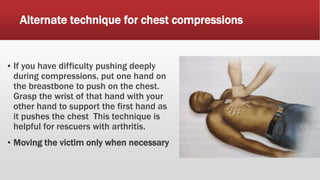
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving technique used when someone's breathing or heartbeat has stopped. It involves hard and fast chest compressions combined with rescue breaths. The guidelines recommend compressing the chest at least 100 times per minute and giving 2 breaths after every 30 compressions. CPR is used for cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, drowning, stroke and other emergencies. It is important to call for emergency help, retrieve an AED if available, check for a pulse, and begin cycles of chest compressions and breaths according to age-specific guidelines until emergency services arrive.



















![2 finger chest compression technique
▪ Place the infant on a firm, flat surface.
▪ Place 2 fingers in the center of the infant’s
chest just below the nipple line. Do not press
on the bottom of the breastbone.
▪ Push hard and fast. To give chest
compressions, press the infant’s breast- bone
down at least one third the depth of the chest
(approximately 4 cm [1½ inches]). Deliver
compressions in a smooth fashion at a rate of
at least 100/min.
▪ At the end of each compression, make sure
you allow the chest to recoil (reexpand)
completely.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cpr3taruni-230808051534-aedcb0ad/85/CPR-22-320.jpg)









