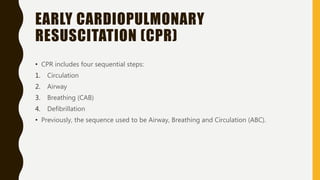
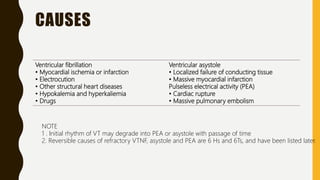
Cardiac arrest is defined as the abrupt loss of cardiac function and can result from ventricular fibrillation, pulseless ventricular tachycardia, asystole, or pulseless electrical activity. Management involves cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) including chest compressions, ventilation, and defibrillation if indicated. The chain of survival links immediate recognition, early CPR, rapid defibrillation if needed, advanced life support, and post-cardiac arrest care. Basic life support involves chest compressions, airway management, rescue breathing, and public access defibrillation with an automated external defibrillator if available. Advanced life support adds establishment of intravenous access, rhythm monitoring/defibrillation, and administration



![MANAGEMENT [CARDIOPULMONARY
RESUSCITATION (CPR)]
• Cardiopulmonary resuscitation provides artificial ventilation and perfusion to the vital
organs, particularly heart and brain until spontaneous cardiopulmonary function is
restored.
• It encompasses both basic life support (BLS) and advanced life support (ALS).
• Successful resuscitation following cardiac arrest requires an integrated set of
coordinated actions represented by the links in the "Chain of Survival".](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiacarrest-200508083507/85/Cardiac-Arrest-5-320.jpg)