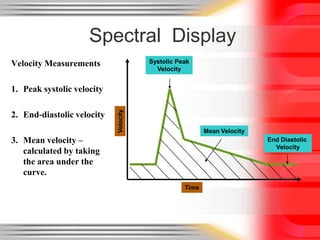
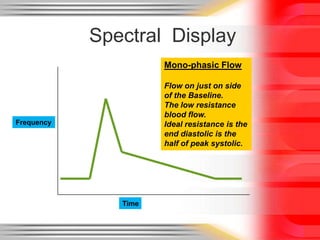
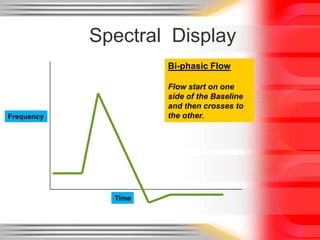
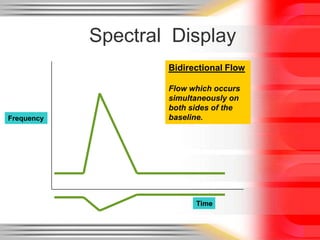
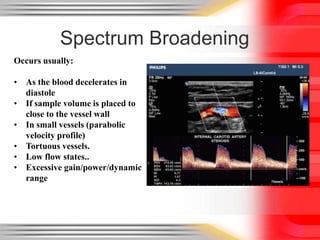
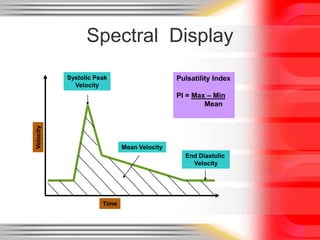
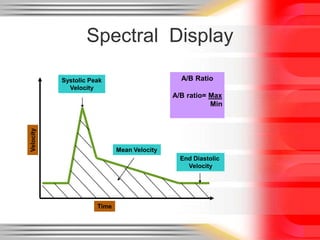
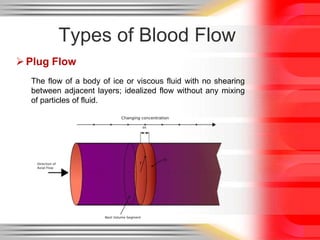
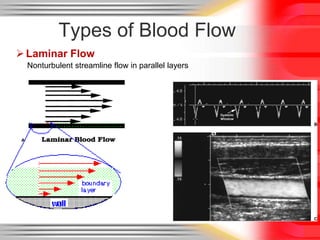
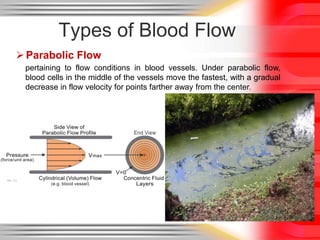
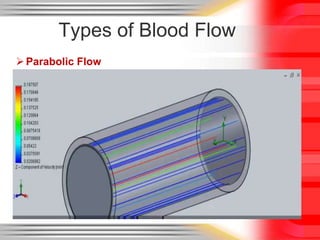
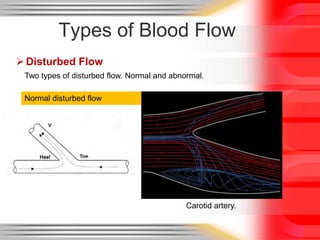
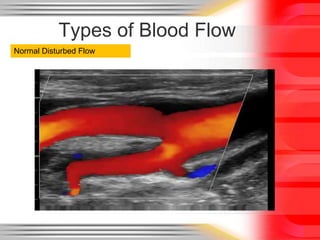
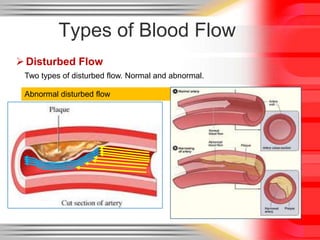
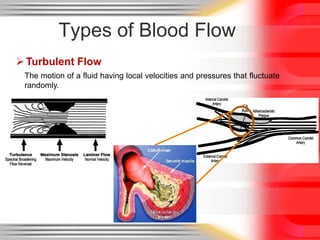
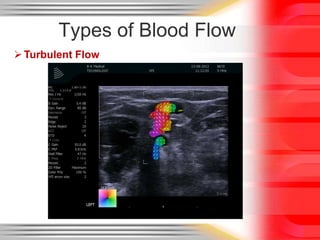
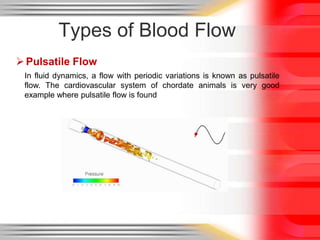
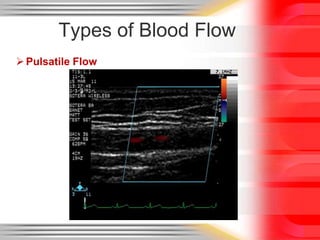
Hemodynamic monitoring involves measuring factors that influence blood flow and pressure to aid in diagnosing and managing critically ill patients. It uses Doppler ultrasound to analyze blood flow spectra and determine velocity measurements. The spectral display shows velocity over time and can reveal flow direction and indices like resistive index. The document defines six types of blood flow seen: plug, laminar, parabolic, disturbed, turbulent, and pulsatile.