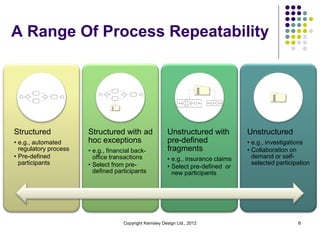
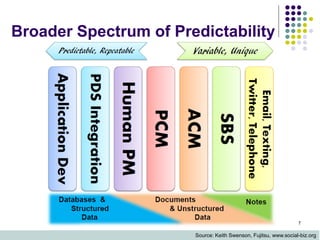
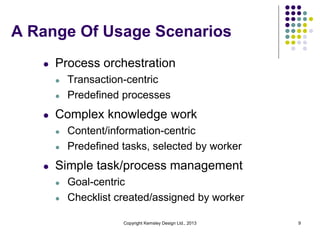
This document discusses case management systems and how they can help knowledge workers. It defines case management as a combination of process, content, rules, and events to support knowledge work in a flexible way. The document outlines how case management provides benefits like improved decision making through contextual information, enforcement of policies and rules, and visibility into work in progress. It provides examples of how case management helps with tasks like loan exception handling, customer support, and insurance claims processing.








![[Adaptive] Case Management
l
Dynamically configurable to meet worker’s
needs
l
Supports rather than controls
l
Case folder as central permanent artifact
l
Reliance on rules and content as well as
process
l
Collaboration on demand
Copyright Kemsley Design Ltd., 2013
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casemanagementrulesprocesscontent-131113181916-phpapp02/85/Case-Management-Where-Rules-Meet-Process-And-Content-12-320.jpg)











