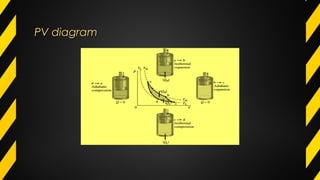
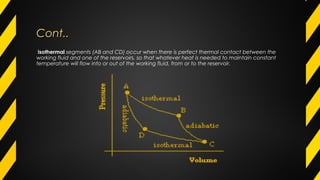
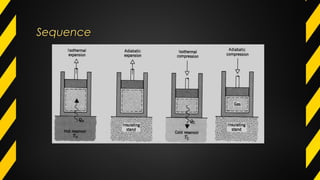
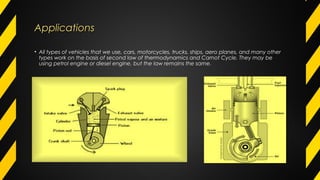
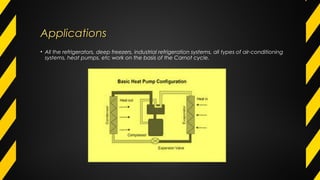
The Carnot cycle describes how a fluid is used to convert thermal energy into work. It involves four stages: (1) reversible isothermal expansion, (2) reversible adiabatic expansion, (3) reversible isothermal compression, and (4) reversible adiabatic compression. The Carnot cycle has high efficiency and can use multiple heat sources. It also has better reliability, flexibility, and safety compared to other engine types. The Carnot cycle establishes the theoretical maximum efficiency that heat engines can achieve between two given temperatures.