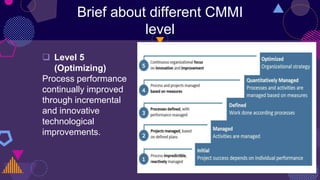
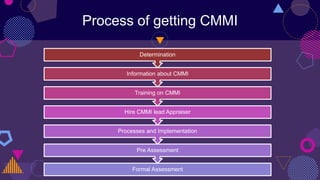
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration) is a framework aimed at improving product quality and development efficiency through five maturity levels, ranging from 'Initial' to 'Optimizing'. Organizations can enhance their processes, although implementing CMMI can require significant investment and shifts in culture. While beneficial for quality and productivity, CMMI may not suit every organization due to potential documentation overhead and resource demands.