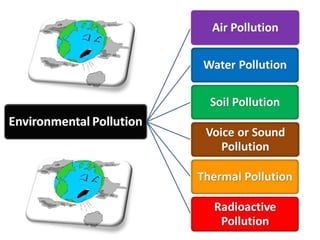
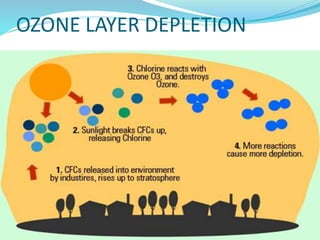
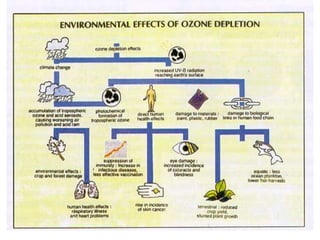
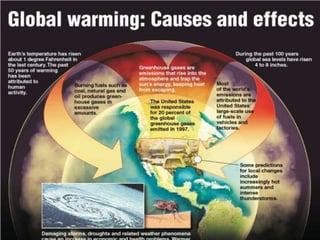
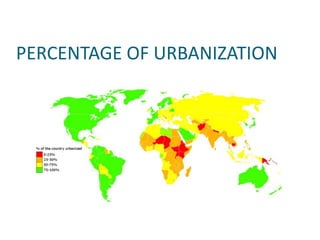
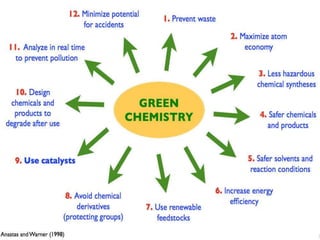
The document discusses the importance of environmental studies and chemistry, highlighting how various pollutants, including air, water, soil, and radioactive pollutants, adversely affect ecosystems and human health. It outlines the causes and effects of pollution, such as acid rain and urbanization, and emphasizes the need for sustainable growth and green practices. Solutions suggested include the use of green chemistry and renewable energy sources like solar and wind energy.