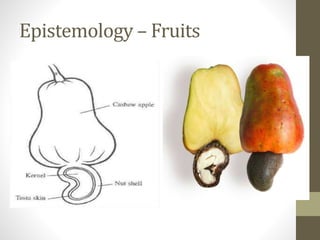
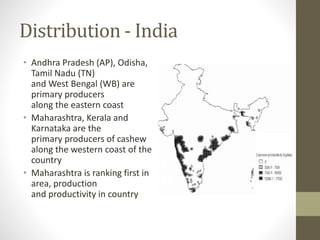
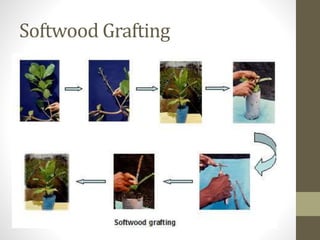
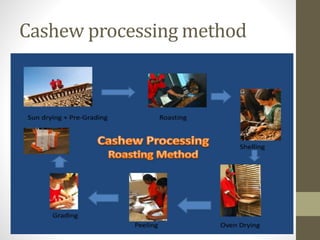
The document provides information on the cashew tree. It describes the cashew tree's origin in northeastern Brazil and introduction to India in the 16th century. It discusses the tree's morphology, cultivation requirements, common varieties, pests and diseases, processing methods, and uses of cashew apples, nuts, and other parts of the tree. The document is an overview of cashew production that is less than 3 sentences.