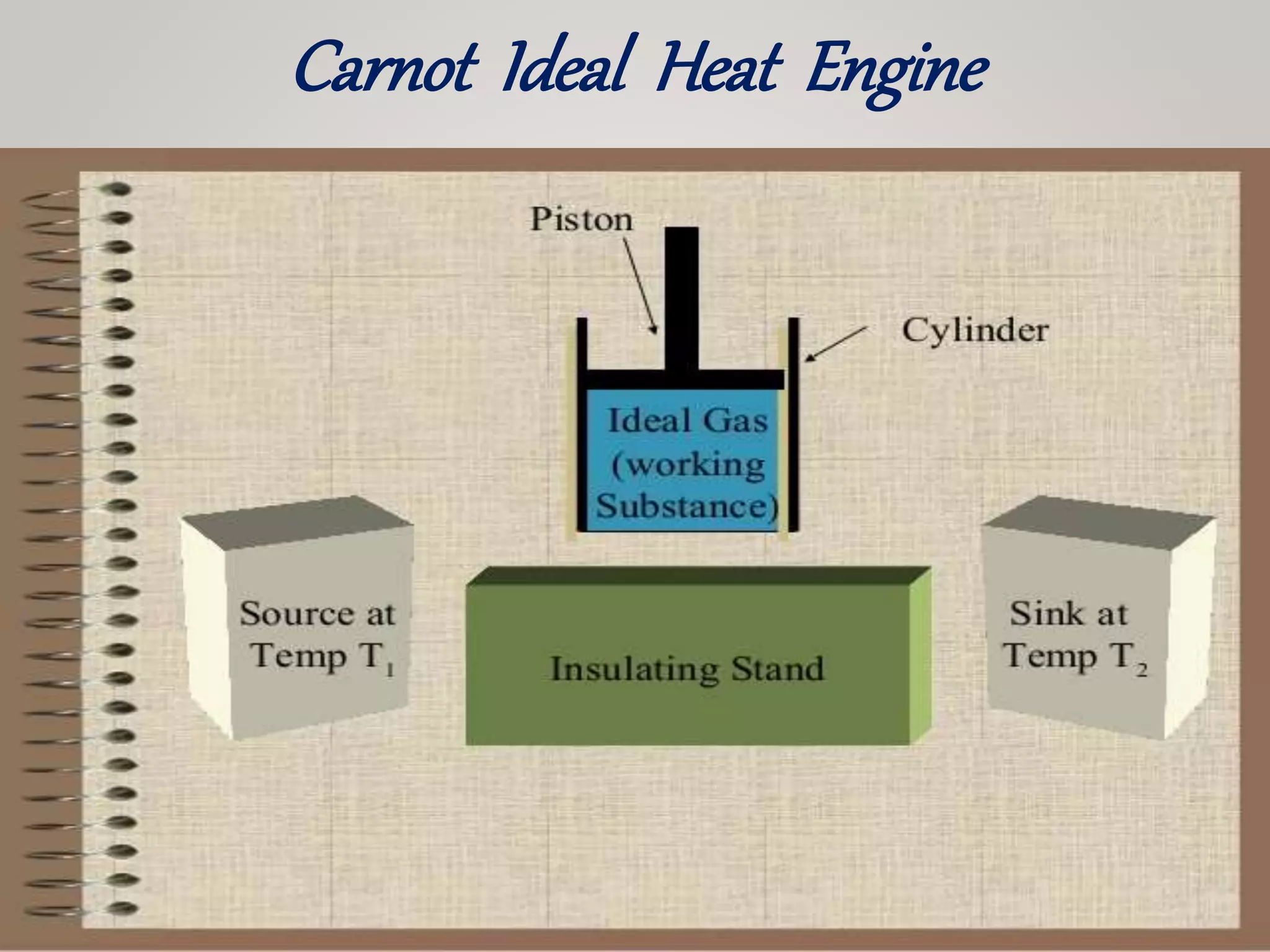
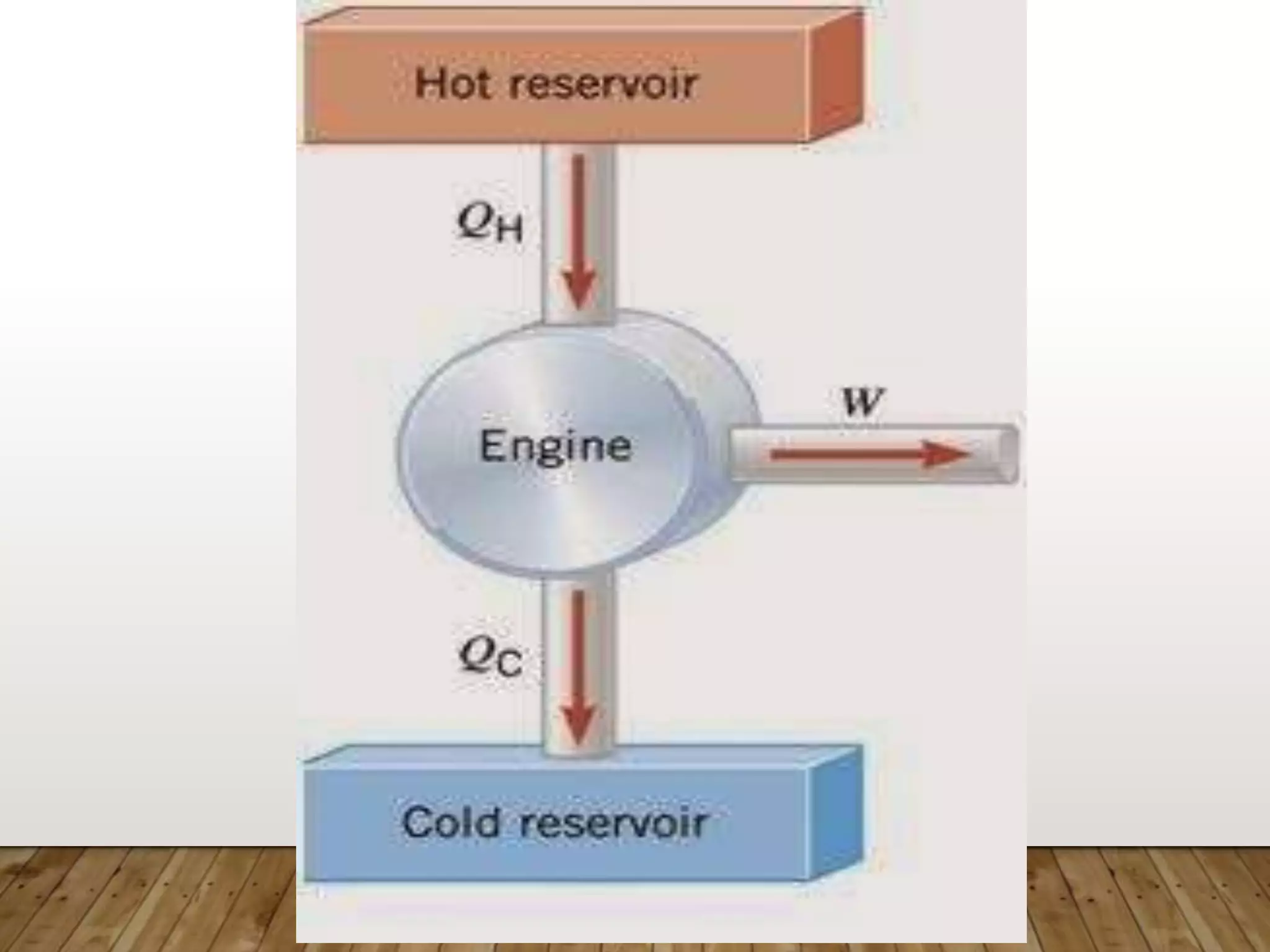
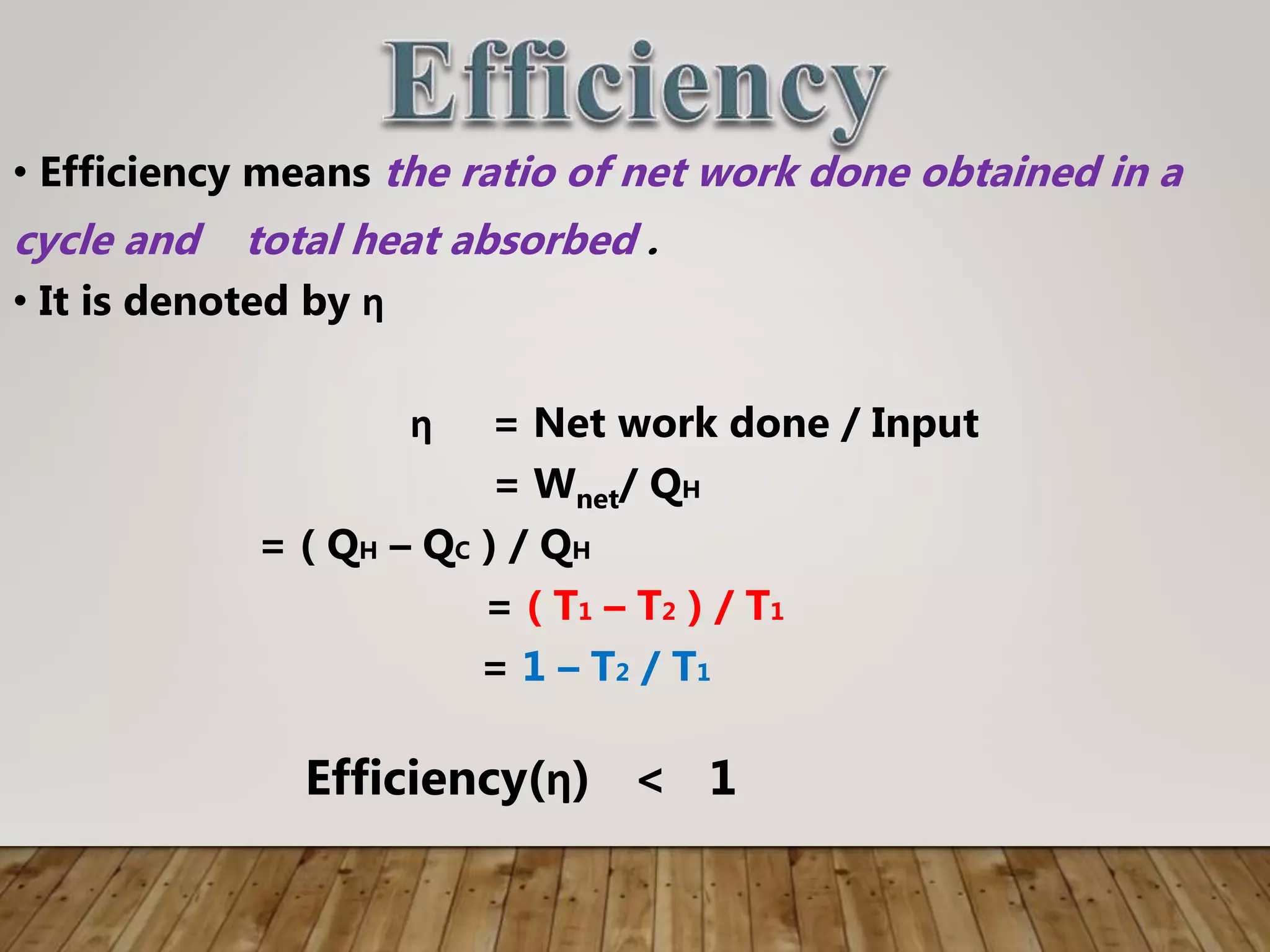
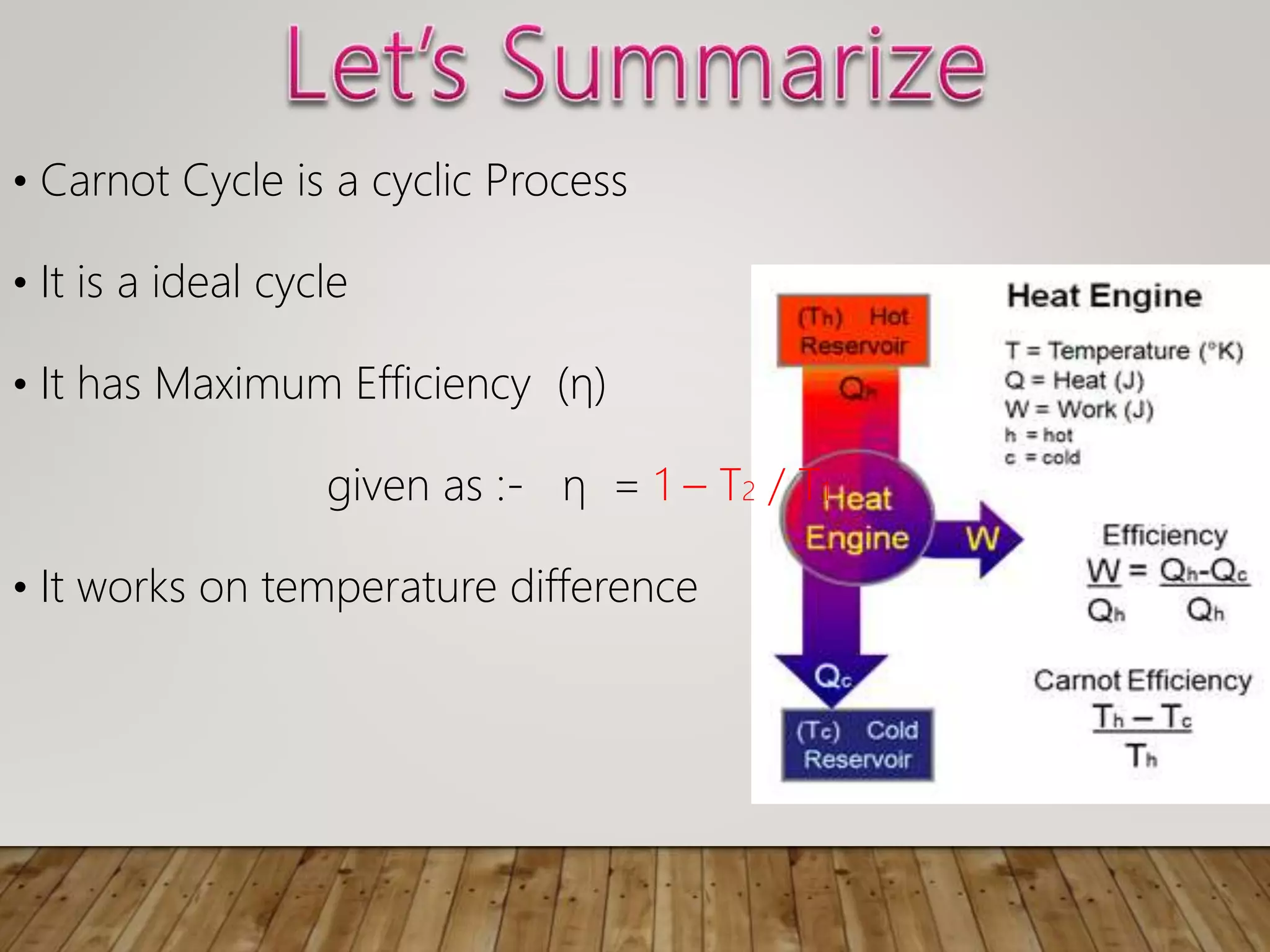
The document discusses the Carnot cycle, a theoretical ideal engine developed by Nicolas Leonard Sadi Carnot in 1824, highlighting its cyclic process consisting of four steps: isothermal expansion, adiabatic expansion, isothermal compression, and adiabatic compression. It explains the efficiency of the Carnot engine, defined as the ratio of net work done to heat absorbed, with a maximum efficiency equation given by η = 1 - t2 / t1. The document also notes that the Carnot cycle operates on the principle of temperature differences and serves as a foundational concept in thermodynamics.