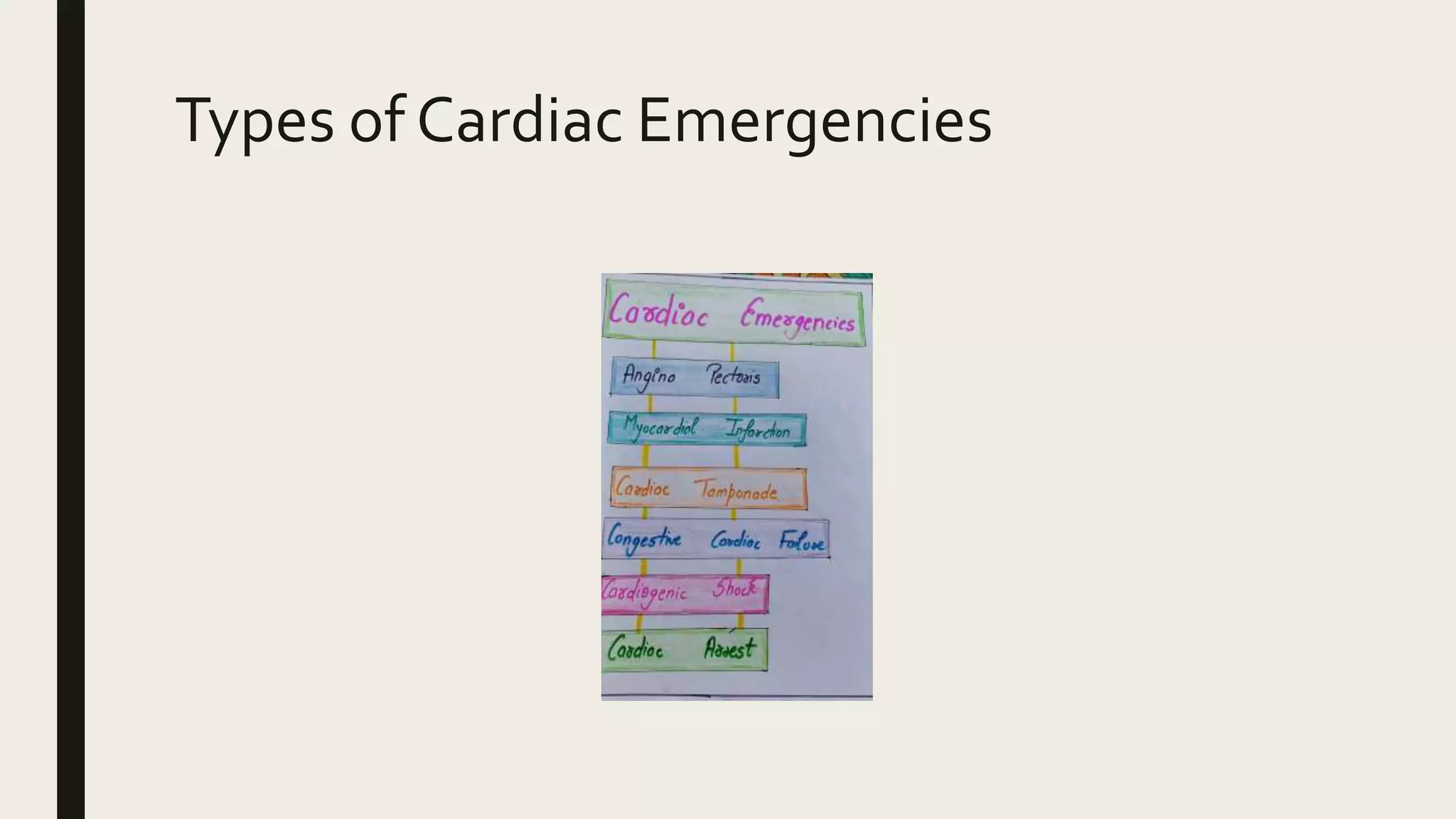
This presentation discusses cardiac emergencies and the nursing responsibilities in managing them. It defines cardiac emergencies as life-threatening conditions requiring immediate recognition and treatment. The main types covered are angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, congestive cardiac failure, cardiac tamponade, cardiogenic shock, and cardiac arrest. For each, it discusses pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and nursing management. The presentation concludes that cardiovascular emergencies must be promptly recognized and treated to minimize morbidity and mortality.