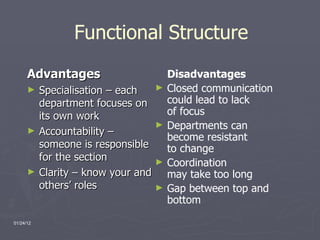
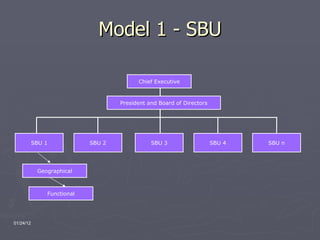
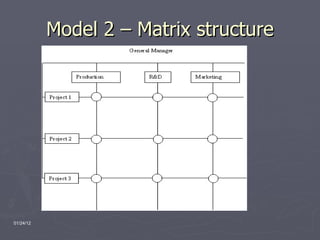
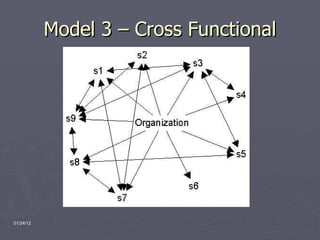
The document provides an overview of the Walt Disney Company, including its history, divisions, executive management, and potential organizational structures. It discusses Disney's reputation as the world's largest entertainment company and describes its media networks, parks and resorts, and consumer products divisions. A SWOT analysis is included, noting Disney's strengths in branding but weaknesses in high costs and investment risks. Three organizational models are proposed: strategic business units, a matrix structure, and cross-functional teams.