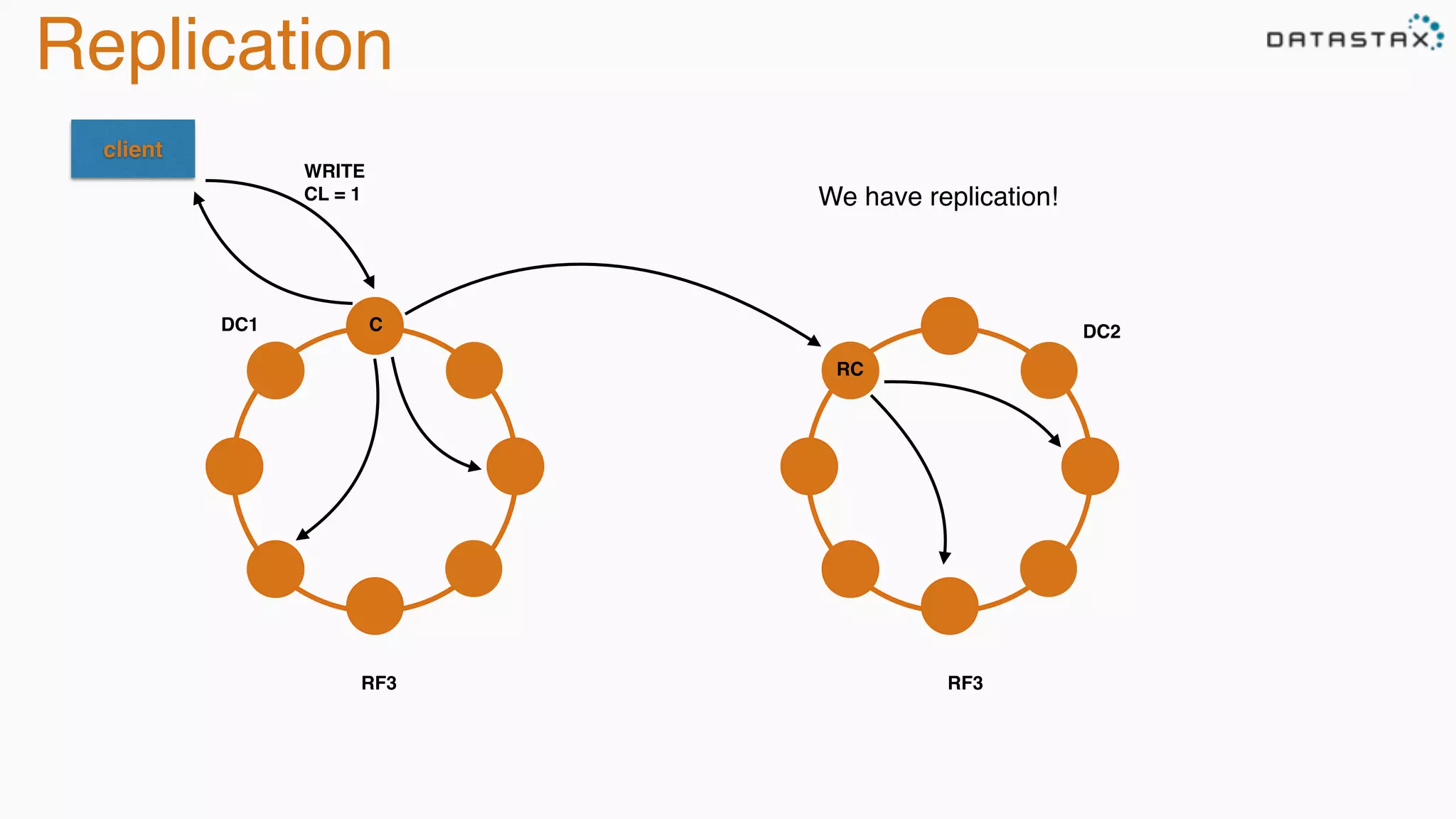
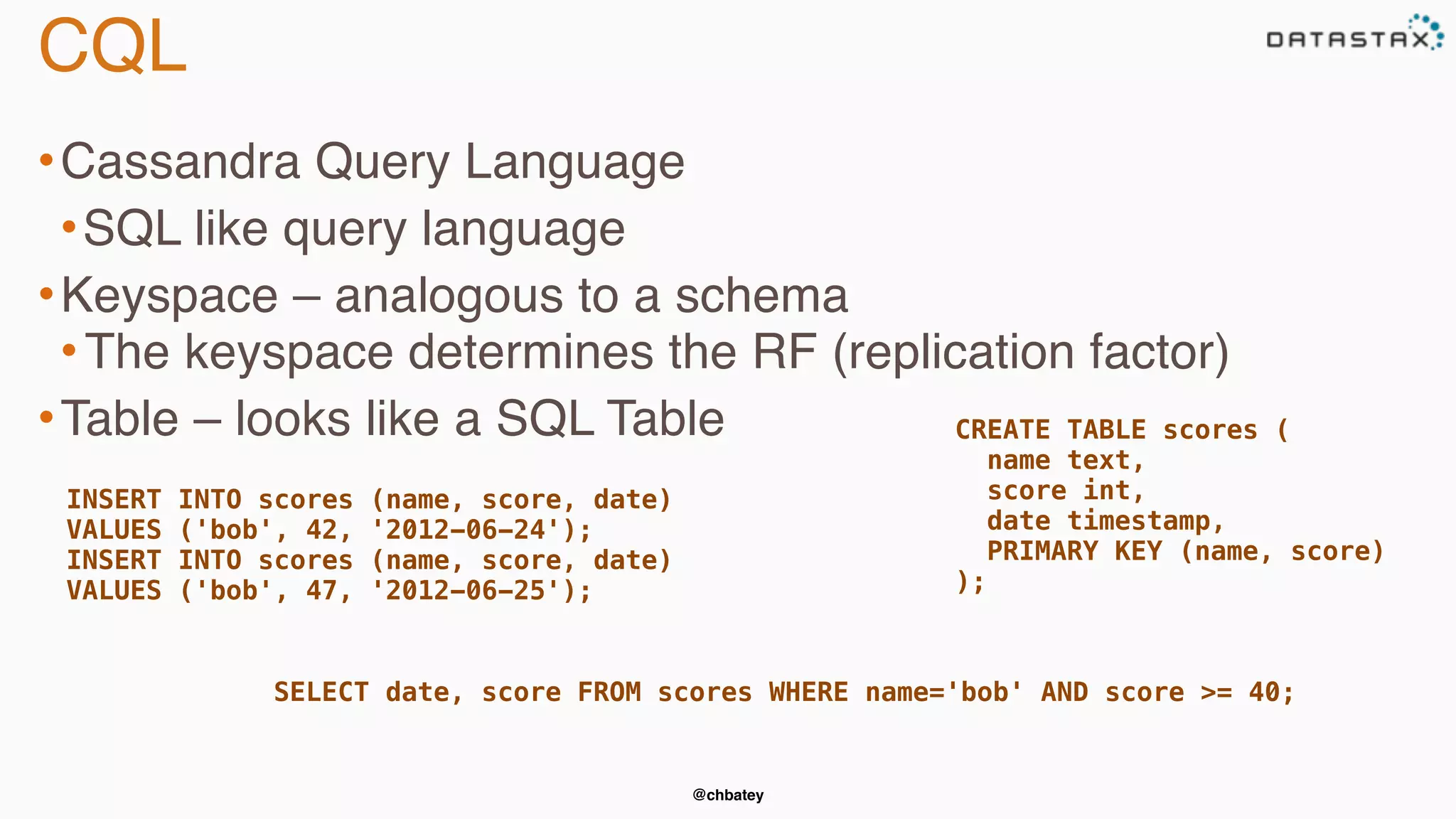
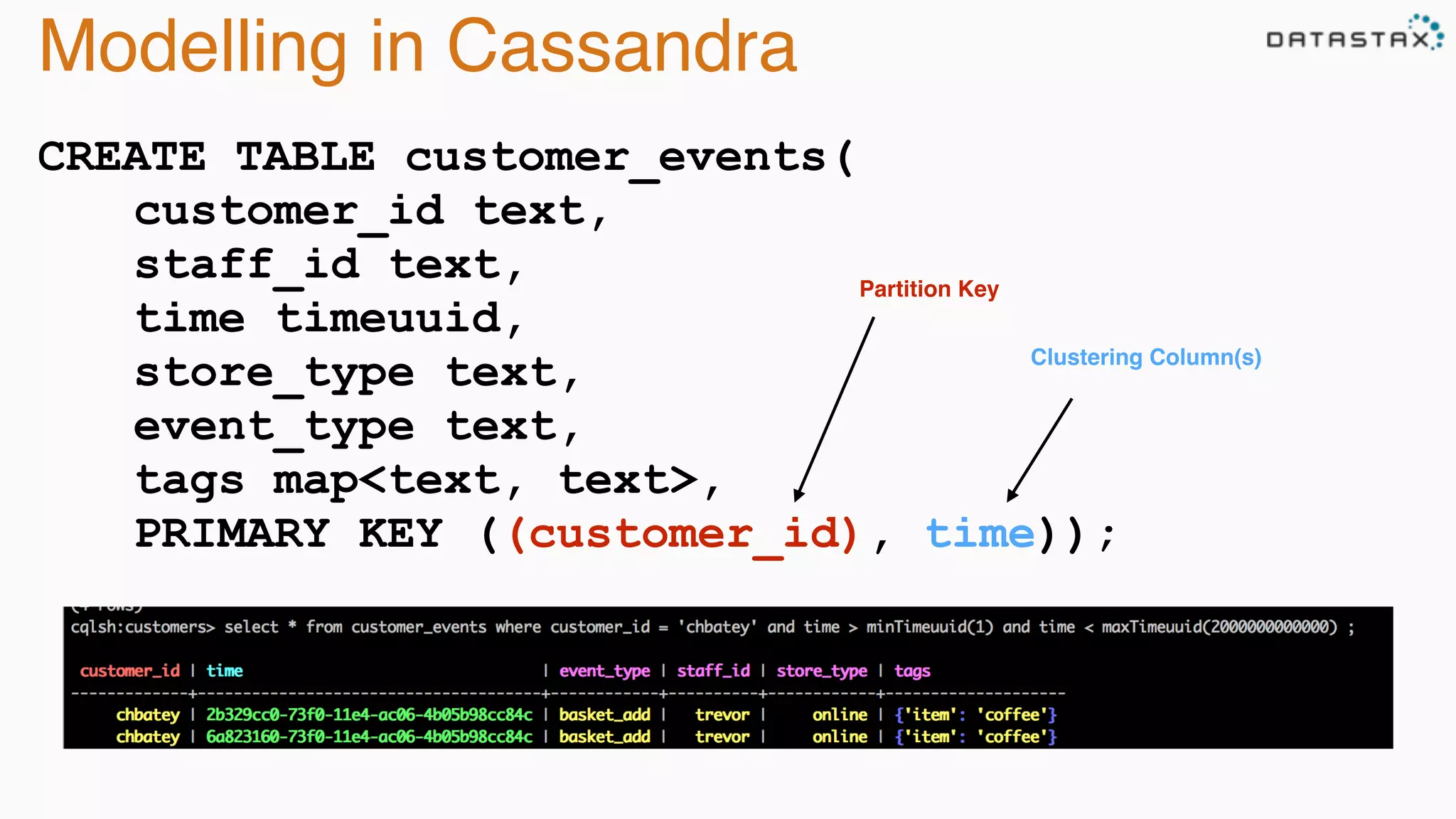
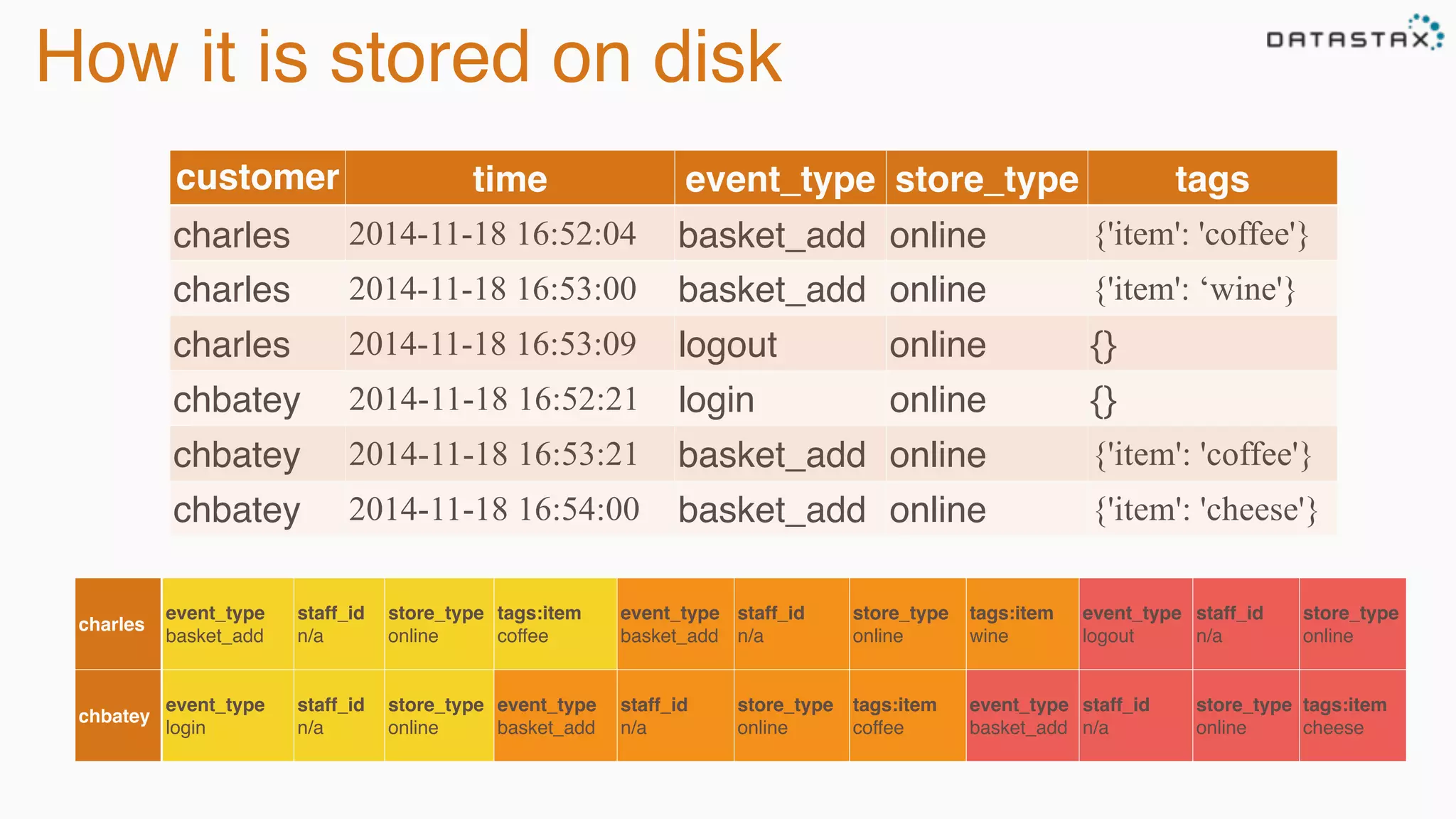
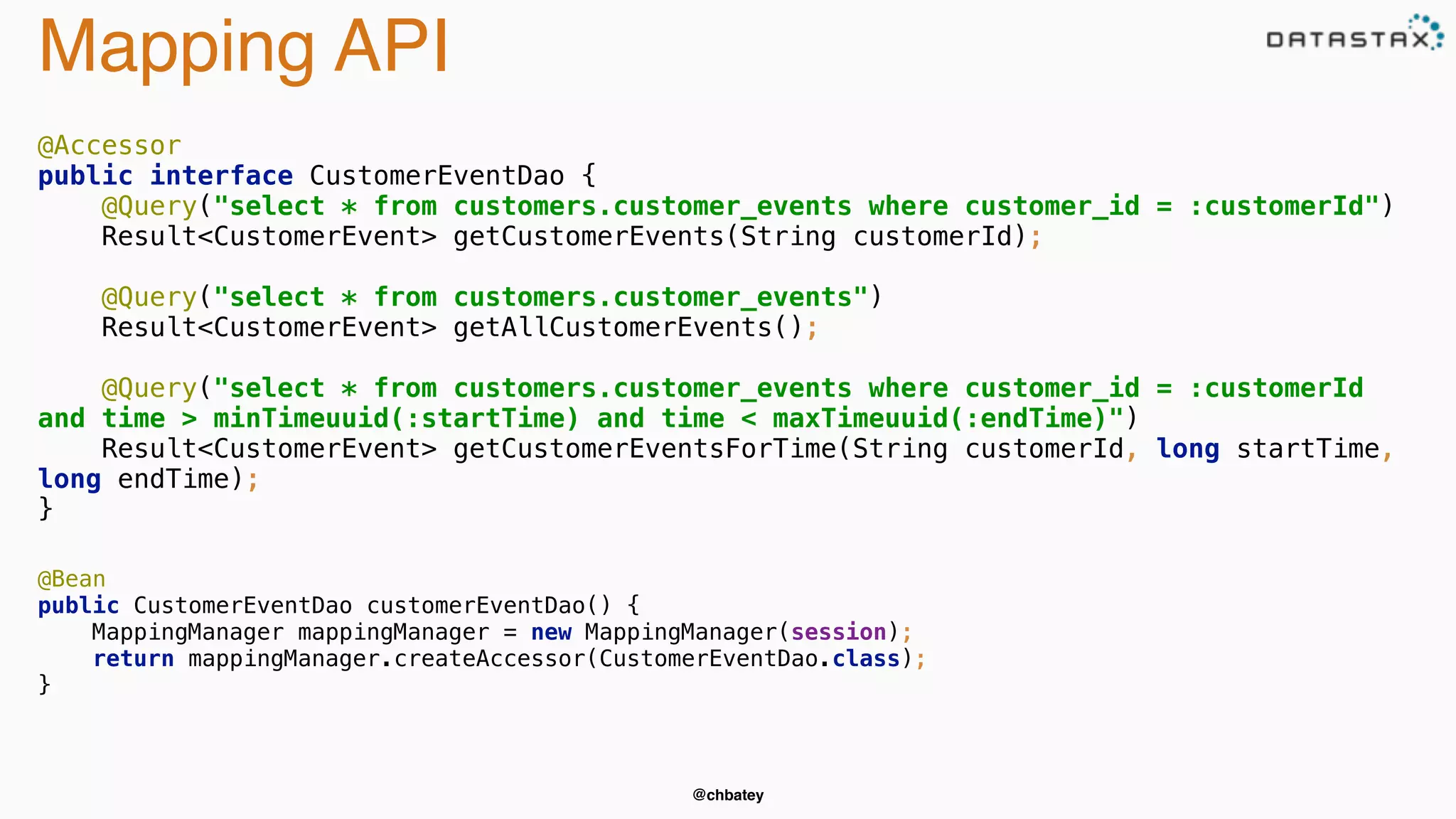
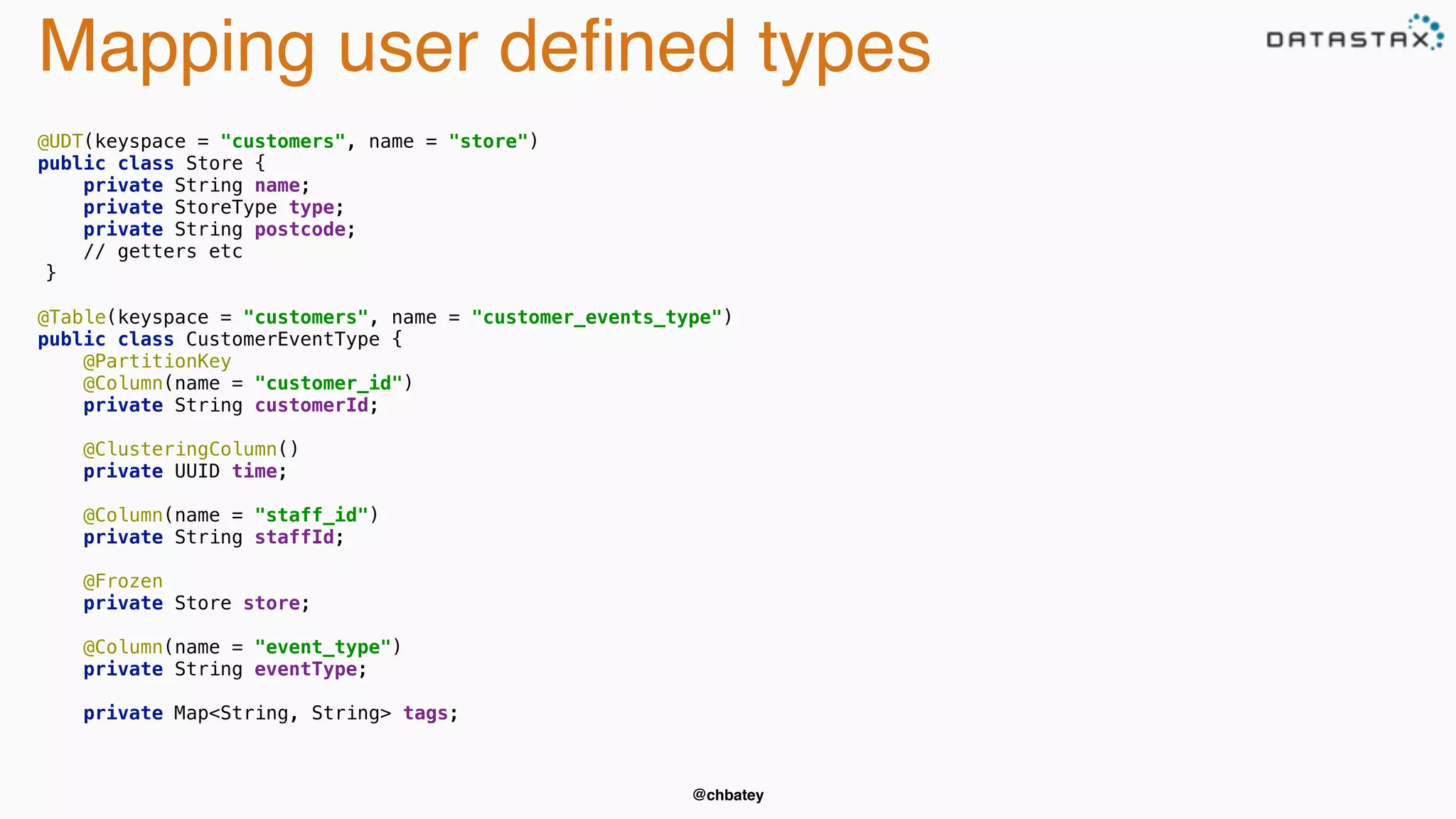
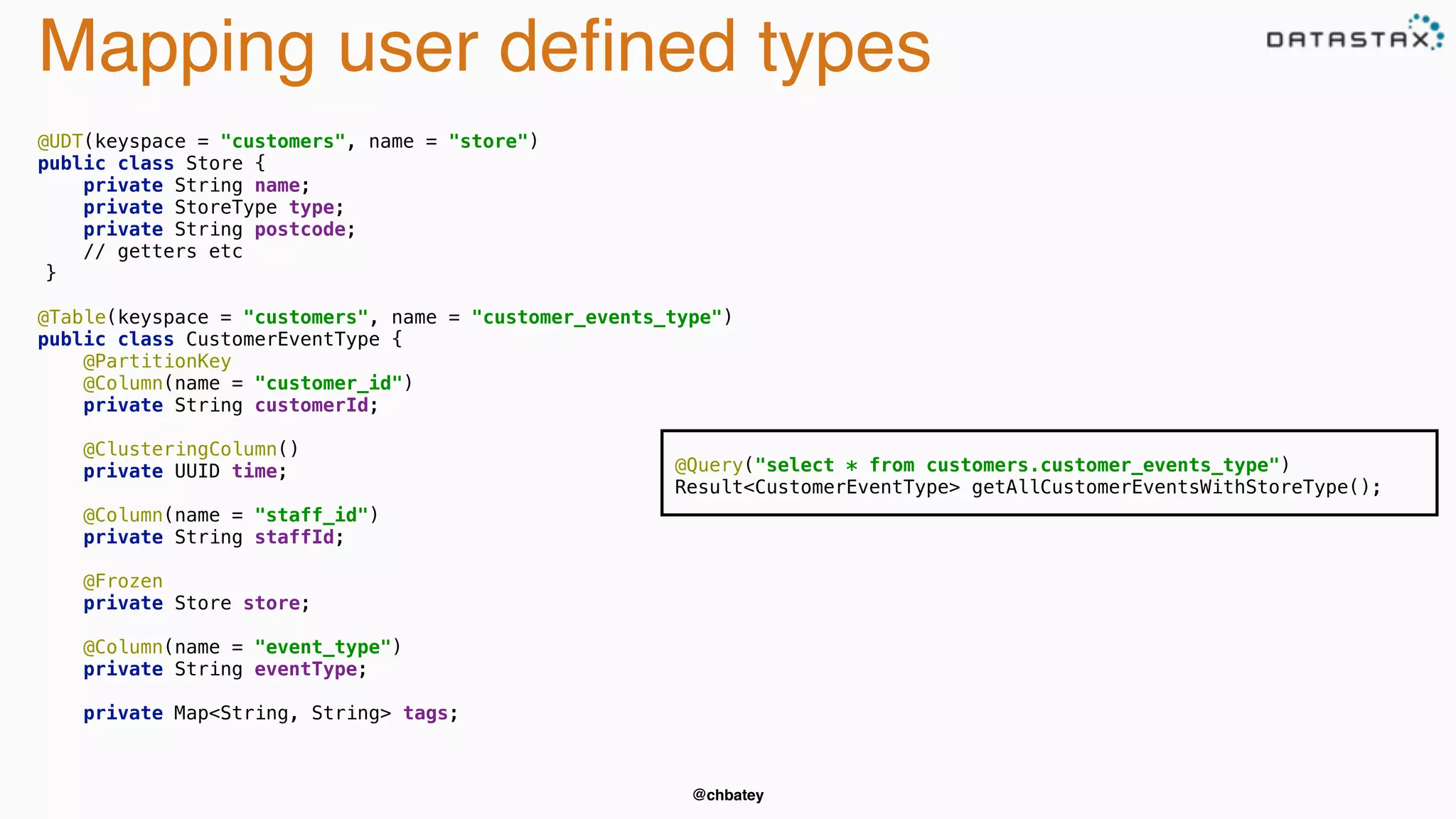
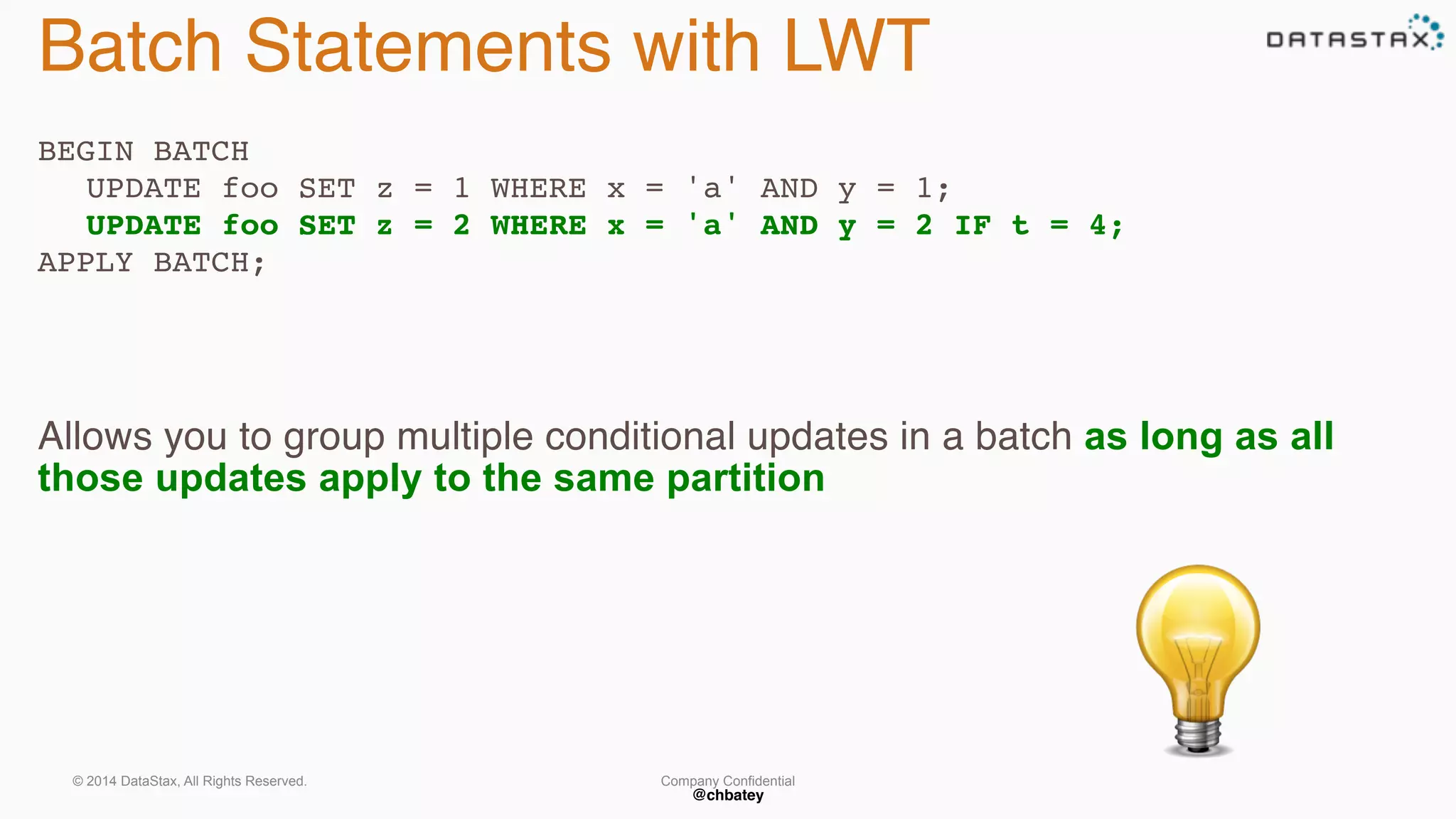
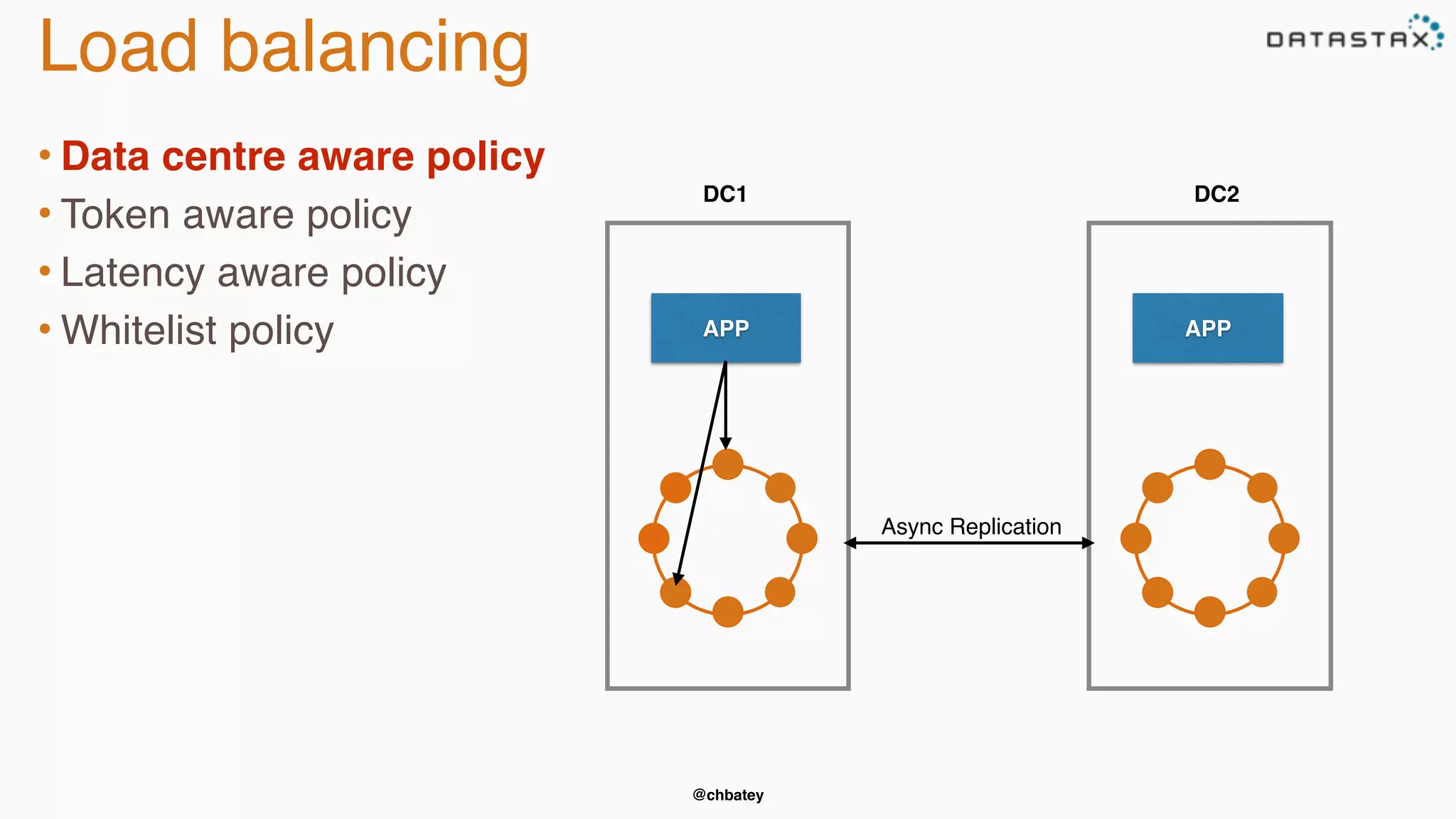
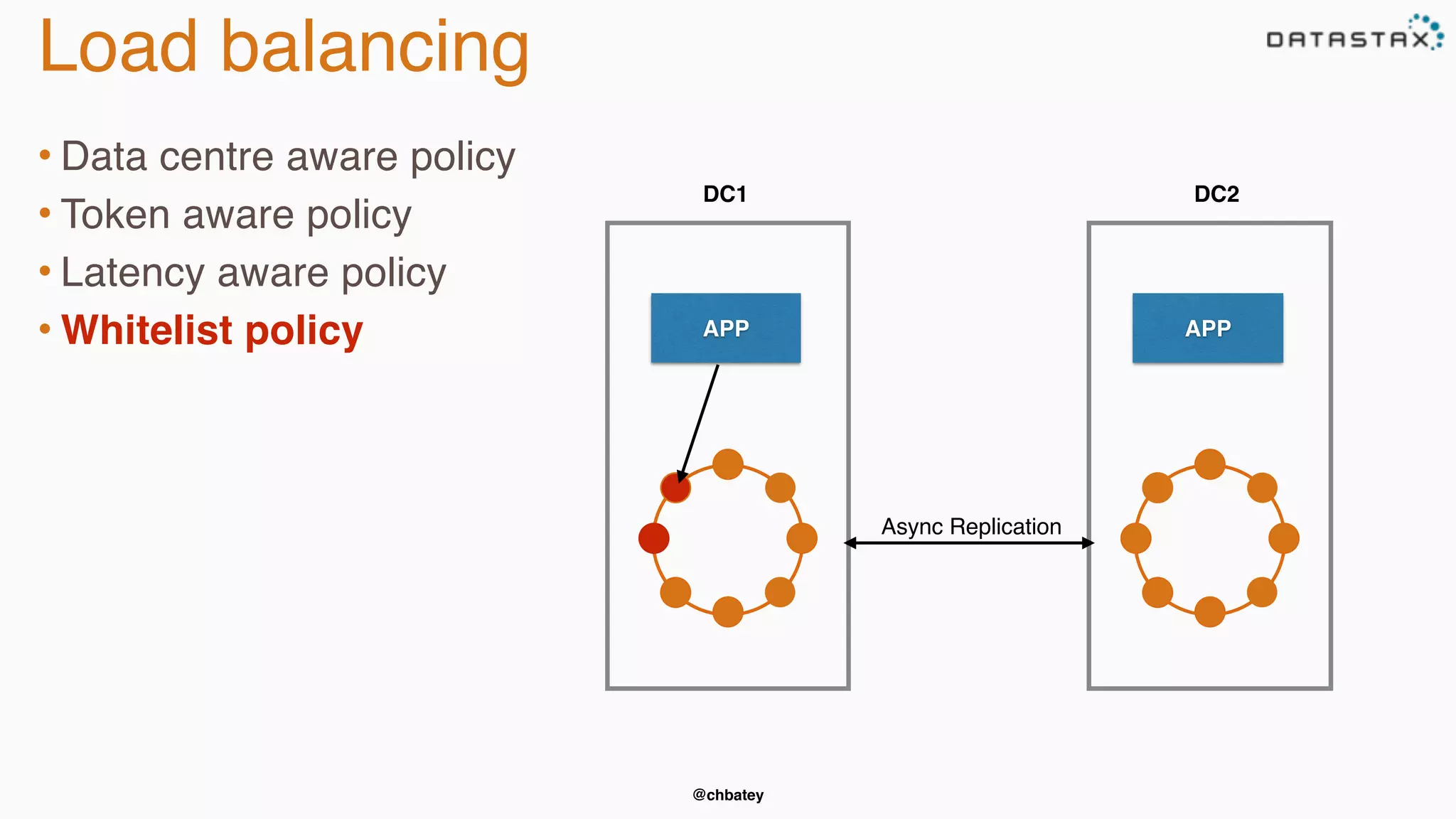
The document provides an overview of Apache Cassandra, covering its architecture, common use cases, and features like lightweight transactions and load balancing. It includes examples of using the DataStax Java driver and the Cassandra Query Language (CQL) for managing customer event data. Additionally, it discusses the mapping API, reconnection policies, and offers insights into upcoming training and conference events related to Cassandra.