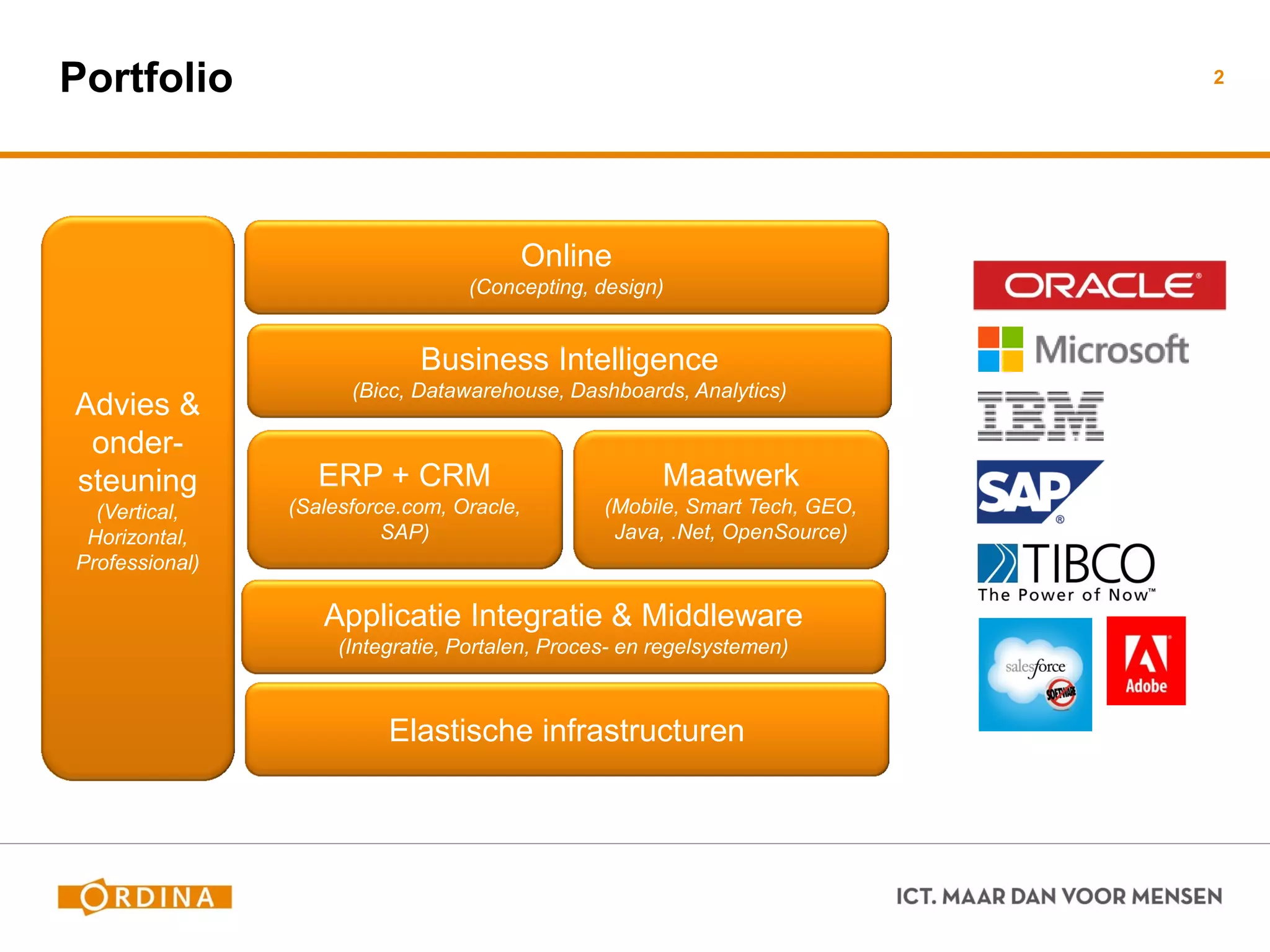
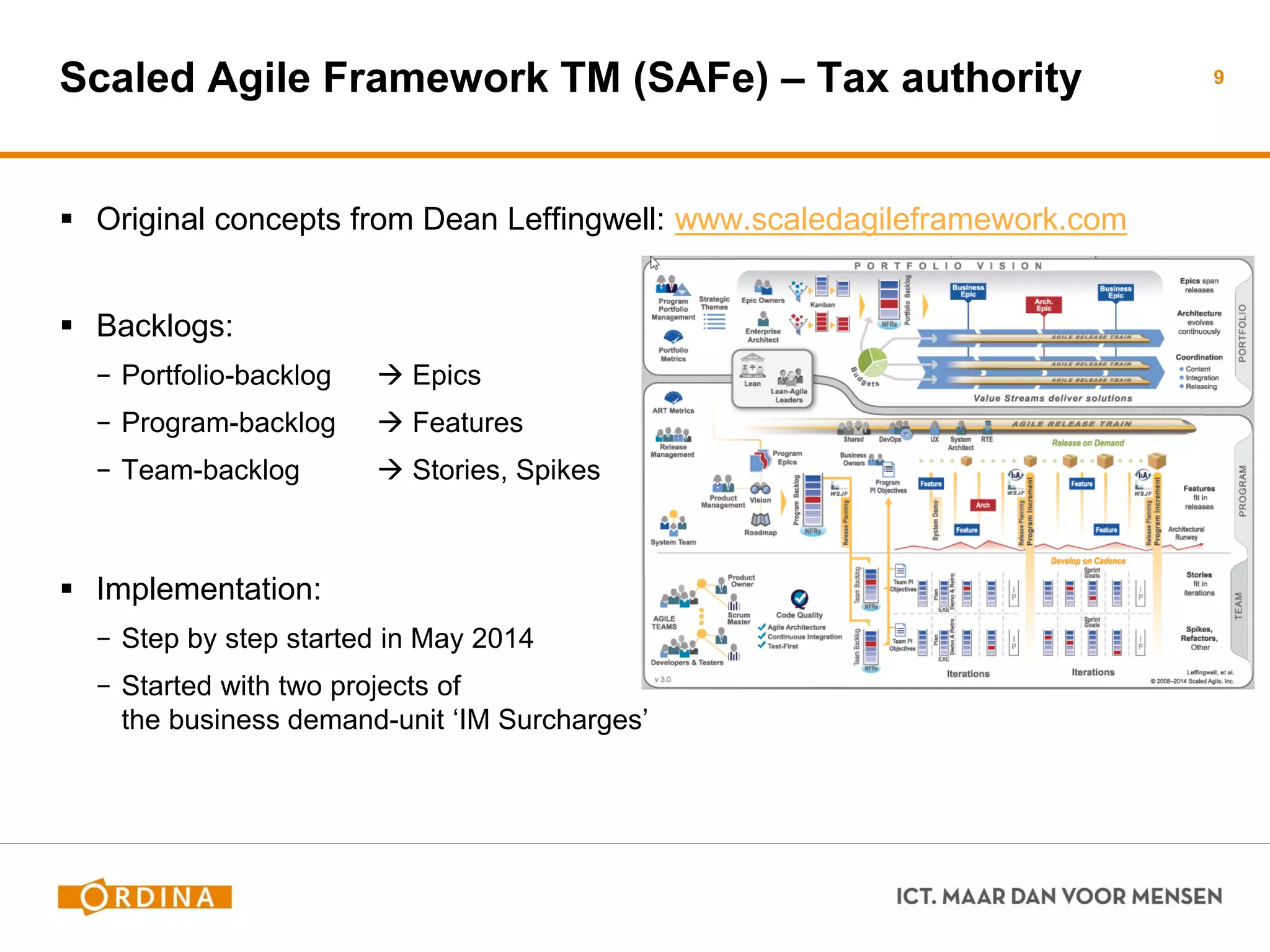
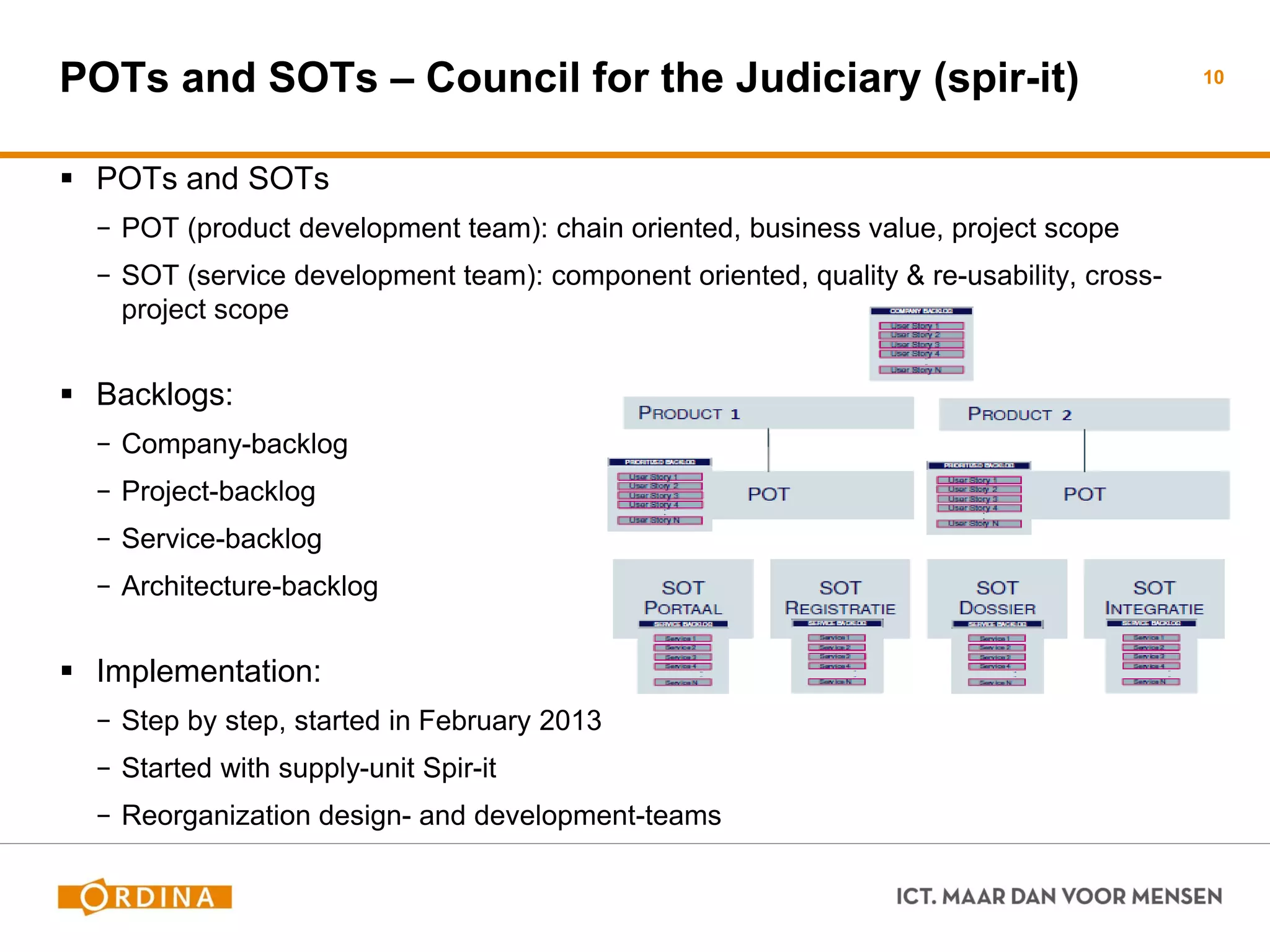
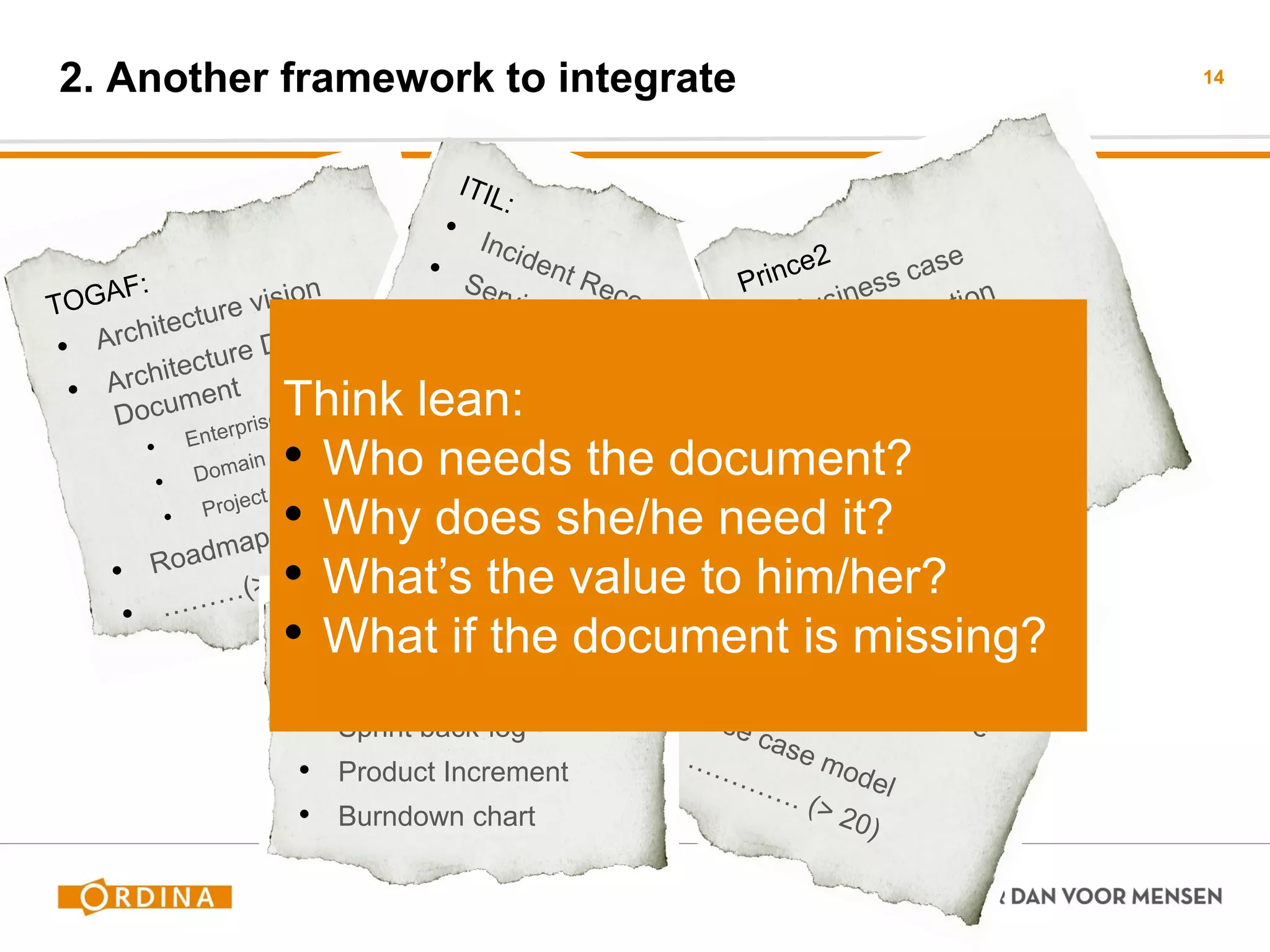
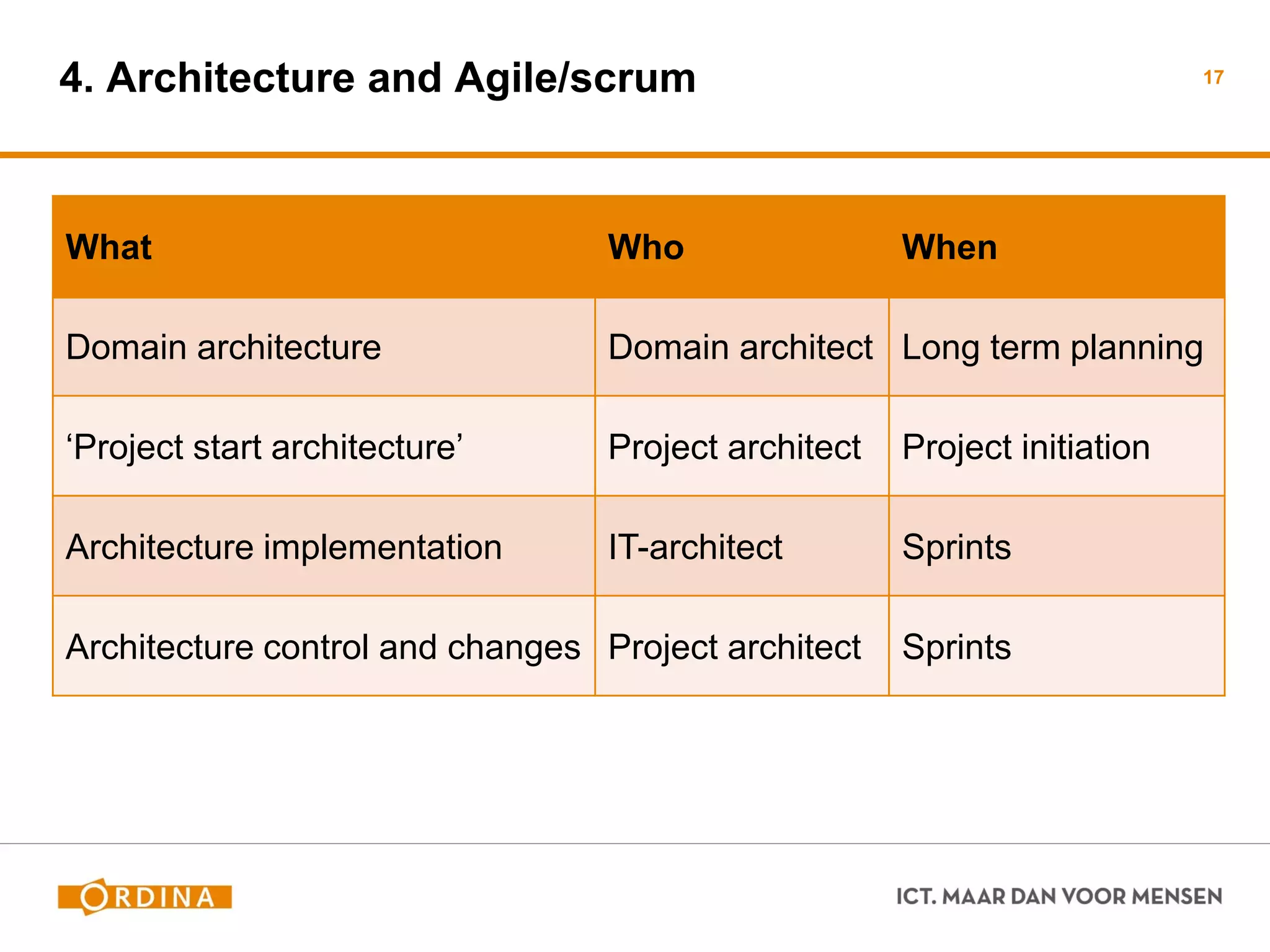
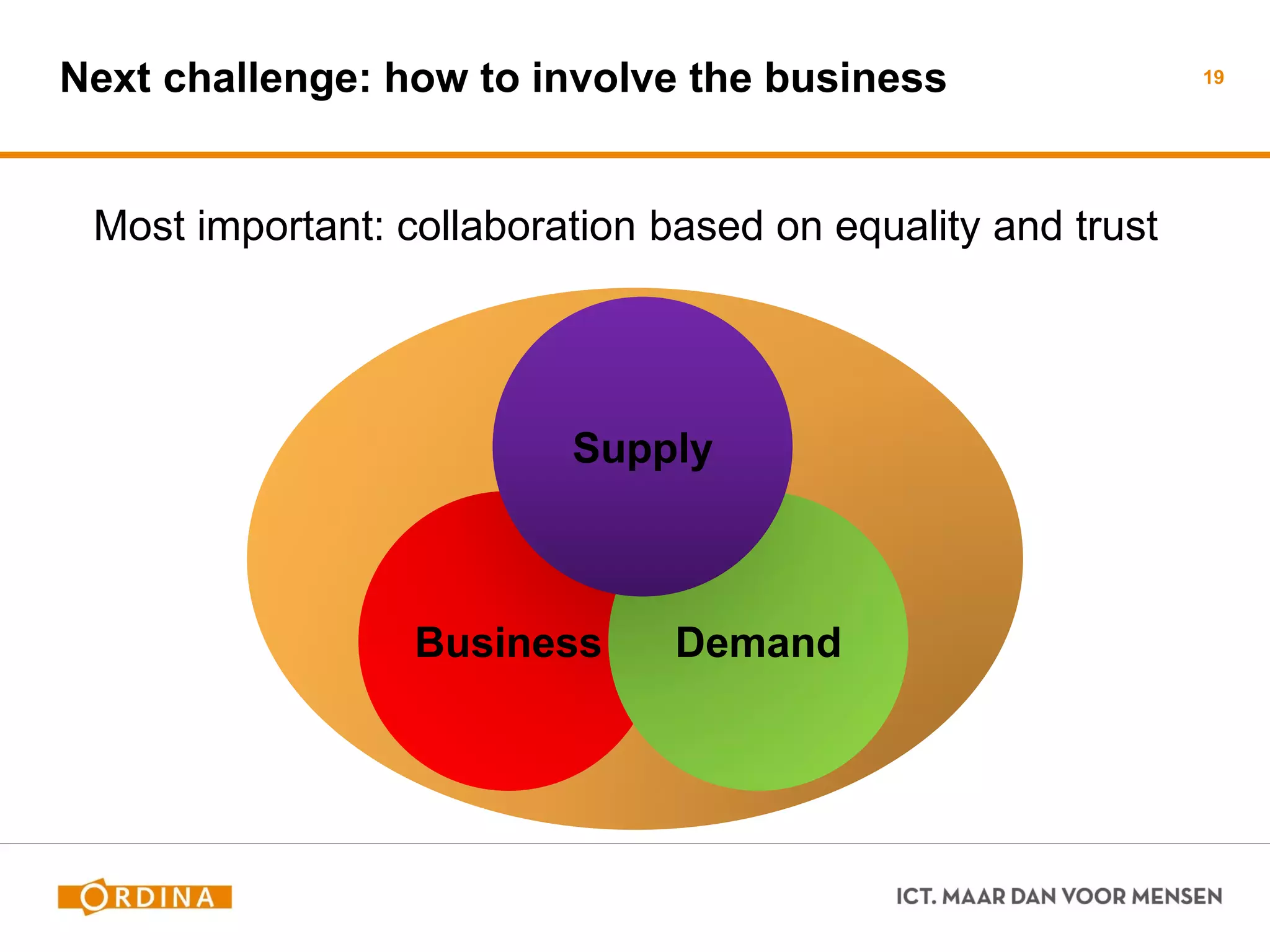
This document discusses implementing scaled agile frameworks like SAFe in large organizations. It describes how SAFe was implemented at a tax authority, using portfolio, program and team backlogs to prioritize work. It also discusses implementing SAFe at a Council for the Judiciary organization using Product and Service development teams. Some challenges discussed are implementing agile within a traditional organization, integrating multiple frameworks, dealing with mixed agile and waterfall teams, and ensuring architecture work aligns with agile. The conclusion emphasizes the need for collaboration beyond models to effectively adopt business needs in IT solutions.