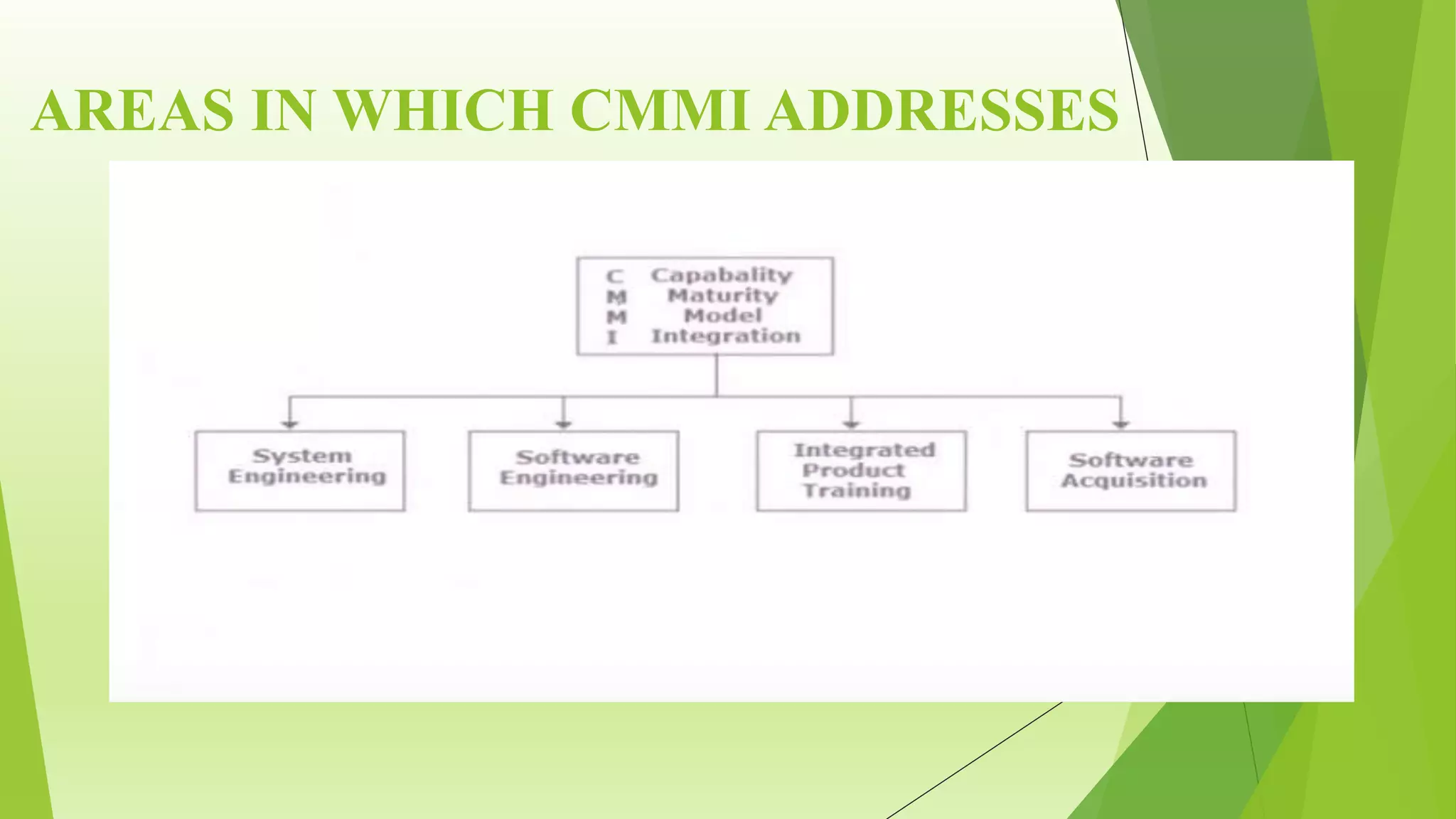
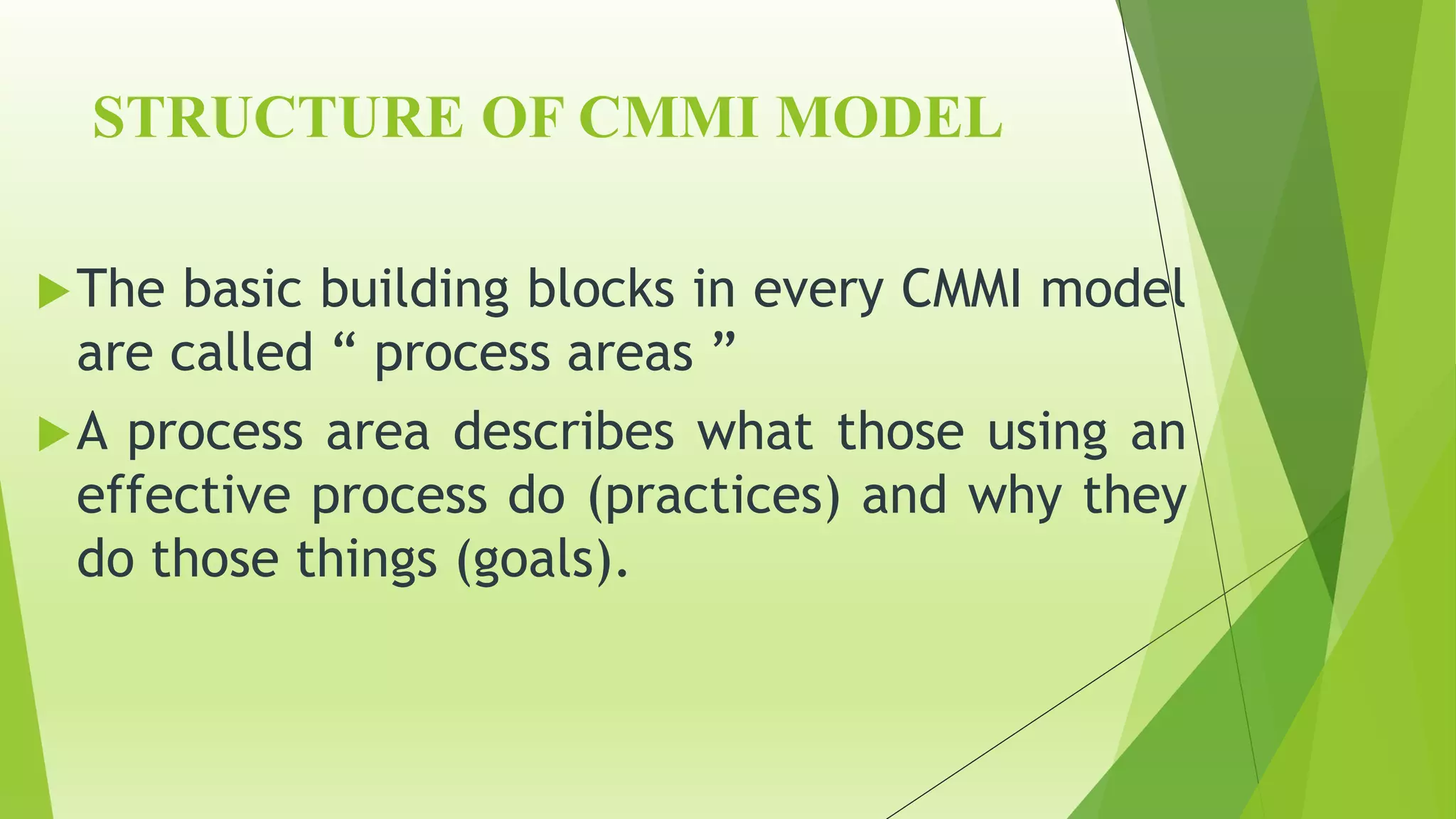
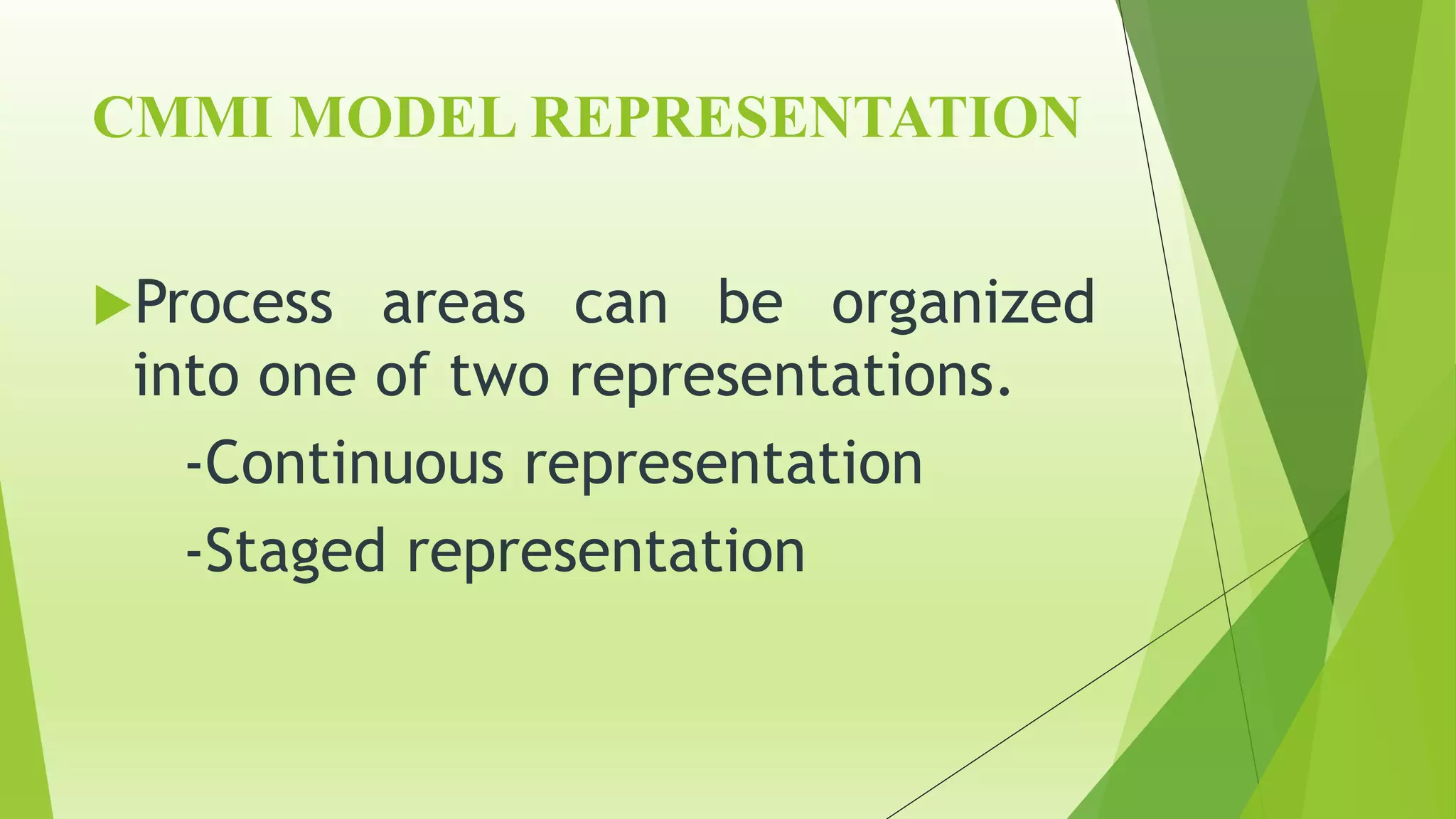
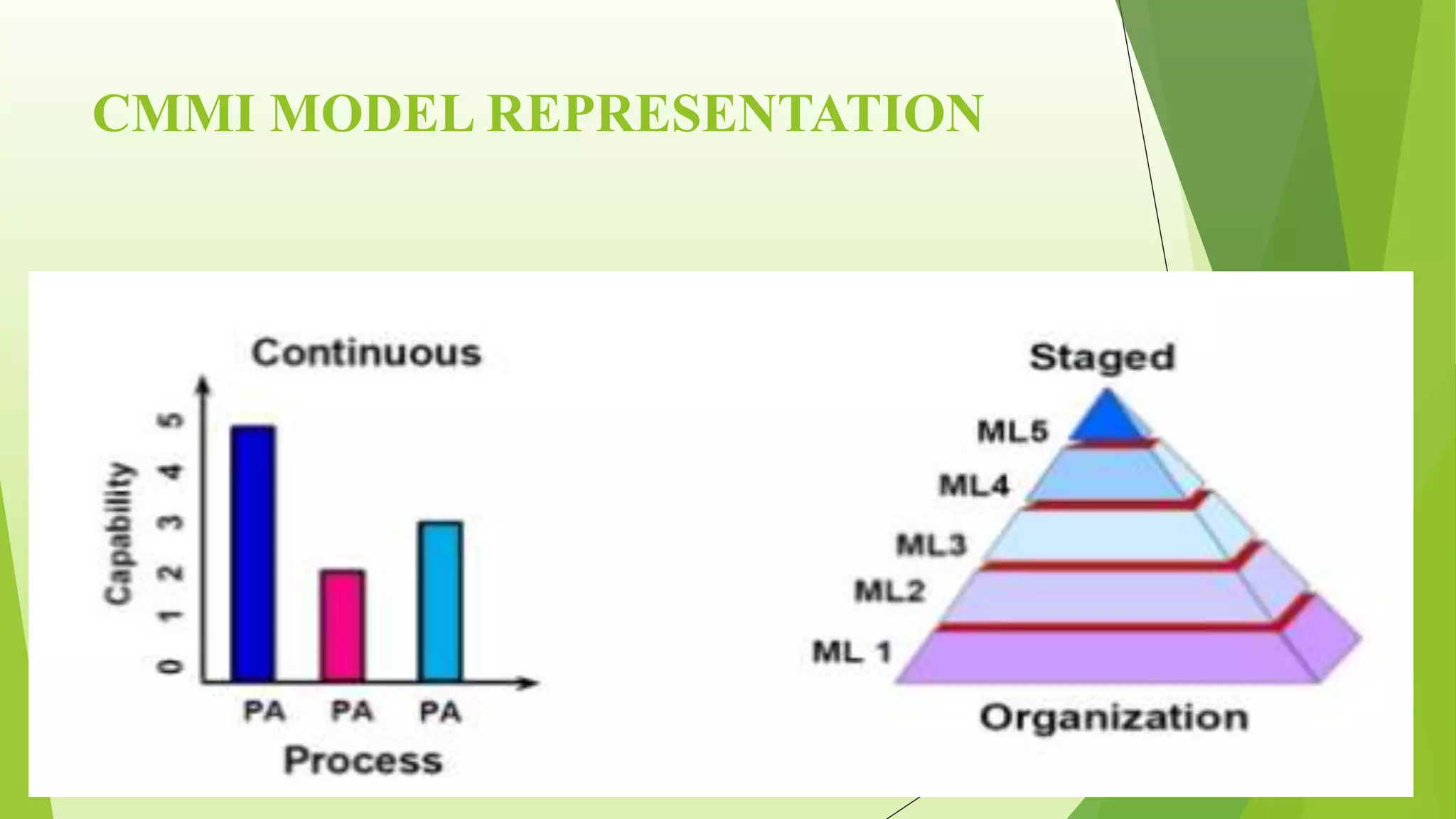
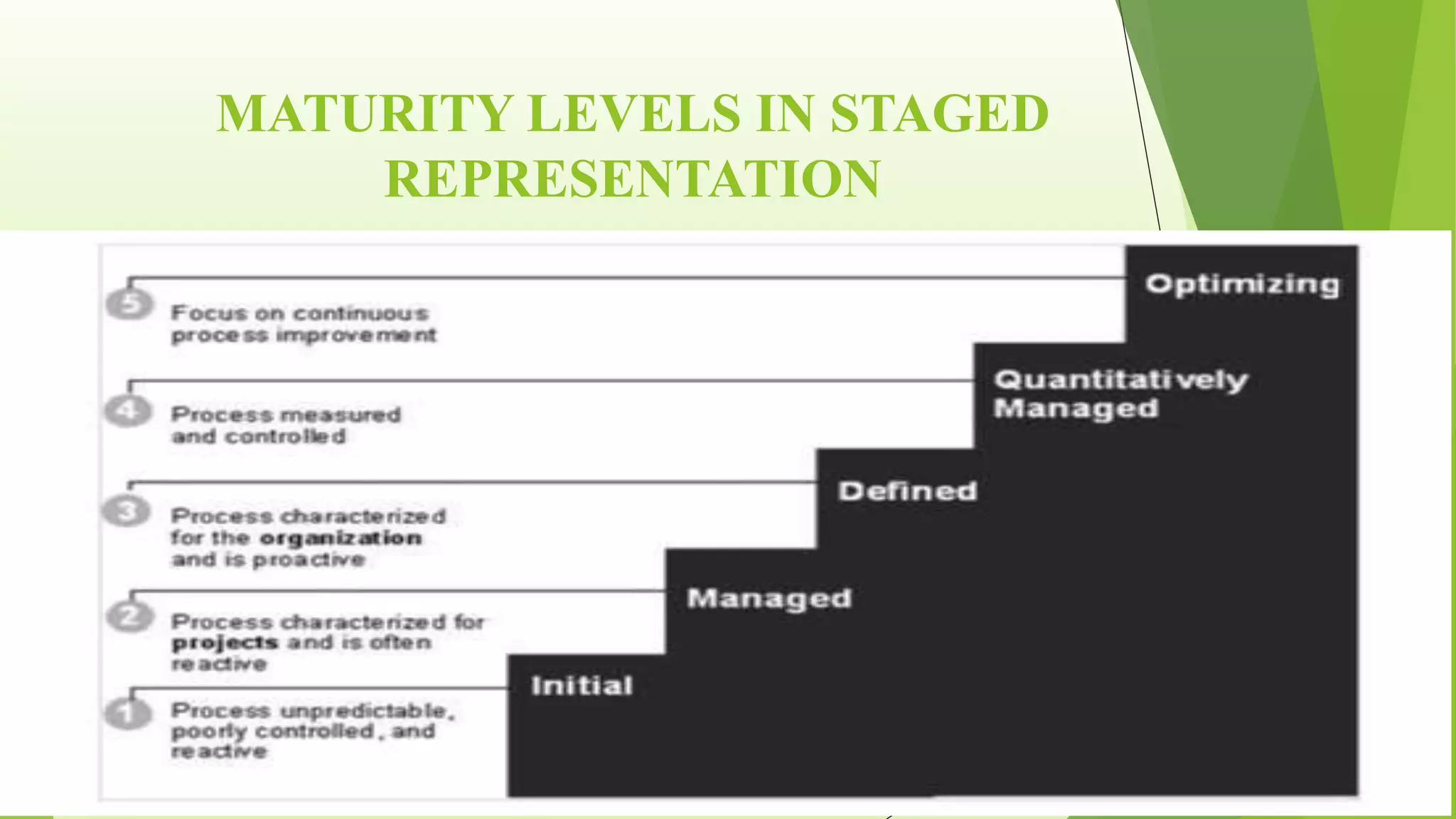
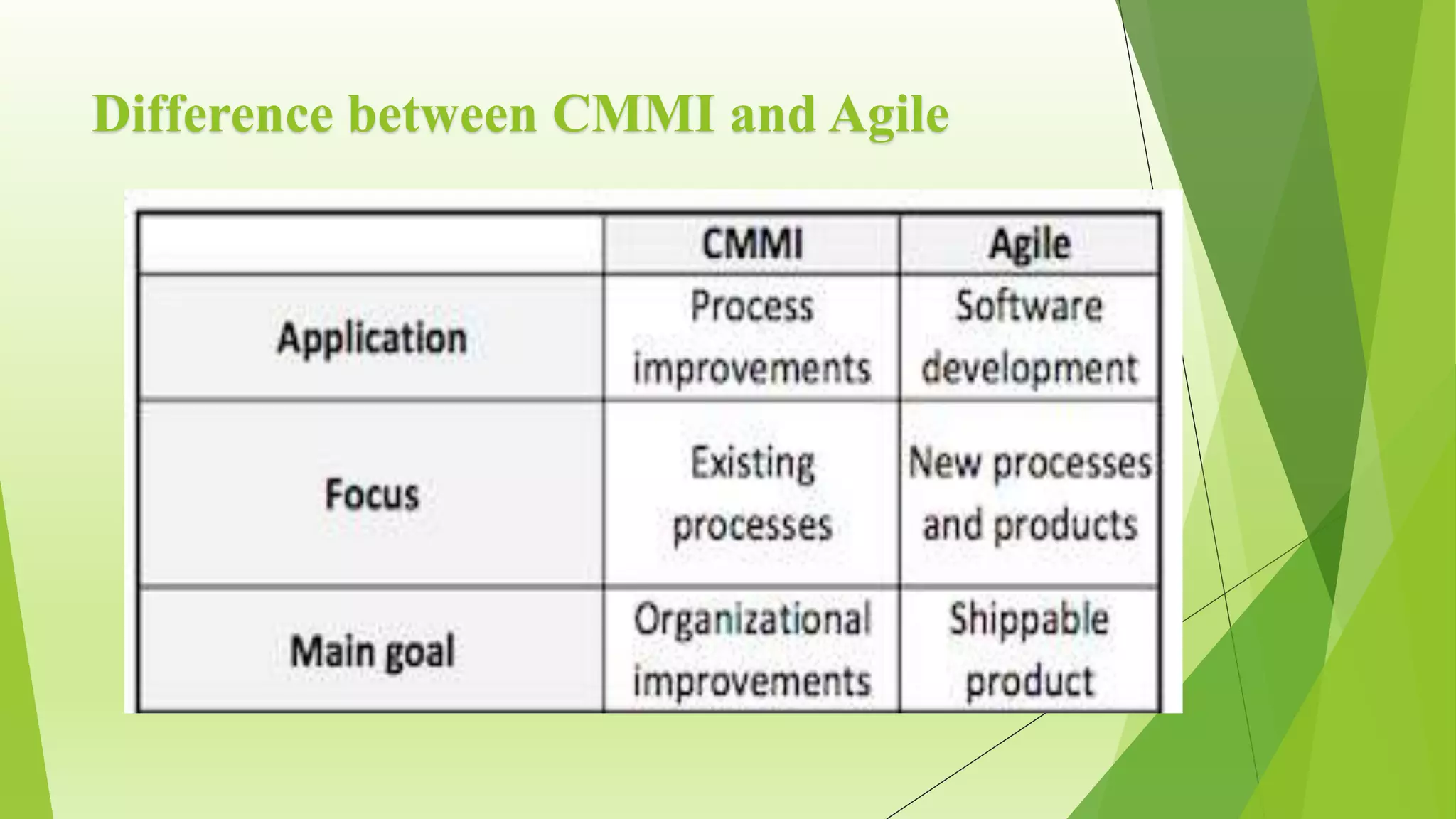
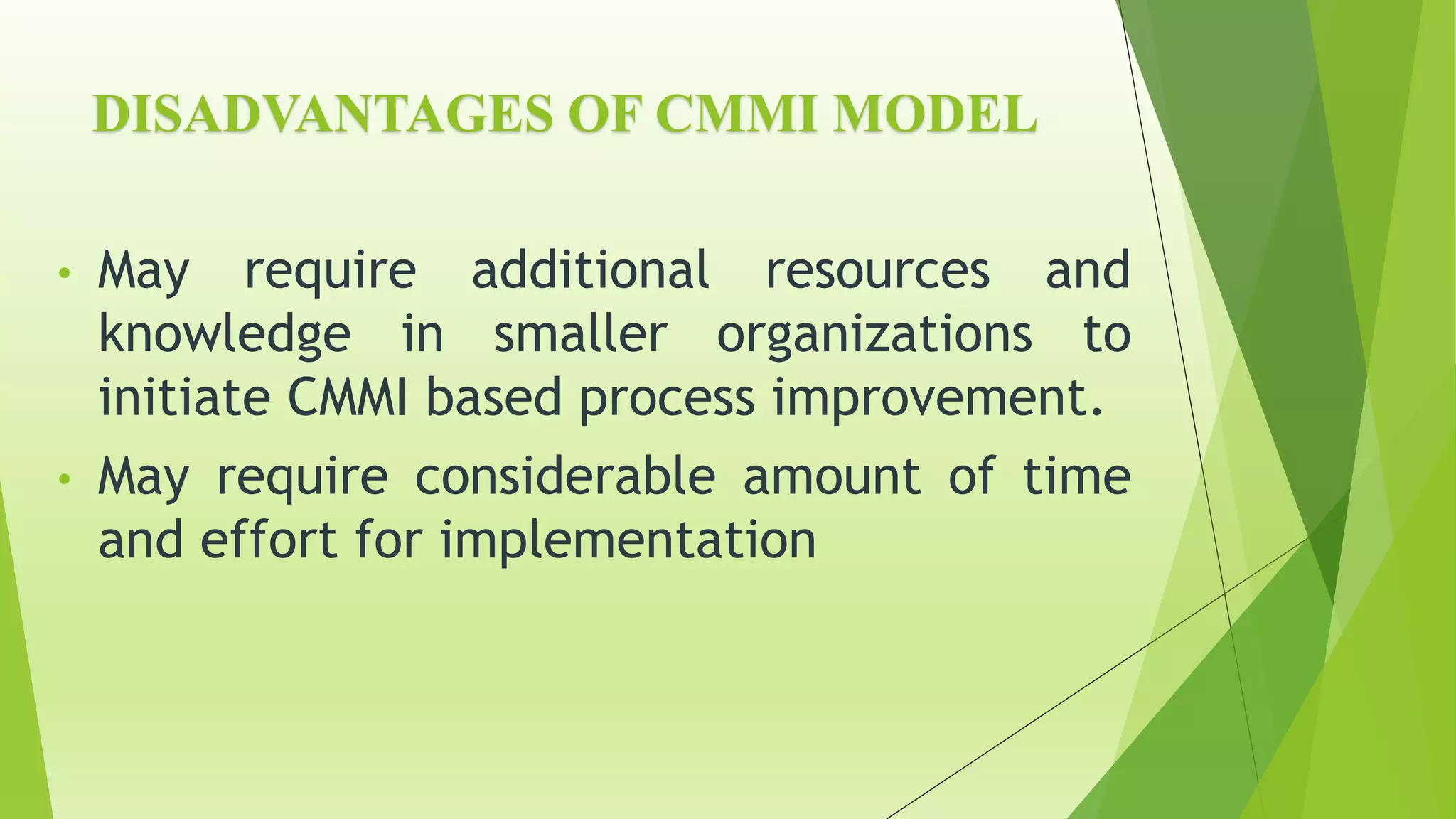
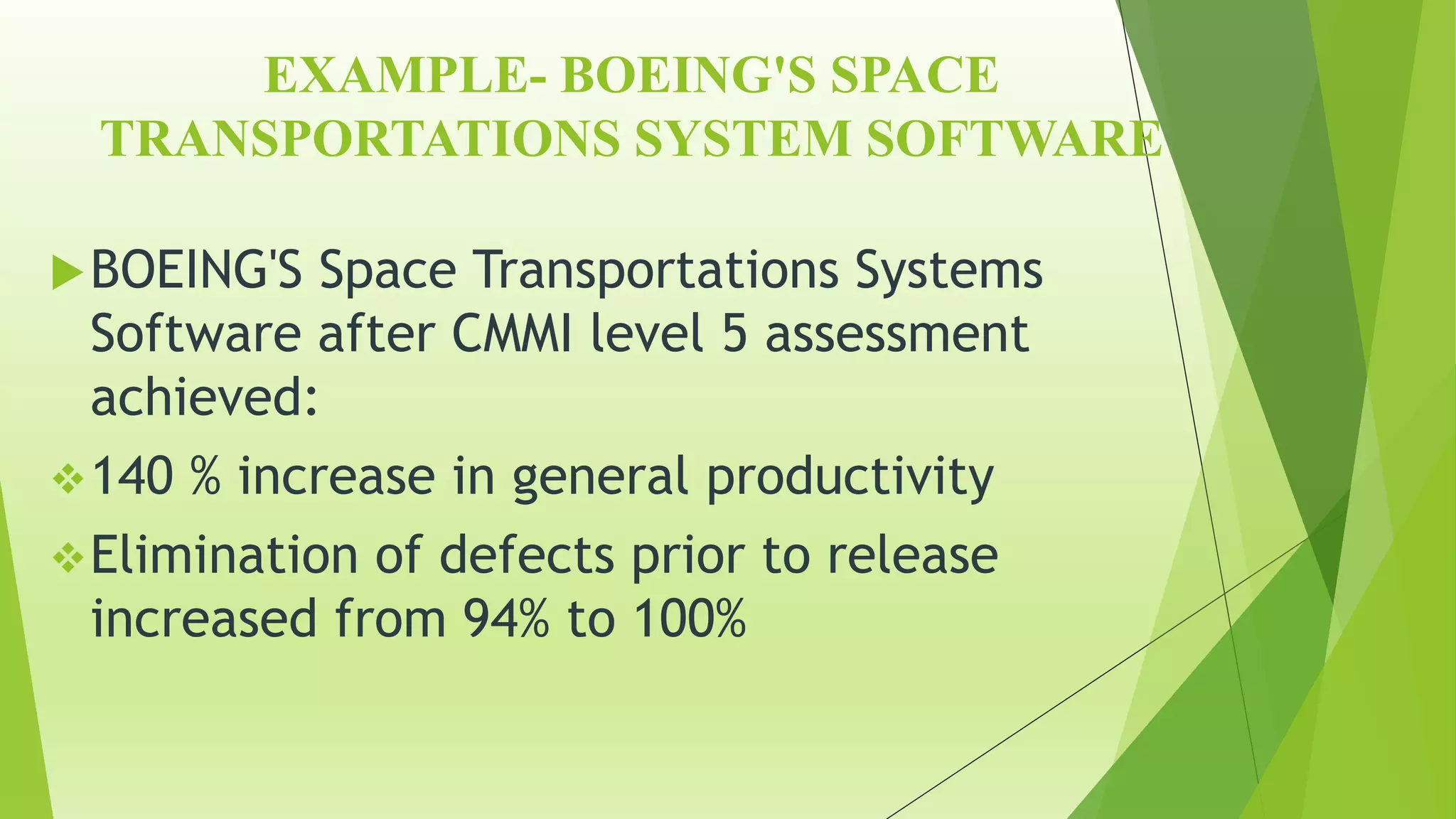
The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a process improvement framework that guides organizations in enhancing their processes through structured models and defined maturity levels ranging from 1 (initial) to 5 (optimizing). CMMI distinguishes itself from other models by focusing on both hardware and software development across the entire lifecycle, while providing a systematic approach for measuring process effectiveness and improvement. Advantages of CMMI include increased productivity, reduced defects, and improved client satisfaction, though its implementation may require additional resources and time, particularly for smaller organizations.